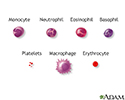
Agranulocytosis
Granulocytopenia; Granulopenia; NeutropeniaWhite blood cells fight infections from bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other germs. One important type of white blood cell is the granulocyte, which is made in the bone marrow and travels in the blood throughout the body. Granulocytes sense infections, gather at sites of infection, and destroy the germs.
When the body has too few granulocytes, the condition is called agranulocytosis. This makes it harder for the body to fight off germs. As a result, the person may get sick from infections.
Causes
Agranulocytosis may be caused by:
-
Autoimmune disorders
Autoimmune disorders
An autoimmune disorder occurs when the body's immune system attacks and destroys healthy body tissue by mistake. There are more than 80 autoimmune d...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Bone marrow diseases, such as myelodysplasia or large granular lymphocyte (LGL) leukemia
- Certain medicines used to treat diseases, including cancer
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Certain street drugs
- Poor nutrition
- Preparation for bone marrow transplant
Bone marrow transplant
A bone marrow transplant is a procedure to replace damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy bone marrow stem cells. Bone marrow is the soft, fatt...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Benign familial neutropenia
- Genetic variants, especially in people of certain African and Caribbean ethnicities
Symptoms
Symptoms of this condition may include:
- Fever
-
Chills
Chills
Chills refers to feeling cold after being in a cold environment. The word can also refer to an episode of shivering along with paleness and feeling ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Malaise
Malaise
Malaise is a general feeling of discomfort, illness, or lack of well-being.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - General weakness
- Sore throat
- Mouth and throat ulcers
Ulcers
An ulcer is a crater-like sore on the skin or mucous membrane. Ulcers form when the top layers of skin or tissue have been removed. They can occur ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Bone pain
Bone pain
Bone pain or tenderness is aching or other discomfort in one or more bones.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). This type of pneu...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Shock
Shock
Septic shock is a serious condition that occurs when a body-wide infection leads to dangerously low blood pressure.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
A white blood cell differential test will be done to measure the percentage of each type of white blood cell in your blood.
White blood cell differential test
The blood differential test measures the percentage of each type of white blood cell (WBC) that you have in your blood. It also reveals if there are...
Other tests to diagnose the condition may include:
-
Bone marrow biopsy
Bone marrow biopsy
A bone marrow biopsy is the removal of marrow from inside one of your bones. Bone marrow is the soft tissue inside bones that helps form blood cells...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Biopsy of mouth ulcer
Biopsy of mouth ulcer
An oropharynx lesion biopsy is surgery in which tissue from an abnormal growth or mouth sore is removed and checked for disease.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Neutrophil antibody tests (blood test)
Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause of the low white blood cell count. For example, if a medicine is the cause, stopping or changing to another medicine may help. In other cases, medicines to help the body make more white blood cells will be used. If the cause is due to normal genes, no treatment is required.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Treating or removing the cause often results in a good outcome.
Prevention
If you are having treatment or taking medicine that could cause agranulocytosis, your health care provider will use blood tests to monitor you.
References
Berliner N. Leukocytosis and leukopenia. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 153.
Klokkevold PR, Mealey BL, Hernandez-Kapila YL. Influence of systemic conditions on the periodontium. In: Newman MG, Klokkevold PR, Elangovan S, Hernandez-Kapila YL, eds. Newman and Carranza's Clinical Periodontology and Implantology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 25.
Murphy MF, Pasi KJ, Roy N. Haematology. In: Feather A, Randall D, Waterhouse M, eds. Kumar and Clark's Clinical Medicine. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 16.
Rice L, Zieske AW, Jung M. Neutrophilic leukocytosis, neutropenia, monocytosis, and monocytopenia. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 49.
Review Date: 6/17/2024
Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.