Adhesion
Pelvic adhesion; Intraperitoneal adhesion; Intrauterine adhesionAdhesions are bands of scar-like tissue that form between two surfaces inside the body and cause them to stick together.
Causes
With movement of the body, internal organs such as the bowel or uterus are normally able to shift and to slide past each other. This is because these tissues and organs in the abdominal cavity have smooth, slippery surfaces. Inflammation (swelling), surgery, or injury can cause adhesions to form and prevent this movement. Adhesions can occur almost anywhere in the body, including:
- Joints, such as the shoulder
- Eyes
- Inside the abdomen or pelvis
Adhesions can become larger or tighter over time. Problems may occur if the adhesions cause an organ or body part to:
- Twist
- Pull out of position
- Be unable to move normally
The risk of forming adhesions is high after bowel or female organ surgeries. Surgery using a laparoscope is less likely to cause adhesions than open surgery.
Other causes of adhesions in the abdomen or pelvis include:
- Appendicitis, most often when the appendix breaks open (ruptures)
Appendicitis
Appendicitis is a condition in which your appendix gets inflamed. The appendix is a small pouch attached to the end of the large intestine.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cancer
- Endometriosis
Endometriosis
Endometriosis occurs when cells from the lining of your womb (uterus) grow in other areas of your body. This can cause pain, heavy vaginal bleeding,...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infections in the abdomen and pelvis, such as appendicitis or fallopian tube infection
- Radiation treatment
Adhesions around the joints may occur:
- After surgery or trauma
- With certain types of arthritis
- With overuse of a joint or tendon
Symptoms
Adhesions in joints, tendons, or ligaments make it harder to move the joint. They may also cause pain.
Adhesions in the belly (abdomen) may cause a blockage of the intestines. Symptoms include:
Blockage of the intestines
Intestinal obstruction is a partial or complete blockage of the bowel. The contents of the intestine cannot pass through it.

- Bloating or swelling of your belly
- Constipation
Constipation
Constipation in infants and children means they have hard stools or have problems passing stools. A child may have pain while passing stools or may ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nausea and vomiting
- No longer being able to pass gas
- Pain in the belly that is severe and crampy
Adhesions in the pelvis may cause long-term (chronic) pelvic pain.
Exams and Tests
Most of the time, the adhesions cannot be seen using x-rays or imaging tests.
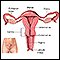
- Hysterosalpingography may help detect adhesions inside the uterus or fallopian tubes.
Hysterosalpingography
Hysterosalpingography is a special x-ray using dye to look at the womb (uterus) and fallopian tubes.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - X-rays of the abdomen, barium contrast studies, and CT scans may help detect a blockage of the intestines caused by adhesions.
Endoscopy (a way of looking inside the body using a flexible tube that has a small camera on the end) may help diagnose adhesions:
- Hysteroscopy looks inside the uterus
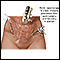
- Laparoscopy looks inside the abdomen and pelvis
Laparoscopy
Diagnostic laparoscopy is a procedure that allows your health care provider to look directly at the contents of the abdomen or pelvis.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Surgery may be done to separate the adhesions. This can let the organ regain normal movement and reduce symptoms. However, the risk for more adhesions goes up with more surgeries.
Depending on the location of the adhesions, a barrier may be placed at the time of surgery to help reduce the chance of the adhesions returning.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outcome is good in most cases.
Possible Complications
Adhesions can cause various disorders, depending on the tissues affected.
- In the eye, adhesion of the iris to the lens can lead to glaucoma.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye conditions that can damage the optic nerve. This nerve sends the images you see to your brain. Most often, optic nerve da...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - In the intestines, adhesions can cause partial or complete bowel obstruction.
Bowel obstruction
Intestinal obstruction is a partial or complete blockage of the bowel. The contents of the intestine cannot pass through it.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Adhesions inside the uterine cavity can cause a condition called Asherman syndrome. This can cause a woman to have irregular menstrual cycles and be unable to get pregnant.
Asherman syndrome
Asherman syndrome is the formation of scar tissue in the uterine cavity. The problem most often develops after uterine surgery.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pelvic adhesions that involve scarring of the fallopian tubes can lead to infertility and reproductive problems.
- Abdominal and pelvic adhesions can cause chronic pain.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you have:
- Abdominal pain
- An inability to pass gas
- Nausea and vomiting that do not go away
- Pain in the belly that is severe and crampy
References
Kuemmerle JF. Inflammatory and anatomic diseases of the intestine, peritoneum, mesentery, and omentum. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 128.
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases website. Abdominal adhesions. www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/abdominal-adhesions. Updated June 2019. Accessed June 3, 2024.
Yepuri N, Pruekprasert N. Cooney RN. Surgical complications. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 12.
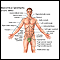
Pelvic adhesions are bands of scar-like tissue that form between two surfaces inside the body. Inflammation from infection, surgery, or trauma can cause tissues to bond to other tissues or organs.
Pelvic adhesions
illustration
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


