Pupil – white
LeukocoriaA white pupil is a condition that causes the pupil of the eye to look white instead of black.
Considerations
The pupil of the human eye is normally black. In flash photographs the pupil may appear red. This is called the "red reflex" by health care providers and is normal.
Sometimes, the pupil of the eye may appear white, or the normal red reflex may appear to be white. This is not a normal condition, and you need to see an eye care provider right away.
There are many different causes of white pupil or white reflex. Other conditions also can mimic white pupil. If the cornea, which is normally clear, becomes cloudy, it may look similar to a white pupil. Although the causes of a cloudy or white cornea are different from those of a white pupil or white reflex, these problems also need medical attention right away.
Cataracts may also cause the pupil to appear white.
Causes
Causes of this condition may include:
- Coats disease - exudative retinopathy
-
Coloboma
Coloboma
Coloboma of the iris is a hole or defect of the iris of the eye. Most colobomas are present since birth (congenital).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Congenital cataract (may be hereditary or may result from other conditions, including congenital rubella, galactosemia, retrolental fibroplasia)
Congenital cataract
A congenital cataract is a clouding of the lens of the eye that is present at birth. The lens of the eye is normally clear. It focuses light that c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCongenital rubella
Congenital rubella is a condition that occurs in an infant whose mother is infected with the virus that causes German measles. Congenital means the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleGalactosemia
Galactosemia is a condition in which the body is unable to use (metabolize) the simple sugar galactose.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleRetrolental fibroplasia
Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) is abnormal blood vessel development in the retina of the eye in infants that are born too early (premature)....
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Persistent primary hyperplastic vitreous
-
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma is a rare eye tumor that usually occurs in children. It is a malignant (cancerous) tumor of the part of the eye called the retina....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Toxocara canis (infection caused by a parasite)
-
Uveitis
Uveitis
Uveitis is swelling and inflammation of the uvea. The uvea is the middle layer of the wall of the eye. The uvea supplies blood for the iris at the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Home Care
Most causes of white pupil will cause decreased vision. This may often occur before the pupil appears to be white.
Detecting a white pupil is especially important in infants. Babies are unable to communicate to others that their vision is decreased. It is also harder to measure an infant's vision during an eye exam.
If you see a white pupil, call your provider right away. Well-child exams routinely screen for a white pupil in children. A child who develops a white pupil or cloudy cornea needs immediate attention, preferably from an eye specialist.
It is important to get diagnosed early if the problem is caused by retinoblastoma since this disease can be fatal.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you notice any color changes in the pupil or cornea of the eye.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
The provider will do a physical exam and ask about your symptoms and medical history.
The physical exam will include a detailed eye examination.
The following tests may be performed:
-
Ophthalmoscopy
Ophthalmoscopy
Ophthalmoscopy is an examination of the back part of the eye (fundus), which includes the retina, optic disc, choroid, and blood vessels.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Slit-lamp exam
Slit-lamp exam
The slit-lamp examination looks at structures that are at the front of the eye.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Standard eye exam
Standard eye exam
A standard eye exam is a series of tests done to check your vision and the health of your eyes.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Visual acuity
Visual acuity
The visual acuity test is used to determine the smallest letters you can read on a standardized chart (Snellen chart) or a card held 20 feet (6 meter...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other tests may be done including a head CT or MRI scan.
Head CT
A head computed tomography (CT) scan uses many x-rays to create pictures of the head, including the skull, brain, eye sockets, and sinuses.

MRI scan
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the body. It does not us...
References
Cioffi GA, Liebmann JM. Diseases of the visual system. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 391.
Kanukollu VM, Tripathy K. Leukocoria. In: StatPearls [Internet] Treasure Island (FL). StatPearls Publishing; 2023. PMID: 32809629 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32809629/.
Olitsky SE, Marsh JD. Abnormalities of pupil and iris. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 640.
Vagge A, Wangtiraumnuay N, Pellegrini M, Scotto R, Iester M, Traverso CE. Evaluation of a free public smartphone application to detect leukocoria in high-risk children aged 1 to 6 years. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2019;56(4):229-232. PMID: 31322712 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31322712/.
-
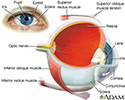
Eye - illustration
The eye is the organ of sight, a nearly spherical hollow globe filled with fluids (humors). The outer layer (sclera, or white of the eye, and cornea) is fibrous and protective. The middle layer (choroid, ciliary body and the iris) is vascular. The innermost layer (retina) is sensory nerve tissue that is light sensitive. The fluids in the eye are divided by the lens into the vitreous humor (behind the lens) and the aqueous humor (in front of the lens). The lens itself is flexible and suspended by ligaments which allow it to change shape to focus light on the retina, which is composed of sensory neurons.
Eye
illustration
-
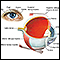
White spots in the pupil - illustration
On occasion, the pupil of the eye may appear white. This is never a normal condition and requires immediate evaluation by an ophthalmologist. The causes of a cloudy or white cornea are different than those of a white pupil but are also significant and require immediate attention. Cataracts can also cause the pupil to appear white.
White spots in the pupil
illustration
-
Eye - illustration
The eye is the organ of sight, a nearly spherical hollow globe filled with fluids (humors). The outer layer (sclera, or white of the eye, and cornea) is fibrous and protective. The middle layer (choroid, ciliary body and the iris) is vascular. The innermost layer (retina) is sensory nerve tissue that is light sensitive. The fluids in the eye are divided by the lens into the vitreous humor (behind the lens) and the aqueous humor (in front of the lens). The lens itself is flexible and suspended by ligaments which allow it to change shape to focus light on the retina, which is composed of sensory neurons.
Eye
illustration
-
White spots in the pupil - illustration
On occasion, the pupil of the eye may appear white. This is never a normal condition and requires immediate evaluation by an ophthalmologist. The causes of a cloudy or white cornea are different than those of a white pupil but are also significant and require immediate attention. Cataracts can also cause the pupil to appear white.
White spots in the pupil
illustration
Review Date: 11/8/2023
Reviewed By: Franklin W. Lusby, MD, Ophthalmologist, Lusby Vision Institute, La Jolla, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.