Frequent or urgent urination
Urgent urination; Urinary frequency or urgency; Urgency-frequency syndrome; Overactive bladder (OAB) syndrome; Urge syndromeFrequent urination means needing to urinate more often than usual. Urgent urination is a sudden, strong need to urinate. This causes a discomfort in your bladder. Urgent urination makes it difficult to delay using the toilet.
A frequent need to urinate at night is called nocturia. Most people can sleep for 6 to 8 hours without having to urinate.
Nocturia
Normally, the amount of urine your body produces decreases at night. This allows most people to sleep 6 to 8 hours without having to urinate. Some p...

Causes
Common causes of these symptoms are:
-
Urinary tract infection (UTI)
Urinary tract infection
A urinary tract infection, or UTI, is an infection of the urinary tract. The infection can occur at different points in the urinary tract, including...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Enlarged prostate in middle-aged and older men
Enlarged prostate
The prostate is a gland that produces some of the fluid that carries sperm during ejaculation. The prostate gland surrounds the urethra, the tube th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Swelling and infection of the urethra
- Vaginitis (swelling of or discharge from the vulva and vagina)
- Nerve related problems
- Caffeine intake
Less common causes include:
- Alcohol use
- Anxiety
-
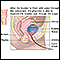
Bladder cancer (not common)
Bladder cancer
Bladder cancer is a cancer that starts in the bladder. The bladder is the body part that holds and releases urine. It is in the center of the lower...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Spine problems
- Diabetes that is not well controlled
- Pregnancy
-
Interstitial cystitis
Interstitial cystitis
Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a long-term (chronic) problem in which pain, pressure, or burning is present in the bladder. It is often associated wi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Medicines such as water pills (diuretics)
- Overactive bladder syndrome
- Radiation therapy to the pelvis, which is used to treat certain cancers
- Stroke and other brain or nervous system diseases
- Tumor or growth in the pelvis
Home Care
Follow the advice of your health care provider to diagnose and treat the cause of the problem.
It may help to write down the times when you urinate and the amount of urine you produce. Bring this record to your visit with the provider. This is called a voiding diary.
In some cases, you may have problems controlling urine (incontinence) for a period of time. You may need to take steps to protect your clothing and bedding.
Incontinence
Urinary (or bladder) incontinence occurs when you are not able to keep urine from leaking out of your urethra. The urethra is the tube that carries ...

For nighttime urination, avoid drinking too much fluid before going to bed. Cut down on the amount of liquids you drink that contain alcohol or caffeine.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider right away if:
- You have fever, back or side pain, vomiting, or shaking chills
- You have increased thirst or appetite, fatigue, or sudden weight loss
Also contact your provider if:
- You have urinary frequency or urgency, but you are not pregnant and you are not drinking large amounts of fluid.
- You have incontinence or you have changed your lifestyle because of your symptoms.
- You have bloody or cloudy urine.
- There is a discharge from the penis or vagina.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will take a medical history and do a physical exam.
Tests that may be done include:
-
Urinalysis
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
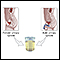
Urine culture
Urine culture
A urine culture is a lab test to check for bacteria or other germs in a urine sample. It can be used to check for a urinary tract infection in adults...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cystometry or urodynamic testing (a measurement of the pressure within the bladder and the flow of urine)
Cystometry
A cystometric study measures the amount of fluid in the bladder when you first feel the need to urinate, when you are able to sense fullness, and whe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cystoscopy
Cystoscopy
Cystoscopy is a surgical procedure. This is done to see the inside of the bladder and urethra using a thin, lighted tube.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nervous system tests (for some urgency problems)
-
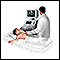
Ultrasound (such as an abdominal ultrasound or a pelvic ultrasound)
Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to make images of organs and structures inside the body.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleAbdominal ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound is a type of imaging test. It is used to look at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidneys...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticlePelvic ultrasound
A pelvic (transabdominal) ultrasound is an imaging test. It is used to examine organs in the pelvis.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment depends on the cause of the urgency and frequency. You may need to take antibiotics and medicine to ease your discomfort.
References
Conway B, Phelan PJ, Stewart GD. Nephrology and urology. In: Penman ID, Ralston SH, Strachan MWJ, Hobson RP, eds. Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicine. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 18.
Rane A, Kulkarni M, Iyer J. Prolapse and disorders of the urinary tract. In: Symonds I, Arulkumaran S, eds. Essential Obstetrics and Gynaecology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 21.
Reynolds WS, Cohn JA. Overactive bladder. In: Partin AW, Dmochowski RR, Kavoussi LR, Peters CA, eds. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 117.
-
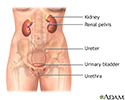
Female urinary tract - illustration
The female and male urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Female urinary tract
illustration
-
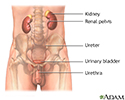
Male urinary tract - illustration
The male and female urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Male urinary tract
illustration
-
Female urinary tract - illustration
The female and male urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Female urinary tract
illustration
-
Male urinary tract - illustration
The male and female urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Male urinary tract
illustration
Review Date: 5/17/2024
Reviewed By: Sovrin M. Shah, MD, Associate Professor, Department of Urology, The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.