HELLP syndrome
HELLP syndrome is a group of symptoms that occur in pregnant women who have:
- H: hemolysis (the breakdown of red blood cells)
- EL: elevated liver enzymes
- LP: low platelet count
Platelet count
A platelet count is a lab test to measure how many platelets you have in your blood. Platelets are particles in the blood that help the blood clot. ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Causes
The cause of HELLP syndrome has not been found. It is considered to be a variant of preeclampsia. Sometimes the presence of HELLP syndrome is due to an underlying disease, such as antiphospholipid antibody syndrome.
Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune disorder that involves frequent blood clots (thromboses). When you have this condition, your body's...

HELLP syndrome occurs in about 1 to 2 out of 1,000 pregnancies. In women with preeclampsia or eclampsia, the condition develops in 10% to 20% of pregnancies.
Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is high blood pressure and signs of liver or kidney damage that occur in women after the 20th week of pregnancy. While it is rare, pree...

Eclampsia
Eclampsia is the new onset of seizures or coma in a pregnant woman with preeclampsia. These seizures are not related to an existing brain condition....

Risk factors for HELLP syndrome include:
- Age greater than 35
- Obesity (metabolic syndrome)
- History of preeclampsia
- History of diabetes or renal disease
- History of multiple births
- History of high blood pressure
Most often, HELLP develops during the third trimester of pregnancy (between 26 to 40 weeks gestation). Sometimes it develops in the week after the baby is born.
Many women have high blood pressure and are diagnosed with preeclampsia before they develop HELLP syndrome. In some cases, HELLP symptoms are the first warning of preeclampsia. The condition is sometimes misdiagnosed as:
- Flu or other viral illness
- Gallbladder disease
- Hepatitis
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is swelling and inflammation of the liver.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) is a bleeding disorder in which the immune system destroys platelets, which are necessary for normal blood clot...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lupus flare
Lupus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease. In this disease, the immune system of the body mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. It c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) is a blood disorder in which platelet clumps form in small blood vessels. This leads to a low platelet cou...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms
Symptoms include:
- Fatigue or feeling unwell
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fluid retention and excess weight gain
- Headache
- Nausea and vomiting that continues to get worse
- Pain in the upper right or mid part of the abdomen
- Blurry vision
- Nosebleed or other bleeding that will not stop easily (rare)
- Seizures or convulsions (rare)
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
During a physical exam, the health care provider may discover:
- Abdominal tenderness, especially in the right upper side
Abdominal tenderness
Abdominal pain is pain that you feel anywhere between your chest and groin. This is often referred to as the stomach region or belly.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Enlarged liver
Enlarged liver
Enlarged liver refers to swelling of the liver beyond its normal size. Hepatomegaly is another word to describe this problem. If both the liver and ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - High blood pressure
High blood pressure
Blood pressure is a measurement of the force exerted against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood to your body. Hypertension is the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Swelling in the legs
Swelling in the legs
Painless swelling of the feet and ankles is a common problem, especially among older people. Abnormal buildup of fluid in the ankles, feet, and legs ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Liver function tests (liver enzymes) may be high. Platelet counts may be low. A CT scan may show bleeding into the liver. Excessive protein (proteinuria) may be found in the urine.
Liver function tests
Liver function tests are common tests that are used to see how well the liver is working. Tests include:AlbuminAlpha-1 antitrypsinAlkaline phosphata...
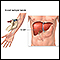
CT scan
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...

Tests of the baby's health will be done. Tests include fetal non-stress test and ultrasound, among others.
Fetal non-stress test
While you are pregnant, your health care provider may do tests to check your baby's health. The tests may be done at any time while you are pregnant...
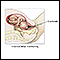
Ultrasound
A pregnancy ultrasound is an imaging test that uses sound waves to create a picture of how a baby is developing in the womb (uterus). It is also use...
Treatment
The main treatment is to deliver the baby as soon as possible, even if the baby is premature. Problems with the liver and other complications of HELLP syndrome can quickly get worse and be harmful to both the mother and child.
Your provider may induce labor by giving you medicines to start labor, or may perform a C-section.
C-section
A C-section is the delivery of a baby by making an opening in the mother's lower belly area. It is also called a cesarean delivery.

You may also receive:
- A blood transfusion if bleeding problems become severe
- Corticosteroid medicines to help the baby's lungs develop faster
- Medicines to treat high blood pressure
- Magnesium sulfate infusion to prevent seizures
Outlook (Prognosis)
Outcomes are most often good if the problem is diagnosed early. It is very important to have regular prenatal checkups. You should also let your provider know right away if you have symptoms of this condition.
When the condition is not treated early, up to 1 of 4 women develop serious complications. Without treatment, a small number of women die.
The death rate among babies born to mothers with HELLP syndrome depends on birth weight and the development of the baby's organs, especially the lungs. Many babies are born prematurely (born before 37 weeks of pregnancy).
Prematurely
A premature infant is a baby born before 37 full weeks of gestation (more than 3 weeks before the due date).
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleHELLP syndrome may return in up to 1 out of 4 future pregnancies.
Possible Complications
There can be complications before and after the baby is delivered, including:
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). A clotting disorder that leads to excess bleeding (hemorrhage).
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a serious disorder in which the proteins that control blood clotting become overactive.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema).
Pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema is an abnormal buildup of fluid in the lungs. This buildup of fluid leads to shortness of breath.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Kidney failure.
Kidney failure
Acute kidney failure is the rapid (less than 2 days) loss of your kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in your b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Liver hemorrhage and failure.
- Separation of the placenta from the uterine wall (placental abruption).
Placental abruption
The placenta is the organ that supplies nutrients and oxygen to the baby during pregnancy. Placental abruption occurs when the placenta detaches fro...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Seizures.
- Stroke.
Stroke.
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fetal complications, including restriction of fetal growth.
After the baby is born, HELLP syndrome goes away in most cases in 2 to 3 days.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
If symptoms of HELLP syndrome occur during pregnancy:
- See your provider right away.
- Call 911 or the local emergency number.
- Get to the hospital emergency room or labor and delivery unit.
There is no known way to prevent HELLP syndrome. All pregnant women should start prenatal care early and continue it through the pregnancy. This allows the provider to find and treat conditions such as HELLP syndrome right away.
References
Bartal MF, Costantine M, Sibai B. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 38.
Mehra S, Reinus JF. Gastrointestinal and hepatic disorders in the pregnant patient. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 40.
Preeclampsia - illustration
Preeclampsia is the development of swelling, elevated blood pressure, sudden and rapid weight gain and protein in the urine during pregnancy. The exact cause is unknown, but it occurs in approximately 5% of the population.
Preeclampsia
illustration
Review Date: 10/15/2024
Reviewed By: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor Emeritus, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.


