Leishmaniasis
Kala-azar; Cutaneous leishmaniasis; Visceral leishmaniasis; Old world leishmaniasis; New world leishmaniasisLeishmaniasis is an infectious disease spread by the bite of the female sandfly.
Causes
Leishmaniasis is caused by a tiny parasite called leishmania protozoa. Protozoa are one-celled organisms.
The different forms of leishmaniasis are:
- Cutaneous leishmaniasis affects the skin and mucous membranes. Skin sores usually start at the site of the sandfly bite. In a few people, sores may develop on mucous membranes.
- Systemic, or visceral, leishmaniasis affects the entire body. This form occurs 2 to 8 months after a person is bitten by the sandfly. Most people do not remember having a skin sore. This form can lead to deadly complications. The parasites damage the immune system by decreasing the numbers of disease-fighting cells.
Cases of leishmaniasis have been reported on all continents except Australia and Antarctica. In the Americas, the disease can be found in Mexico and South America. It has also been reported in military personnel who have returned from the Persian Gulf.
Symptoms
Symptoms of cutaneous leishmaniasis depend on where the lesions are located and may include:
- Breathing difficulty
- Skin sores, which may become a skin ulcer that heals very slowly
- Stuffy nose, runny nose, and nosebleeds
- Swallowing difficulty
- Ulcers and wearing away (erosion) in the mouth, tongue, gums, lips, nose, and inner nose
Systemic visceral infection in children usually begins suddenly with:
- Cough
- Diarrhea
- Fever
-
Vomiting
Vomiting
Nausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach. "Vomiting or throwing-up forces the contents of the stomach up t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Adults usually have a fever for 2 weeks to 2 months, along with symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and appetite loss. Weakness increases as the disease gets worse.
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.

Other symptoms of systemic visceral leishmaniasis may include:
- Abdominal discomfort
- Fever that lasts for weeks; may come and go in cycles
- Night sweats
- Scaly, gray, dark, ashen skin
- Thinning hair
- Weight loss
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will examine you and may find that your spleen, liver, and lymph nodes are enlarged. You will be asked if you recall being bitten by sandflies or if you've been in an area where leishmaniasis is common.
Tests that may be done to diagnose the condition include:
-
Biopsy of the spleen and culture
Biopsy
A biopsy is the removal of a small piece of tissue for lab examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Bone marrow biopsy and culture
Bone marrow biopsy
A bone marrow biopsy is the removal of marrow from inside one of your bones. Bone marrow is the soft tissue inside bones that helps form blood cells...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Direct agglutination assay
- Indirect immunofluorescent antibody test
- Leishmania-specific PCR test
-
Liver biopsy and culture
Liver biopsy
A liver biopsy is a test that takes a sample of tissue from the liver for examination.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Lymph node biopsy and culture
Lymph node biopsy
A lymph node biopsy is the removal of lymph node tissue for examination under a microscope. The lymph nodes are small glands that make white blood ce...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Montenegro skin test (not approved in the United States)
-
Skin biopsy and culture
Skin biopsy
A skin lesion biopsy is when a small amount of skin is removed so it can be examined under a microscope. The skin is tested to look for skin conditi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other tests that may be done include:
-
Complete blood count with differential
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleDifferential
The blood differential test measures the percentage of each type of white blood cell (WBC) that you have in your blood. It also reveals if there are...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Serologic testing
-
Serum albumin
Serum albumin
Albumin is a protein made by the liver. A serum albumin test measures the amount of this protein in the clear liquid portion of the blood. Albumin c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Serum immunoglobulin levels
Serum immunoglobulin levels
Serum immunoelectrophoresis is a lab test that measures proteins called immunoglobulins in the blood. Immunoglobulins are proteins that function as ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Serum protein
Protein
Proteins are the building blocks of life. Every cell in the human body contains protein. The basic structure of protein is a chain of amino acids. ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Antimony-containing compounds are the main medicines used to treat leishmaniasis. These include:
- Meglumine antimoniate
- Sodium stibogluconate
Other medicines that may be used include:
- Amphotericin B
- Ketoconazole
- Miltefosine
- Paromomycin
- Pentamidine
Plastic surgery may be needed to correct the disfigurement caused by sores on the face (cutaneous leishmaniasis).
Outlook (Prognosis)
Cure rates are high with the proper medicine, mostly when treatment is started before it affects the immune system. Cutaneous leishmaniasis may lead to disfigurement.
Death is usually caused by complications (such as other infections), rather than from the disease itself. Death often occurs within 2 years.
Possible Complications
Leishmaniasis may lead to the following:
- Bleeding (hemorrhage)
- Deadly infections due to immune system damage
- Disfigurement of the face
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of leishmaniasis after visiting an area where the disease is known to occur.
Prevention
Taking measures to avoid sandfly bites can help prevent leishmaniasis:
- Putting fine mesh netting around the bed (in areas where the disease occurs)
- Screening windows
- Wearing insect repellent
- Wearing protective clothing
Public health measures to reduce sandflies are important. There are no vaccines or medicines that prevent leishmaniasis.
References
Aronson NE, Copeland NK, Magill AJ. Leishmania species: visceral (kala-azar), cutaneous, and mucosal leishmaniasis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 275.
Dinulos JGH. Infestations and bites. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 15.
-
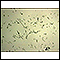
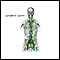
Leishmaniasis - illustration
Leishmaniasis is a parasitic disease spread by the bite of the sandfly and can cause skin disease and systemic disease. The systemic form can be fatal, but treatment with antimony-containing compounds produces a high cure rate.
Leishmaniasis
illustration
-
Leishmaniasis, mexicana - lesion on the cheek - illustration
Parasites are deposited in the skin by the bite of a sand-fly. These parasites (leishmania) produce a local sore at the site of the bite and migrate throughout the body, causing tissue destruction at distant sites.
Leishmaniasis, mexicana - lesion on the cheek
illustration
-
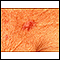
Leishmaniasis on the finger - illustration
Leishmaniasis is seen in the United States mainly in people who have traveled outside the U.S. There are several different types of leishmaniasis, but all are transmitted by the bite of a sandfly. An initial sore develops at the site of the bite, as shown here. The infection may spread through the body from that point.
Leishmaniasis on the finger
illustration
-
Leishmania panamensis on the foot - illustration
Leishmaniasis is seen in the United States mainly in people who have traveled outside the U.S. There are several different types of leishmaniasis, but all are transmitted by the bite of a sandfly. An initial sore develops at the site of the bite, as shown here. The infection may spread through the body from that point.
Leishmania panamensis on the foot
illustration
-
Leishmania panamensis - close-up - illustration
Leishmaniasis is seen in the United States mainly in people who travel outside the U.S. There are several different types of leishmaniasis, but all are transmitted by the bite of a sandfly. This is the typical appearance of the early stage of leishmaniasis.
Leishmania panamensis - close-up
illustration
-
Leishmaniasis - illustration
Leishmaniasis is a parasitic disease spread by the bite of the sandfly and can cause skin disease and systemic disease. The systemic form can be fatal, but treatment with antimony-containing compounds produces a high cure rate.
Leishmaniasis
illustration
-
Leishmaniasis, mexicana - lesion on the cheek - illustration
Parasites are deposited in the skin by the bite of a sand-fly. These parasites (leishmania) produce a local sore at the site of the bite and migrate throughout the body, causing tissue destruction at distant sites.
Leishmaniasis, mexicana - lesion on the cheek
illustration
-
Leishmaniasis on the finger - illustration
Leishmaniasis is seen in the United States mainly in people who have traveled outside the U.S. There are several different types of leishmaniasis, but all are transmitted by the bite of a sandfly. An initial sore develops at the site of the bite, as shown here. The infection may spread through the body from that point.
Leishmaniasis on the finger
illustration
-
Leishmania panamensis on the foot - illustration
Leishmaniasis is seen in the United States mainly in people who have traveled outside the U.S. There are several different types of leishmaniasis, but all are transmitted by the bite of a sandfly. An initial sore develops at the site of the bite, as shown here. The infection may spread through the body from that point.
Leishmania panamensis on the foot
illustration
-
Leishmania panamensis - close-up - illustration
Leishmaniasis is seen in the United States mainly in people who travel outside the U.S. There are several different types of leishmaniasis, but all are transmitted by the bite of a sandfly. This is the typical appearance of the early stage of leishmaniasis.
Leishmania panamensis - close-up
illustration
Review Date: 8/26/2023
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Associate Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Associate in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.