Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) blood test
Aspartate aminotransferase; Serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase; SGOTThe aspartate aminotransferase (AST) blood test measures the level of the enzyme AST in the blood.
Enzyme
Enzymes are complex proteins that cause a specific chemical change. For example, they can help break down the foods we eat so the body can use them....
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleHow the Test is Performed
A blood sample is needed.
Blood sample
Venipuncture is the collection of blood from a vein. It is most often done for laboratory testing.

How to Prepare for the Test
No special preparation is needed.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or stinging. Afterward, there may be some throbbing or a slight bruise. This soon goes away.
Why the Test is Performed
AST is an enzyme found in high levels in the liver, heart, and muscles. It is also found in lesser amounts in other tissues. An enzyme is a protein that causes a specific chemical change in the body.
Injury to the liver results in release of AST into the blood.
This test is mainly done along with other tests (such as ALT, ALP, and bilirubin) to diagnose and monitor liver disease.
ALT
The alanine transaminase (ALT) blood test measures the level of the enzyme ALT in the blood.

ALP
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is a protein found in all body tissues. Tissues with higher amounts of ALP include the liver, bile ducts, and bone. A blo...

Bilirubin
The bilirubin blood test measures the level of bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin is a yellowish pigment found in bile, a fluid made by the liver. Bi...

Liver disease
The term "liver disease" applies to many conditions that stop the liver from working or prevent it from functioning well. Abdominal pain or swelling...

Normal Results
The normal range is 8 to 33 U/L (0.13 to 0.55 µkat/L).
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different labs. Some labs use different measurements or may test different samples. Talk to your health care provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An increased AST level is often a sign of liver disease. Liver disease is even more likely when the levels of substances checked by other liver blood tests have also increased.
An increased AST level may be due to any of the following:
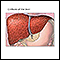
- Scarring of the liver (cirrhosis)
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is scarring of the liver and poor liver function. It is the last stage of chronic liver disease.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Death of liver tissue
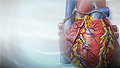
- Heart attack
Heart attack
Most heart attacks are caused by a blood clot that blocks one of the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries bring blood and oxygen to the heart. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Too much iron in the body (hemochromatosis)
Hemochromatosis
Hemochromatosis is a condition in which there is too much iron in the body. It is also called iron overload.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Swollen and inflamed liver (hepatitis)
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is swelling and inflammation of the liver.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lack of blood flow to the liver (liver ischemia)
Liver ischemia
Hepatic ischemia is a condition in which the liver does not get enough blood or oxygen. This causes injury to liver cells.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Liver cancer or tumor
Liver cancer
Hepatocellular carcinoma is cancer that starts in the liver.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Use of medicines and drugs that are toxic to the liver, especially alcohol or acetaminophen use
- Mononucleosis (mono)
Mononucleosis
Mononucleosis, or mono, is a viral infection that causes fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph glands, most often in the neck.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Muscle disease or trauma
- Swollen and inflamed pancreas (pancreatitis)
Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis is sudden swelling and inflammation of the pancreas.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
AST level may also increase after:
- Burns (deep)
- Heart procedures
- Seizures
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Surgery
Pregnancy and exercise may also cause an increased AST level.
Risks
There is little risk involved with having your blood taken. Veins vary in size from one person to another and from one side of the body to the other. Taking blood from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Risks associated with having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Excessive bleeding
- Multiple punctures to locate veins
- Hematoma (blood collecting under the skin)
Hematoma
A bruise is an area of skin discoloration. A bruise occurs when small blood vessels break and leak their contents into the soft tissue beneath the s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
References
Daniels L, Khalili M, Goldstein E, Bluth MH, Bowne WB, Pincus MR. Evaluation of liver function. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 22.
Pratt DS. Liver chemistry and function tests. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 73.
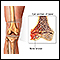
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
Review Date: 1/1/2025
Reviewed By: Frank D. Brodkey, MD, FCCM, Associate Professor, Section of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, WI. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


