Leukocyte esterase urine test
WBC esteraseLeukocyte esterase is a urine test to look for white blood cells and other signs of infection.
How the Test is Performed
A clean-catch urine sample is preferred. The clean-catch method is used to prevent germs from the penis or vagina from getting into a urine sample. To collect your urine, the health care provider may give you a special clean-catch kit that contains a cleansing solution and sterile wipes. Follow instructions exactly so that the results are accurate.
Clean-catch urine sample
A clean catch is a method of collecting a urine sample to be tested. The clean-catch urine method is used to prevent germs from the penis or vagina ...
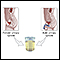
After you provide a urine sample, it is tested right away. The provider uses a dipstick made with a color-sensitive pad. The color of the dipstick changes to tell the provider if you have white blood cells in your urine.
How to Prepare for the Test
No special steps are needed to prepare for this test.
How the Test will Feel
The test will involve only normal urination. There is no discomfort.
Why the Test is Performed
Leukocyte esterase is a screening test used to detect a substance that suggests there are white blood cells in the urine. This may mean you have a urinary tract infection.
Urinary tract infection
A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. The infection can occur at different points in the urinary tract, including...
If this test is positive, the urine should be examined under a microscope for white blood cells and other signs that point to an infection.
Normal Results
A negative test result is normal.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An abnormal result indicates a possible urinary tract infection.
The following may cause an abnormal test result, even when you do not have a urinary tract infection:
- Trichomonas infection (such as trichomoniasis)
- Vaginal secretions (such as blood or heavy mucus discharge)
The following may interfere with a positive result, even when you do have a urinary tract infection:
- High level of protein
- High level of vitamin C
References
Castle EP, Wolter CE, Woods ME. Evaluation of the urologic patient: testing and imaging. In: Partin AW, Dmochowski RR, Kavoussi LR, Peters CA, eds. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 2.
Riley RS, McPherson RA. Basic examination of urine. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 29.
Sobel JD, Brown P. Urinary tract infections. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 72.
Review Date: 8/20/2023
Reviewed By: Jacob Berman, MD, MPH, Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine, Division of General Internal Medicine, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.