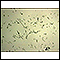
Hydatidiform mole
Hydatid mole; Molar pregnancy; Hyperemesis - molarHydatidiform mole (HM) is a rare mass or growth that forms inside the womb (uterus) at the beginning of a pregnancy. It is a type of gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD).
Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD)
Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) is a group of pregnancy-related conditions that develop inside a woman's uterus (womb). The abnormal cells s...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleCauses
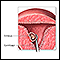
HM, or molar pregnancy, results from abnormal fertilization of the oocyte (egg). It results in an abnormal fetus. The placenta grows normally with little or no growth of the fetal tissue. The placental tissue forms a mass in the uterus. On ultrasound, this mass often has a grape-like appearance, as it contains many small cysts.
The chance of mole formation is higher in older women. A history of mole in earlier years is also a risk factor.
Molar pregnancy can be of two types:
- Partial molar pregnancy: There is an abnormal placenta and some fetal development.
- Complete molar pregnancy: There is an abnormal placenta and no fetus.
There is no way to prevent formation of a molar pregnancy.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a molar pregnancy may include:
- Abnormal growth of the uterus, either bigger or smaller than usual
- Severe nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach. "Vomiting or throwing-up forces the contents of the stomach up t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Vaginal bleeding during the first 3 months of pregnancy
Vaginal bleeding
Vaginal bleeding in pregnancy is any discharge of blood from the vagina during pregnancy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Symptoms of hyperthyroidism, including heat intolerance, loose stools, rapid heart rate, restlessness or nervousness, warm and moist skin, trembling hands, or unexplained weight loss
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone. The condition is often called overactive thyroid.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleHeat intolerance
Heat intolerance is a feeling of being overheated when the temperature around you rises. It can often cause heavy sweating. Heat intolerance usually...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleRapid heart rate
A bounding pulse is a strong throbbing felt over one of the arteries in the body. It is due to a forceful heartbeat.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleRestlessness
Agitation is an unpleasant state of extreme arousal. An agitated person may feel stirred up, excited, tense, confused, or irritable.
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleTrembling hands
A tremor is a type of shaking movement. A tremor is most often noticed in the hands and arms. It may affect any body part, including the head, tong...
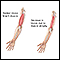 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleUnexplained weight loss
Unexplained weight loss is a decrease in body weight, when you did not try to lose the weight on your own. Many people gain and lose weight. Uninten...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Symptoms similar to preeclampsia that occur in the first trimester or early second trimester, including high blood pressure and swelling in the feet, ankles, and legs (this is almost always a sign of a hydatidiform mole, because preeclampsia is extremely rare this early in a normal pregnancy)
Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is high blood pressure and signs of liver or kidney damage that occur in women after the 20th week of pregnancy. While it is rare, pree...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleSwelling in the feet
Painless swelling of the feet and ankles is a common problem, especially among older people. Abnormal buildup of fluid in the ankles, feet, and legs ...
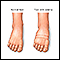 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a pelvic exam, which may show signs similar to a normal pregnancy. However, the size of the womb may be abnormal and there may be no heart sounds from the baby. Also, there may be some vaginal bleeding.
A pregnancy ultrasound will show a snowstorm appearance with an abnormal placenta, with or without some development of a baby.
Tests done may include:
- hCG (or HCG, both quantitative) blood test
HCG (or HCG, both quantitative) blood t...
A qualitative human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG or hCG) blood test checks if there is a hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin in your blood. H...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Abdominal or vaginal ultrasound of the pelvis
- Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - CT or MRI of the abdomen (imaging tests)
CT
An abdominal CT scan is an imaging test that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the belly area. CT stands for computed tomography....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMRI
An abdominal magnetic resonance imaging scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves. The waves create pictures of the inside ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Complete blood count (CBC)
CBC
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood clotting tests
- Kidney and liver function tests
Liver function tests
Liver function tests are common tests that are used to see how well the liver is working. Tests include:AlbuminAlpha-1 antitrypsinAlkaline phosphata...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
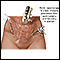
If your provider suspects a molar pregnancy, removal of the abnormal tissue with a dilation and curettage (D&C) will most likely be suggested. D&C may also be done using suction. This is called suction aspiration (The method uses a suction cup to remove contents from the uterus).
D&C
An abortion is a medical procedure that ends an undesired pregnancy by removing the fetus and placenta from the woman's uterus (womb). A medication ...
Very rarely, a partial molar pregnancy can continue. A woman may choose to continue her pregnancy in the hope of having a successful birth and delivery. However, these are very high-risk pregnancies. Risks may include bleeding, problems with blood pressure, and premature delivery (having the baby before it is fully developed). In rare cases, the fetus is genetically normal. Women need to completely discuss the risks with their provider before continuing the pregnancy.
A hysterectomy (surgery to remove the uterus) may be an option for older women who do not wish to become pregnant in the future.
Surgery to remove the uterus
Hysterectomy is surgery to remove a woman's womb (uterus). The uterus is a hollow muscular organ that nourishes the developing baby during pregnancy...
After treatment, your hCG level will be followed. It is important to avoid another pregnancy and to use a reliable contraceptive for 6 to 12 months after treatment for a molar pregnancy. This time allows for accurate testing to be sure that the abnormal tissue does not grow back. Women who get pregnant too soon after a molar pregnancy are at high risk of having another molar pregnancy.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most HMs are noncancerous (benign). Treatment is usually successful. Close follow-up by your provider is important to ensure that signs of the molar pregnancy are gone and pregnancy hormone levels return to normal.
Benign
Benign refers to a condition, tumor, or growth that is not cancerous. This means that it does not spread to other parts of the body. It does not in...
About 15% of cases of HM can become invasive. These moles can grow deep into the uterine wall and cause bleeding or other complications. This type of mole most often responds well to medicines.
In very few cases of complete HM, moles develop into a choriocarcinoma. This is a fast-growing cancer. It is usually successfully treated with chemotherapy, but can be life threatening.
Possible Complications
Complications of molar pregnancy may include:
- Change to invasive molar disease or choriocarcinoma
- Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is high blood pressure and signs of liver or kidney damage that occur in women after the 20th week of pregnancy. While it is rare, pree...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Thyroid problems
- Molar pregnancy that continues or comes back
Complications from surgery to remove a molar pregnancy may include:
- Excessive bleeding, possibly requiring a blood transfusion
- Side effects of anesthesia
Anesthesia
General anesthesia is treatment with certain medicines that puts you into a deep sleep-like state so you do not feel pain during surgery. After you ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
References
Nica A, Bouchard-Fortier G, Covens A. Gestational trophoblastic disease: hydatidiform mole, nonmetastatic and metastatic gestational trophoblastic tumor: diagnosis and management. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 34.
Soper JT. Gestational trophoblastic disease. In: Creasman WT, Mutch DG, Mannel RS, Tewari KS, eds. DiSaia and Creasman Clinical Gynecologic Oncology. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 7.
Tidy J. Gestational trophoblastic disease. In: Magowan B, ed. Clinical Obstetrics and Gynaecology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Limited; 2023:chap 15.
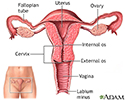
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
Normal uterine anatomy (cut section) - illustration
The uterus is a muscular organ with thick walls, two upper openings to the fallopian tubes and an inferior opening to the vagina.
Normal uterine anatomy (cut section)
illustration
Uterus - illustration
The uterus is a hollow muscular organ located in the female pelvis between the bladder and rectum. The ovaries produce the eggs that travel through the fallopian tubes. Once the egg has left the ovary it can be fertilized and implant itself in the lining of the uterus. The main function of the uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior to birth.
Uterus
illustration
Normal uterine anatomy (cut section) - illustration
The uterus is a muscular organ with thick walls, two upper openings to the fallopian tubes and an inferior opening to the vagina.
Normal uterine anatomy (cut section)
illustration
Review Date: 10/15/2024
Reviewed By: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor Emeritus, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.