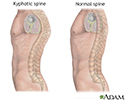
Kyphosis
Scheuermann disease; Roundback; Hunchback; Postural kyphosis; Neck pain - kyphosisKyphosis is a curving of the spine that causes a bowing or rounding of the back. This leads to a hunchback or slouching posture.
Causes
Kyphosis can occur at any age, although it is rare at birth.
A type of kyphosis that occurs in young teens is known as Scheuermann disease. It is caused by the wedging together of several bones of the spine (vertebrae) in a row. The cause of this condition is unknown. Kyphosis can also occur in young teens who have cerebral palsy.
Cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of disorders that involve the brain. This affects nervous system functions, such as movement, learning, hearing, seei...
In adults, kyphosis can be caused by:
- Degenerative diseases of the spine (such as arthritis or disk degeneration)
Arthritis
Arthritis is inflammation or degeneration of one or more joints. A joint is the area where 2 bones meet. There are more than 100 different types of...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fractures caused by osteoporosis (osteoporotic compression fractures)
Fractures
If more pressure is put on a bone than it can stand, it will split or break. A break of any size is called a fracture. If the broken bone punctures...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleOsteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become fragile and more likely to break (fracture).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Injury (trauma)
- Slipping of one vertebra forward on another (spondylolisthesis)
Spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis is a condition in which a bone (vertebra) in the spine moves forward, out of its proper position, in relation to the bone below it....
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Previous surgeries or fusion on the spine
Other causes of kyphosis include:
- Certain hormone (endocrine) diseases
Endocrine
Endocrine glands release (secrete) hormones into the bloodstream. The endocrine glands include:AdrenalHypothalamusIslets of Langerhans in the pancrea...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Connective tissue disorders
- Infection (such as tuberculosis)
Tuberculosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection that involves the lungs. It may spread to other organs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Muscular dystrophy (group of inherited disorders that cause muscle weakness and loss of muscle tissue)
Muscular dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy (MD) is a group of inherited disorders that cause muscle weakness and loss of muscle tissue, which get worse over time.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Neurofibromatosis (disorder in which nerve tissue tumors form)
Neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatosis-1 (NF1) is an inherited disorder in which nerve tissue tumors (neurofibromas) form in the:Upper and lower layers of the skinNerves ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Paget disease (disorder that involves abnormal bone destruction and regrowth)
Paget disease
Paget disease is a disorder that involves abnormal bone destruction and regrowth. This results in deformity of the affected bones.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Polio
Polio
Polio is a viral disease that can affect nerves and can lead to partial or full paralysis. The medical name for polio is poliomyelitis.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Scoliosis (curving of the spine often looks like a C or S when viewed from behind)
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is an abnormal curving of the spine. Your spine is your backbone. It runs straight down your back. Everyone's spine naturally curves a b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Spina bifida (birth defect in which the backbone and spinal canal don't close before birth)
Spina bifida
Myelomeningocele is a birth defect in which the backbone and spinal canal do not close fully before birth. The condition is a type of neural tube de...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tumors of the spine or the area nearby
Symptoms
Pain in the middle or lower back is the most common symptom. Other symptoms may include any of the following:
- Round back appearance
- Tenderness and stiffness in the spine
-
Fatigue
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
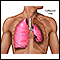
Difficulty breathing (in severe cases)
Difficulty breathing
Most people take breathing for granted. People with certain illnesses may have breathing problems that they deal with on a regular basis. This arti...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
A physical exam by your health care provider can confirm the abnormal curve of the spine. Your provider will also look for any nervous system (neurological) changes. These include weakness, paralysis, or changes in sensation below the curve. Your provider will also check for differences in your reflexes.
Tests that may be ordered include:
-
Spine x-ray
Spine x-ray
A thoracic spine x-ray is an x-ray of the 12 chest (thoracic) bones (vertebrae) of the spine. The vertebrae are separated by flat pads of cartilage ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Pulmonary function tests (if kyphosis affects breathing)
Pulmonary function tests
Pulmonary function tests are a group of tests that measure breathing and how well the lungs are functioning.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
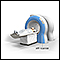
MRI of the spine (if there may be a tumor, infection, or nervous system symptoms)
MRI
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the body. It does not us...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Bone density test (to check for osteoporosis)
Bone density test
A bone mineral density (BMD) test measures how much calcium and other types of minerals are in an area of your bone. This test helps your health care...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause of the disorder:
- Congenital kyphosis needs corrective surgery at an early age.
- Scheuermann disease is treated with a brace and physical therapy. Sometimes surgery is needed for large (greater than 60 degrees), painful curves.
-
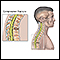
Compression fractures from osteoporosis can be left alone if there are no nervous system problems or pain. But the osteoporosis needs to be treated to help prevent future fractures. For severe deformity or pain from osteoporosis, surgery is an option.
Compression fractures
Compression fractures of the back are broken vertebrae. Vertebrae are the bones of the spine.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Kyphosis caused by infection or tumor needs prompt treatment, often with surgery and medicines.
Treatment for other types of kyphosis depends on the cause. Surgery is needed if nervous system symptoms or constant pain develop.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Young teens with Scheuermann disease tend to do well, even if they need surgery. The disease stops once they stop growing. If the kyphosis is due to degenerative joint disease or multiple compression fractures, surgery is needed to correct the defect and improve pain.
Degenerative joint disease
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common joint disorder. It is due to aging and wear and tear on a joint.
Possible Complications
Untreated kyphosis can cause any of the following:
- Decreased lung capacity
- Disabling back pain
- Nervous system symptoms, including leg weakness or paralysis
- Round back deformity
- Increased self-consciousness or body awareness
Prevention
Treating and preventing osteoporosis can prevent many cases of kyphosis in older adults. Early diagnosis and bracing for Scheuermann disease can reduce the need for surgery, but there is no way to prevent the disease.
References
Magee DJ, Manske RC. Thoracic (dorsal) spine. In: Magee DJ, Manske RC, eds. Orthopedic Physical Assessment. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 8.
McClincy MP, Olgun ZD, Dede O. Orthopedics. In: Zitelli BJ, McIntire SC, Nowalk AJ, Garrison J, eds. Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 22.
Warner WC, Sawyer JR. Scoliosis and kyphosis. In: Azar FM, Beaty JH, eds. Campbell's Operative Orthopaedics. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 44.
-
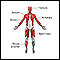
Skeletal spine - illustration
The spine is divided into several sections. The cervical vertebrae make up the neck. The thoracic vertebrae comprise the chest section and have ribs attached. The lumbar vertebrae are the remaining vertebrae below the last thoracic bone and the top of the sacrum. The sacral vertebrae are caged within the bones of the pelvis, and the coccyx represents the terminal vertebrae or vestigial tail.
Skeletal spine
illustration
-
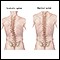
Kyphosis - illustration
Kyphosis is a curving of the spine that causes a bowing of the back, such that the apex of the angle points backwards leading to a hunchback or slouching posture.
Kyphosis
illustration
-
Skeletal spine - illustration
The spine is divided into several sections. The cervical vertebrae make up the neck. The thoracic vertebrae comprise the chest section and have ribs attached. The lumbar vertebrae are the remaining vertebrae below the last thoracic bone and the top of the sacrum. The sacral vertebrae are caged within the bones of the pelvis, and the coccyx represents the terminal vertebrae or vestigial tail.
Skeletal spine
illustration
-
Kyphosis - illustration
Kyphosis is a curving of the spine that causes a bowing of the back, such that the apex of the angle points backwards leading to a hunchback or slouching posture.
Kyphosis
illustration
Review Date: 8/27/2024
Reviewed By: C. Benjamin Ma, MD, Professor, Chief, Sports Medicine and Shoulder Service, UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, San Francisco, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.