CSF myelin basic protein
CSF myelin basic protein is a test to measure the level of myelin basic protein (MBP) in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
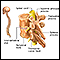
Myelin
Myelin is an insulating layer, or sheath that forms around nerves, including those in the brain and spinal cord. It is made up of protein and fatty ...

CSF is a clear liquid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord.
MBP is found in the material that covers many of your nerves.
How the Test is Performed
A sample of spinal fluid is needed. This is done using a lumbar puncture.
Lumbar puncture
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...

Why the Test is Performed
This test is done to see if myelin is breaking down. Multiple sclerosis is the most common cause for this, but other causes may include:
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease that affects the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system).
- Bleeding of the central nervous system
-
Central nervous system trauma
Central nervous system trauma
Spinal cord trauma is damage to the spinal cord. It may result from direct injury to the cord itself or indirectly from disease of the nearby bones,...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Certain brain diseases (encephalopathies)
- Infection of the central nervous system
-
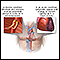
Stroke
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Traumatic brain injury
Normal Results
In general, there should be less than 4 ng/mL of myelin basic protein in the CSF.
Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your health care provider about the meaning of your specific test results.
The example above shows the common measurement result for this test. Some laboratories use different measurements or may test different specimens.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Myelin basic protein levels from 4 to 8 ng/mL may be a sign of a long-term (chronic) breakdown of myelin. It may also indicate recovery from an acute episode of myelin breakdown.
Chronic
Chronic refers to something that continues over an extended period of time. A chronic condition is usually long-lasting and does not easily or quick...
Acute
Acute means sudden. Acute symptoms appear, change, or worsen rapidly. It is the opposite of chronic.

If the myelin basic protein level is 9 ng/mL or greater, myelin is actively breaking down.
References
Euerle BD. Spinal puncture and cerebrospinal fluid examination. In: Roberts JR, Custalow CB, Thomsen TW, eds. Roberts and Hedges' Clinical Procedures in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 60.
Fabian MT, Krieger SC, Lublin FD. Multiple sclerosis and other inflammatory demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022: chap 80.
Karcher DS, McPherson RA. Cerebrospinal, synovial, serous body fluids, and alternative specimens. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 30.
-
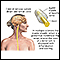
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) - illustration
A lumbar puncture, or spinal tap, is a procedure to collect cerebrospinal fluid to check for the presence of disease or injury. A spinal needle is inserted, usually between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae in the lower spine. Once the needle is properly positioned in the subarachnoid space (the space between the spinal cord and its covering, the meninges), pressures can be measured and fluid can be collected for testing.
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
illustration
-
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) - illustration
A lumbar puncture, or spinal tap, is a procedure to collect cerebrospinal fluid to check for the presence of disease or injury. A spinal needle is inserted, usually between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae in the lower spine. Once the needle is properly positioned in the subarachnoid space (the space between the spinal cord and its covering, the meninges), pressures can be measured and fluid can be collected for testing.
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
illustration
Review Date: 4/29/2023
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School of Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.



