Thyroid cancer
Tumor - thyroid; Cancer - thyroid; Nodule - thyroid cancer; Papillary thyroid carcinoma; Medullary thyroid carcinoma; Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma; Follicular thyroid cancerThyroid cancer is a cancer that starts in the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located in the front of your lower neck.
Causes
Thyroid cancer can occur in people of any age.
Radiation to the thyroid increases the risk of developing thyroid cancer. Exposure may occur from:
-
Radiation therapy to the neck (especially in childhood)
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-powered radiation (such as x-rays or gamma rays), particles, or radioactive seeds to kill cancer cells.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Radiation exposure from nuclear plant disasters
Other risk factors are a family history of thyroid cancer and chronic goiter (enlarged thyroid). Being overweight or having obesity may be a risk factor for papillary carcinoma of the thyroid.
Goiter
A simple goiter is an enlargement of the thyroid gland. It is usually not a tumor or cancer.
There are several types of thyroid cancer:
-
Anaplastic carcinoma (also called giant and spindle cell cancer) is the most dangerous form of thyroid cancer. It is rare, and spreads quickly.
Anaplastic carcinoma
Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma is a rare and aggressive form of cancer of the thyroid gland.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Follicular carcinoma is more likely to come back and spread.
-
Medullary carcinoma is a cancer of non-thyroid hormone-producing cells that are normally present in the thyroid gland. This form of thyroid cancer tends to occur in families.
Medullary carcinoma
Medullary carcinoma of the thyroid is cancer of the thyroid gland that starts in cells that release a hormone called calcitonin. These cells are cal...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Papillary carcinoma is the most common type, and it usually affects women of childbearing age. It spreads slowly and is the least dangerous type of thyroid cancer.
Papillary carcinoma
Papillary carcinoma of the thyroid is the most common cancer of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is located in front of the lower neck.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on the type of thyroid cancer, but may include:
- Cough
- Difficulty swallowing
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland
- Hoarseness or changing voice
- Neck swelling
- Thyroid lump (nodule)
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam. This may reveal a lump in your thyroid or swollen lymph nodes in your neck.
The following tests may be done:
-
Calcitonin blood test to check for medullary thyroid cancer
Calcitonin
The calcitonin blood test measures the level of the hormone calcitonin in the blood.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - An examination of the airway with a fiberoptic scope (laryngoscopy) may show a paralyzed vocal cord.
Laryngoscopy
Laryngoscopy is an exam of the back of your throat, including your voice box (larynx). Your voice box contains your vocal cords and allows you to sp...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Thyroid biopsy, which may include genetic testing of the cells obtained in the biopsy
-
Thyroid scan
Thyroid scan
A thyroid scan uses a radioactive iodine tracer to examine the structure and function of the thyroid gland. This test is often done together with a ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
TSH, free T4 (blood tests for thyroid function)
TSH
A TSH test measures the amount of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) in your blood. TSH is produced by the pituitary gland. It prompts the thyroid g...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleT4
T4 (thyroxine) is the main hormone produced by the thyroid gland. A laboratory test can be done to measure the amount of free T4 in your blood. Fre...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
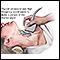
Ultrasound of the thyroid and the lymph nodes of the neck
Ultrasound of the thyroid
A thyroid ultrasound is an imaging method to see the thyroid, a gland in the neck that regulates metabolism (the many processes that control the rate...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
CT scan of the neck (to determine the extent of the cancerous mass)
CT scan
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
PET scan
PET scan
A positron emission tomography (PET) scan is a type of imaging test. It uses a radioactive substance called a tracer to look for disease in the body...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Treatment depends on the type of thyroid cancer. Treatment of most thyroid cancer types is effective if diagnosed early.
Surgery is most often the initial treatment. All or part of the thyroid gland may be removed. If your provider suspects that the cancer has spread to lymph nodes in the neck, these will also be removed. If some of your thyroid gland remains, you will need follow-up ultrasound and possibly other studies to detect any regrowth of thyroid cancer.
Thyroid gland may be removed
Thyroid gland removal is surgery to remove all or part of the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland located inside the front ...
Radiation therapy may be done with or without surgery. It may be performed by:
- Taking radioactive iodine by mouth
- Aiming external beam (x-ray) radiation at the thyroid
After treatment for thyroid cancer, you must take thyroid hormone pills for the rest of your life. The dosage is usually slightly higher than what your body needs. This helps keep the cancer from coming back. The pills also replace the thyroid hormone your body needs to function normally.
If the cancer does not respond to surgery or radiation, and has spread to other parts of the body, chemotherapy or targeted therapy may be used. These are only needed by a small number of people.
Chemotherapy
The term chemotherapy is used to describe cancer-killing drugs. Chemotherapy may be used to:Cure the cancerShrink the cancerPrevent the cancer from ...
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy uses medicines to stop cancer from growing and spreading. It does this with less harm to normal cells than other treatments. Stand...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleSupport Groups
You can ease the stress of illness by joining a cancer support group. Sharing with others who have common experiences and problems can help you not feel alone.
Cancer support group
The following organizations are good resources for information on cancer:American Cancer Society. Support and online communities. www. cancer. org/...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticlePossible Complications
Complications of thyroid cancer may include:
- Injury to the voice box and hoarseness after thyroid surgery
- Low calcium level from accidental removal of the parathyroid glands during surgery
- Spread of the cancer to the lungs, bones, or other parts of the body
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you notice a lump in your neck.
Prevention
Awareness of risk (such as previous radiation therapy to the neck) can allow earlier diagnosis and treatment.
Sometimes, people with family histories and genetic mutations related to medullary thyroid cancer will have their thyroid gland removed to prevent cancer.
References
Kitahara CM, Pfeiffer RM, Sosa JA, Shiels MS. Impact of overweight and obesity on US Papillary Thyroid Cancer Incidence Trends (1995-2015). J Natl Cancer Inst. 2020;112(8):810. PMID: 31638139 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31638139/.
National Cancer Institute website. Thyroid cancer treatment (PDQ) - health provisional version. www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/pdq/treatment/thyroid/HealthProfessional. Updated April 11, 2024. Accessed May 7, 2024.
Pearce EN, Hollenberg AN. Thyroid. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 207.
Suh I, Sosa JA. Thyroid. In: Townsend CM Jr, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL, eds. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. 21st ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022:chap 37.
Thompson LDR. Malignant neoplasms of the thyroid gland. In: Thompson LDR, Bishop JA, eds. Head and Neck Pathology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 25.
-
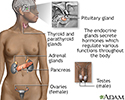
Endocrine glands - illustration
Endocrine glands release hormones (chemical messengers) into the bloodstream to be transported to various organs and tissues throughout the body. For instance, the pancreas secretes insulin, which allows the body to regulate levels of sugar in the blood. The thyroid gets instructions from the pituitary to secrete hormones which determine the rate of metabolism in the body (the more hormone in the bloodstream, the faster the chemical activity; the less hormone, the slower the activity).
Endocrine glands
illustration
-
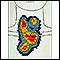
Thyroid cancer - CT scan - illustration
This CT scan of the upper chest (thorax) shows a malignant thyroid tumor (cancer). The dark area around the trachea (marked by the white U-shaped tip of the respiratory tube) is an area where normal tissue has been eroded and died (necrosis) as a result of tumor growth.
Thyroid cancer - CT scan
illustration
-
Thyroid cancer - CT scan - illustration
This CT scan shows a thyroid cancer tumor in the throat, encircling, narrowing, and displacing the windpipe (trachea).
Thyroid cancer - CT scan
illustration
-
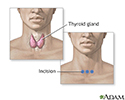
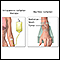
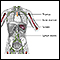
Incision for thyroid gland surgery - illustration
The thyroid is a gland located in the neck. It is a part of the endocrine (hormone) system, and plays a major role in regulating the body's metabolism. If surgery or an open excisional biopsy is needed, an incision is made in front of the neck to gain access to the thyroid gland.
Incision for thyroid gland surgery
illustration
-
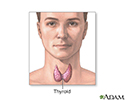
Thyroid gland - illustration
The thyroid gland, a part of the endocrine (hormone) system, plays a major role in regulating the body's metabolism.
Thyroid gland
illustration
-
Endocrine glands - illustration
Endocrine glands release hormones (chemical messengers) into the bloodstream to be transported to various organs and tissues throughout the body. For instance, the pancreas secretes insulin, which allows the body to regulate levels of sugar in the blood. The thyroid gets instructions from the pituitary to secrete hormones which determine the rate of metabolism in the body (the more hormone in the bloodstream, the faster the chemical activity; the less hormone, the slower the activity).
Endocrine glands
illustration
-
Thyroid cancer - CT scan - illustration
This CT scan of the upper chest (thorax) shows a malignant thyroid tumor (cancer). The dark area around the trachea (marked by the white U-shaped tip of the respiratory tube) is an area where normal tissue has been eroded and died (necrosis) as a result of tumor growth.
Thyroid cancer - CT scan
illustration
-
Thyroid cancer - CT scan - illustration
This CT scan shows a thyroid cancer tumor in the throat, encircling, narrowing, and displacing the windpipe (trachea).
Thyroid cancer - CT scan
illustration
-
Incision for thyroid gland surgery - illustration
The thyroid is a gland located in the neck. It is a part of the endocrine (hormone) system, and plays a major role in regulating the body's metabolism. If surgery or an open excisional biopsy is needed, an incision is made in front of the neck to gain access to the thyroid gland.
Incision for thyroid gland surgery
illustration
-
Thyroid gland - illustration
The thyroid gland, a part of the endocrine (hormone) system, plays a major role in regulating the body's metabolism.
Thyroid gland
illustration
Review Date: 2/28/2024
Reviewed By: Sandeep K. Dhaliwal, MD, board-certified in Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Metabolism, Springfield, VA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.