His bundle electrography
His bundle electrogram; HBE; His bundle recording; Electrogram - His bundle; Arrhythmia - His; Heart block - HisHis bundle electrography is a test that measures electrical activity in a part of the heart that carries the signals that control the time between heartbeats (contractions).
How the Test is Performed
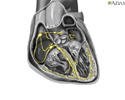
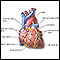
The bundle of His is a group of fibers that carry electrical impulses through the center of the heart. If these signals are blocked, you will have problems with your heartbeat.
The His bundle electrography is part of an electrophysiology study (EPS). An intravenous catheter (IV line) is inserted into your arm so that you can be given medicines during the test.
Electrophysiology
Intracardiac electrophysiology study (EPS) is a test to look at how well the heart's electrical signals are working. It is used to evaluate abnormal...
Intravenous
Intravenous means "within a vein. " Most often it refers to giving medicines or fluids through a needle or tube inserted into a vein. This allows th...
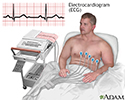
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleElectrocardiogram (ECG) leads are placed on your arms and legs. Your arm, neck, or groin will be cleaned and numbed with a local anesthetic. After the area is numb, the cardiologist (heart doctor) makes a small cut in a vein and inserts a thin tube called a catheter inside.
Electrocardiogram
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.

The catheter is carefully moved through the vein up into the heart. An x-ray method called fluoroscopy helps guide the doctor to the right place. During the test, you are watched for any abnormal heartbeats (arrhythmias). The catheter has a sensor on the end, which is used to measure the electrical activity of the bundle of His.
x-ray
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation, just like visible light. An x-ray machine sends individual x-ray waves through the body. The images...

Arrhythmias
An arrhythmia is a disorder of the heart rate (pulse) or heart rhythm. The heart can beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or irregul...

How to Prepare for the Test
You will be told not to eat or drink anything for 6 to 8 hours before the test. The test will be done in a hospital. Some people may need to check into the hospital the night before the test. Otherwise, you will check in the morning of the test. Although the test may take some time, most people do not need to stay in the hospital overnight.
Your health care provider will explain the procedure and its risks. You must sign a consent form before the test starts.
About half an hour before the procedure, you will be given a mild sedative to help you relax. You will wear a hospital gown. The procedure may last from 1 to several hours.
How the Test will Feel
You are awake during the test. You may feel some discomfort when the IV is placed into your arm, and some pressure at the site when the catheter is inserted.
Why the Test is Performed
This test may be done to:
- Determine if you need a pacemaker or other treatment
- Diagnose arrhythmias
- Find the specific location where electrical signals through the heart are blocked
Normal Results
The time it takes for the electrical signals to travel through the bundle of His is normal.
What Abnormal Results Mean
A pacemaker may be needed if the test results are abnormal.
Risks
Risks of the procedure include:
- Arrhythmias
- Cardiac tamponade
Cardiac tamponade
Cardiac tamponade is pressure on the heart that occurs when blood or fluid builds up in the space between the heart muscle and the outer covering sac...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Embolism from blood clots at the tip of the catheter
Embolism from blood clots at the tip of...
Blood clots are clumps that occur when blood hardens from a liquid to a solid. A blood clot that forms inside one of your veins or arteries is calle...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heart attack
- Hemorrhage
- Infection
- Injury to the vein or artery
- Low blood pressure
- Stroke
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
References
Curtis AB, Tomaselli GF. Approach to the patient with cardiac arrhythmias. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 61.
Issa ZF, Miller JM, Zipes DP. Atrioventricular conduction abnormalities. In: Issa ZF, Miller JM, Zipes DP, eds. Clinical Arrhythmology and Electrophysiology: A Companion to Braunwald's Heart Disease. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 10.
Cardiac conduction system
Animation
ECG - illustration
The electrocardiogram (ECG) is used extensively in the diagnosis of heart disease, from congenital heart disease in infants to myocardial infarction and myocarditis in adults. Several different types of electrocardiogram exist.
ECG
illustration
Review Date: 5/8/2024
Reviewed By: Thomas S. Metkus, MD, Assistant Professor of Medicine and Surgery, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.