Burkitt lymphoma
B-cell lymphoma; High-grade B-cell lymphoma; Small noncleaved cell lymphoma; Burkitt's lymphomaBurkitt lymphoma (BL) is a very fast growing form of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is cancer of the lymph tissue. Lymph tissue is found in the lymph nodes, spleen, and other organs of the immune system. W...

Causes
BL was first discovered in children in certain parts of Africa. It also occurs in the United States.
The African type of BL is closely associated with the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), the main cause of infectious mononucleosis. The North American form of BL is not commonly linked to EBV.
Infectious mononucleosis
Mononucleosis, or mono, is a viral infection that causes fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph glands, most often in the neck.

People with HIV/AIDS have an increased risk for this condition. BL is most often seen in males.
HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...

Symptoms
BL may first be noticed as a swelling of the lymph nodes (glands) in the head and neck. These swollen lymph nodes are often painless, but can grow very rapidly.
Swelling of the lymph nodes
Lymph nodes are present throughout your body. They are an important part of your immune system. Lymph nodes help your body recognize and fight germ...
In the types commonly seen in the United States, the cancer often starts in the belly area (abdomen). The disease can also start in the ovaries, testes, brain, kidneys, liver, and spinal fluid.
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleOther general symptoms may include:
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Unexplained weight loss
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam. Tests that may be done include:
- Bone marrow biopsy
Bone marrow biopsy
A bone marrow biopsy is the removal of marrow from inside one of your bones. Bone marrow is the soft tissue inside bones that helps form blood cells...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - CT scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis
CT scan of the chest
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleAbdomen
An abdominal CT scan is an imaging test that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the belly area. CT stands for computed tomography....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticlePelvis
A computed tomography (CT) scan of the pelvis is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the area between the hip bo...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Complete blood count (CBC)
Complete blood count (CBC)
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Examination of the spinal fluid
Examination of the spinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lymph node biopsy
Lymph node biopsy
A lymph node biopsy is the removal of lymph node tissue for examination under a microscope. The lymph nodes are small glands that make white blood ce...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - MRI of the abdomen or other affected body area
- PET scan
PET scan
A positron emission tomography (PET) scan is a type of imaging test. It uses a radioactive substance called a tracer to look for disease in the body...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Chemotherapy is used to treat this type of cancer. If the cancer does not respond to chemotherapy alone, a bone marrow transplant may be done.
Chemotherapy
The term chemotherapy is used to describe cancer-killing drugs. Chemotherapy may be used to:Cure the cancerShrink the cancerPrevent the cancer from ...
Bone marrow transplant
A bone marrow transplant is a procedure to replace damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy bone marrow stem cells. Bone marrow is the soft, fatt...

Outlook (Prognosis)
More than one half of people with BL can be cured with intensive chemotherapy. The cure rate may be lower if the cancer spreads to the bone marrow or spinal fluid. The outlook is poor if the cancer comes back after a remission or does not go into remission as a result of the first cycle of chemotherapy.
Possible Complications
Possible complications of BL include:
- Complications of treatment
- Spread of the cancer
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of BL.
References
Abramson JS. Non-Hodgkin lymphomas. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Kastan MB, Doroshow JH, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff's Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 103.
Said JW. Immunodeficiency-related lymphoproliferative disorders. In: Hsi ED, ed. Hematopathology: Foundations of Diagnostic Pathology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 10.
Schooley RT, Allen UD. Epstein-Barr virus infection. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 348.
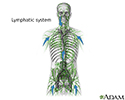
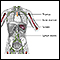
Lymphatic system - illustration
The lymphatic system filters fluid from around cells. It is an important part of the immune system. When people refer to swollen glands in the neck, they are usually referring to swollen lymph nodes. Common areas where lymph nodes can be easily felt, especially if they are enlarged, are the groin, armpits (axilla), above the clavicle (supraclavicular), in the neck (cervical), and the back of the head just above hairline (occipital).
Lymphatic system
illustration
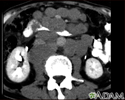
Lymphoma, malignant - CT scan - illustration
This abdominal CT scan shows tumor masses (malignant lymphomas) in the area behind the peritoneal cavity (retroperitoneal space).
Lymphoma, malignant - CT scan
illustration
Lymphatic system - illustration
The lymphatic system filters fluid from around cells. It is an important part of the immune system. When people refer to swollen glands in the neck, they are usually referring to swollen lymph nodes. Common areas where lymph nodes can be easily felt, especially if they are enlarged, are the groin, armpits (axilla), above the clavicle (supraclavicular), in the neck (cervical), and the back of the head just above hairline (occipital).
Lymphatic system
illustration
Lymphoma, malignant - CT scan - illustration
This abdominal CT scan shows tumor masses (malignant lymphomas) in the area behind the peritoneal cavity (retroperitoneal space).
Lymphoma, malignant - CT scan
illustration
Review Date: 6/17/2024
Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.