Hemangioma
Infantile hemangioma; Cavernous hemangioma; Strawberry nevus; Birthmark - hemangiomaA hemangioma is an abnormal buildup of blood vessels in the skin or internal organs.
Causes
About one third of hemangiomas are present at birth. The rest appear in the first several months of life.
The hemangioma may be:
- In the top skin layers (capillary hemangioma)
Capillary hemangioma
Red birthmarks are skin markings created by blood vessels close to the skin surface. They develop before or shortly after birth.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Deeper in the skin (cavernous hemangioma)
- A mixture of both layers of skin
- In an internal organ and not visible
Symptoms
Symptoms of a hemangioma are:
- A red to reddish-purple, raised growth on the skin
- A massive, raised, bluish lump with visible blood vessels
Most hemangiomas are on the head, neck, or extremities.
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will do a physical exam to diagnose a hemangioma. If the buildup of blood vessels is deep inside the body, a CT or MRI scan may be needed.
CT
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...

MRI
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the body. It does not us...
A hemangioma may occur with other rare conditions. Other tests to check for related problems may be done.
Treatment
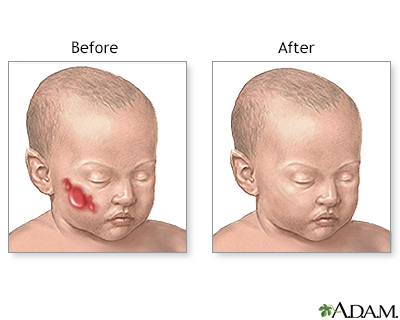
The majority of small or uncomplicated hemangiomas may not need treatment. They often go away on their own and the appearance of the skin returns to normal. Sometimes, a laser may be used to remove the small blood vessels.
Taking beta-blocker medicines may also help reduce the size of a hemangioma.
Cavernous hemangiomas that involve the eyelid and block vision can be treated with lasers or steroid injections to shrink them. This allows vision to develop normally. Large cavernous hemangiomas or mixed hemangiomas may be treated with steroids, taken by mouth or injected into the hemangioma.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Small superficial hemangiomas will often disappear on their own. About one half go away by age 5, and almost all disappear by age 7.
Possible Complications
These complications can occur from a hemangioma:
- Bleeding (especially if the hemangioma is injured)
-
Problems with breathing and eating
Problems with breathing
Most people take breathing for granted. People with certain illnesses may have breathing problems that they deal with on a regular basis. This arti...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Psychological problems, from skin appearance
-
Secondary infections and sores
Secondary infections
A secondary infection is an infection that occurs during or after treatment for another infection. It may be caused by the first treatment or by cha...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Visible changes in the skin
-
Vision problems
Vision problems
There are many types of eye problems and vision disturbances, such as: Halos Blurred vision (the loss of sharpness of vision and the inability to see...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
All birthmarks, including hemangiomas, should be evaluated by your provider during a regular exam.
Hemangiomas of the eyelid that may cause problems with vision must be treated soon after birth. Hemangiomas that interfere with eating or breathing also need to be treated early.
Contact your provider if a hemangioma is bleeding or develops a sore.
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent hemangiomas.
References
Dinulos JGH. Vascular tumors and malformations. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 23.
Martin KL. Vascular anomalies. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 691.
Patterson JW. Vascular tumors. In: Patterson JW, ed. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Limited; 2021:chap 39.
-
Hemangioma - angiogram - illustration
This angiogram (an X-ray taken after dye has been injected into the blood stream) shows a mass of blood vessels (hemangioma) in the liver.
Hemangioma - angiogram
illustration
-
Hemangioma excision - series
Presentation
-
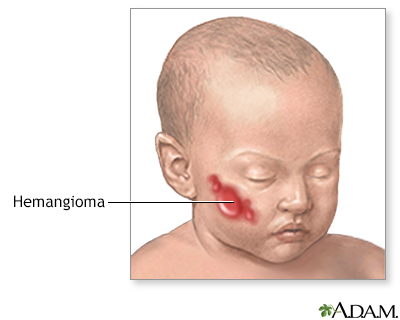
Hemangioma on the face (nose) - illustration
Hemangiomas are tumors made up of dilated blood vessels that usually appear shortly after birth, although they may be present at birth. Hemangiomas on the face can be disfiguring and may interfere with visual development or cause obstruction of the airway.
Hemangioma on the face (nose)
illustration
-
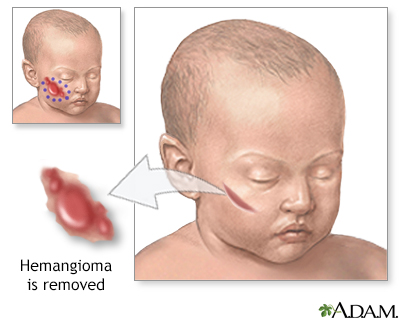
Hemangioma excision - illustration
A hemangioma is a non-cancerous (benign) growth of blood vessels. They are the most common benign blood vessel (vascular) growths in infants and children. Most resolve with time and occasionally with medication. Large or disfiguring hemangiomas may require surgical excision.
Hemangioma excision
illustration
-
Hemangioma - angiogram - illustration
This angiogram (an X-ray taken after dye has been injected into the blood stream) shows a mass of blood vessels (hemangioma) in the liver.
Hemangioma - angiogram
illustration
-
Hemangioma excision - series
Presentation
-
Hemangioma on the face (nose) - illustration
Hemangiomas are tumors made up of dilated blood vessels that usually appear shortly after birth, although they may be present at birth. Hemangiomas on the face can be disfiguring and may interfere with visual development or cause obstruction of the airway.
Hemangioma on the face (nose)
illustration
-
Hemangioma excision - illustration
A hemangioma is a non-cancerous (benign) growth of blood vessels. They are the most common benign blood vessel (vascular) growths in infants and children. Most resolve with time and occasionally with medication. Large or disfiguring hemangiomas may require surgical excision.
Hemangioma excision
illustration
Review Date: 10/14/2024
Reviewed By: Elika Hoss, MD, Assistant Professor of Dermatology, Mayo Clinic, Scottsdale, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.