Cervical dysplasia
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia - dysplasia; CIN - dysplasia; Precancerous changes of the cervix - dysplasia; Cervical cancer - dysplasia; Squamous intraepithelial lesion - dysplasia; LSIL - dysplasia; HSIL - dysplasia; Low-grade dysplasia; High-grade dysplasia; Carcinoma in situ - dysplasia; CIS - dysplasia; ASCUS - dysplasia; Atypical glandular cells - dysplasia; AGUS - dysplasia; Atypical squamous cells - dysplasia; Pap smear - dysplasia; HPV - dysplasia; Human papilloma virus - dysplasia; Cervix - dysplasia; Colposcopy - dysplasiaCervical dysplasia refers to abnormal changes in the cells on the surface of the cervix. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus (womb) that opens at the top of the vagina.
Cervix
The cervix is the lower end of the womb (uterus). It is at the top of the vagina. It is about 2. 5 to 3. 5 centimeters (1 to 1. 3 inches) long. Th...
The changes are not cancer, but they can lead to cancer of the cervix if not treated.
Causes
Cervical dysplasia can develop at any age. However, treatment and follow-up will depend on your age. Cervical dysplasia is most commonly caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a common virus that is spread through sexual contact. There are many types of HPV. Some types lead to cervical dysplasia or cancer. Other types of HPV can cause genital warts.
The following may increase your risk for cervical dysplasia:
- Having sex before age 18
- Having a baby at very young age
- Having had multiple sexual partners
- Having other illnesses, such as tuberculosis or HIV
- Using medicines that suppress your immune system
- Smoking
- Maternal history of exposure to DES (diethylstilbestrol)
Symptoms
Most of the time, there are no symptoms.
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a pelvic exam to check for cervical dysplasia. The initial test is usually a Pap test and a test for the presence of HPV.
Cervical dysplasia that is seen on a Pap test is called squamous intraepithelial lesion (SIL). On the Pap test report, any abnormal changes will be described as:
Pap test
The Pap test mainly checks for changes in the cervix that may turn into cervical cancer. Cells scraped from the opening of the cervix are examined u...

- Low-grade (LSIL)
- High-grade (HSIL)
- Possibly cancerous (malignant)
- Atypical glandular cells (AGC)
- Atypical squamous cells (ASC)
You will need more tests if a Pap test shows abnormal cells or cervical dysplasia. If the changes were mild, follow-up Pap tests may be all that is needed.
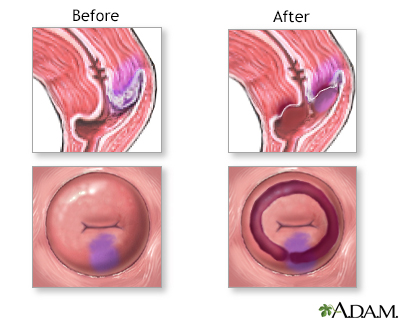
The provider may perform a biopsy to confirm the condition. This may be done with the use of colposcopy. Any areas of concern will be biopsied. The biopsies are very small and most women feel only a small cramp.
Colposcopy
A colposcopy is a special way of looking at the cervix. The cervix is the lower part of the uterus (womb) that opens at the top of the vagina. Abno...

Dysplasia that is seen on a biopsy of the cervix is called cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). It is grouped into 3 categories:
- CIN I -- mild dysplasia
- CIN II -- moderate to marked dysplasia
- CIN III -- severe dysplasia to carcinoma in situ
Some strains of HPV are known to cause cervical cancer. An HPV DNA test can identify the high-risk types of HPV linked to this cancer. This test may be done:
- As a screening test for women age 30 or more
- For women of any age who have a slightly abnormal Pap test result
Treatment
Treatment depends on the degree of dysplasia. Mild dysplasia (LSIL or CIN I) may go away without treatment. Changes due to HPV infection may also go away without treatment or dysplasia.
- You may only need careful follow-up by your provider with repeat Pap tests every 6 to 12 months.
- If the changes do not go away or get worse, treatment is needed.
Treatment for moderate-to-severe dysplasia or mild dysplasia that does not go away may include:
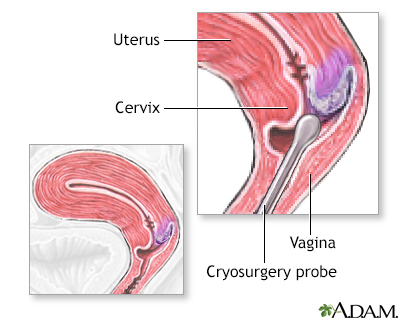
- Cryosurgery to freeze abnormal cells
- Laser therapy, which uses light to burn away abnormal tissue
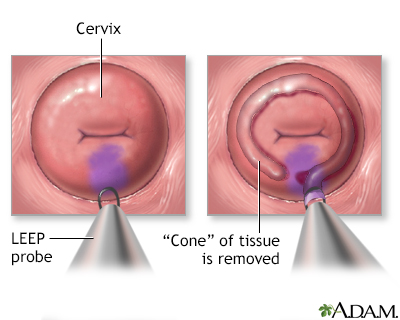
- LEEP (loop electrosurgical excision procedure), which uses electricity to remove abnormal tissue
- Surgery to remove the abnormal tissue (cone biopsy)
- Hysterectomy (in rare cases)
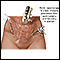
Hysterectomy
Hysterectomy is surgery to remove a woman's womb (uterus). The uterus is a hollow muscular organ that nourishes the developing baby during pregnancy...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
If you have had dysplasia, you will need to have repeat exams every 12 months or as suggested by your provider.
Make sure to get the HPV vaccine when it is offered to you. This vaccine prevents many cervical cancers.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment cures most cases of cervical dysplasia. However, the condition may return.
Without treatment, severe cervical dysplasia may change into cervical cancer.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if your age is 21 or older and you have never had a pelvic exam and Pap test.
Prevention
Ask your provider about the HPV vaccine. Girls who receive this vaccine before they become sexually active reduce their chance of getting cervical cancer.
HPV vaccine
The human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine protects against infection by certain strains of HPV. HPV can cause cervical cancer and genital warts. HPV ha...
You can reduce your risk of developing cervical dysplasia by taking the following steps:
- Get vaccinated for HPV between ages 9 to 45.
- Do not smoke. Smoking increases your risk of developing more severe dysplasia and cancer.
- Do not have sex until you are 18 or older.
- Practice safe sex. Use a condom.
- Practice monogamy. This means you have only one sexual partner at a time.
References
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists website. Practice advisory: updated cervical cancer screening guidelines. www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance/practice-advisory/articles/2021/04/updated-cervical-cancer-screening-guidelines. Updated April 2021. Accessed June 25, 2024.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists' Committee on Adolescent Health Care, American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists' Immunization, Infectious Disease, and Public Health Preparedness Expert Work Group. Human papillomavirus vaccination: ACOG committee opinion, number 809. Obstet Gynecol. 2020;136(2):e15-e21 PMID: 32732766 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32732766/.
Armstrong DK. Gynecologic cancers. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 184.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists website. Updated guidelines for management of cervical cancer screening abnormalities. www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance/practice-advisory/articles/2020/10/updated-guidelines-for-management-of-cervical-cancer-screening-abnormalities. Reaffirmed October 2023. Accessed June 3, 2024.
Fontham ETH, Wolf AMD, Church TR, et al. Cervical cancer screening for individuals at average risk: 2020 guideline update from the American Cancer Society. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(5):321-346. PMID: 32729638 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32729638/.
Hacker NF. Cervical dysplasia and cancer. In: Hacker NF, Gambone JC, Hobel CJ, eds. Hacker & Moore's Essentials of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2016:chap 38.
Murthy N, Wodi AP, McNally V, Cineas S, Ault K. Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommended immunization schedule for adults aged 19 years or older - United States, 2023. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2023;72(6):141-144. PMID: 36757861 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36757861/.
Salcedo MP, Phoolcharoen N , Schmeler KM. Intraepithelial neoplasia of the lower genital tract (cervix, vagina, vulva): etiology, screening, diagnosis, management. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 29.
US Preventive Services Task Force, Curry SJ, Krist AH, Owens DK, et al. Screening for cervical cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2018;320(7):674-686. PMID: 30140884 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30140884/.
Wodi AP, Murthy N, McNally VV, Daley MF, Cineas S. Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommended immunization schedule for children and adolescents aged 18 years or younger - United States, 2024. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2024;73(1):6-10. PMID: 38206855 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38206855/.
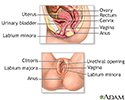
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
Internal structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the uterus, ovaries, and cervix. External structures include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
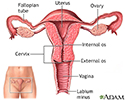
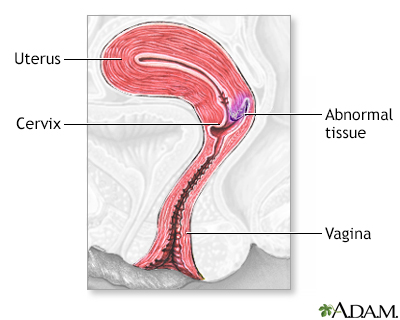
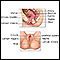
Cervical neoplasia - illustration
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) is the presence of abnormal cells on the surface of the cervix. A Pap smear and colposcopy are two of the procedures performed to monitor the cells and appearance of the cervix.
Cervical neoplasia
illustration
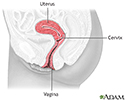
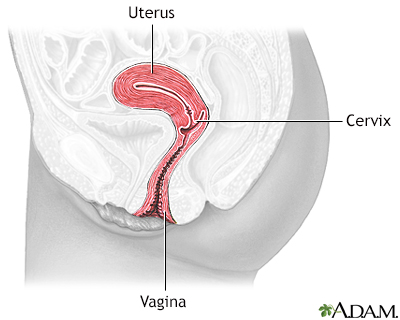
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
Cervical dysplasia - series
Presentation
Female reproductive anatomy - illustration
Internal structures of the female reproductive anatomy include the uterus, ovaries, and cervix. External structures include the labium minora and majora, the vagina and the clitoris.
Female reproductive anatomy
illustration
Cervical neoplasia - illustration
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) is the presence of abnormal cells on the surface of the cervix. A Pap smear and colposcopy are two of the procedures performed to monitor the cells and appearance of the cervix.
Cervical neoplasia
illustration
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
Cervical dysplasia - series
Presentation
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.