Shingles
Herpes zoster - shinglesShingles is a painful, blistering skin rash. It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, a member of the herpes family of viruses. This is the virus that also causes chickenpox.
Chickenpox
Chickenpox is a viral infection in which a person develops very itchy blisters all over the body. It was more common in the past. The illness is ra...

Causes
After you get chickenpox, your body does not get rid of the virus. Instead, the virus remains in the body but is inactive (becomes dormant) in certain nerves in the body. Shingles occur after the virus becomes active again in these nerves, often after many years. Many people had such a mild case of chickenpox that they do not realize they have had the infection.
The reason the virus suddenly becomes active again is not clear. Often only one attack occurs.
Shingles can develop in any age group. You are more likely to develop the condition if:
- You are older than age 60 years
- You had chickenpox before age 1
- Your immune system is weakened by medicines or diseases
If an adult or child has direct contact with the shingles rash and did not have chickenpox as a child or get the chickenpox vaccine, they can develop chickenpox, not shingles.
Chickenpox vaccine
All content below is taken in its entirety from the CDC Chickenpox Vaccine Information Statement (VIS): www. cdc. gov/vaccines/hcp/current-vis/varice...

Symptoms
The first symptom is usually pain, tingling, or burning that occurs on one side of the body. The pain and burning may be severe and are usually present before any rash appears.
Red patches on the skin, followed by small blisters, form in most people:
- The blisters break, forming small sores that begin to dry and form crusts. The crusts fall off in 2 to 3 weeks. Scarring is rare.
- The rash usually involves a narrow area from the spine around to the front of the abdomen or chest.
- The rash may instead involve the face, eyes, mouth, and ears.
Other symptoms may include:
- Fever and chills
- General ill feeling
General ill feeling
Malaise is a general feeling of discomfort, illness, or lack of well-being.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Headache
- Joint pain
- Swollen glands (lymph nodes)
Swollen glands
Lymph nodes are present throughout your body. They are an important part of your immune system. Lymph nodes help your body recognize and fight germ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
You may also have pain, muscle weakness, and a rash involving different parts of your face if shingles affects a nerve in your face. The symptoms may include:
- Difficulty moving some of the muscles in the face
- Drooping eyelid (ptosis)
Drooping eyelid
Eyelid drooping is excess sagging of the upper eyelid. The edge of the upper eyelid may be lower than it should be (ptosis) or there may be excess b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hearing loss
- Loss of eye motion
- Taste problems
- Vision problems
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider can make the diagnosis by looking at your skin and asking about your medical history.
Tests are rarely needed, but may include taking a skin sample to see if the skin is infected with the virus.
Blood tests may show an increase in white blood cells and antibodies to the chickenpox virus. But blood tests cannot confirm that the rash is due to shingles.
White blood cells
A WBC count is a blood test to measure the number of white blood cells (WBCs) in the blood. It is a part of a complete blood count (CBC). WBCs are a...
Treatment
Your provider may prescribe a medicine that fights the virus, called an antiviral medicine. This medicine helps reduce pain, prevent complications, and shorten the course of the disease.
The medicines are most effective when started within 72 hours of when you first feel pain or burning. It is best to start taking them before the blisters appear. The medicines are usually given in pill form. Some people may need to receive the medicine through a vein (by IV).
IV
Intravenous means "within a vein. " Most often it refers to giving medicines or fluids through a needle or tube inserted into a vein. This allows th...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleStrong anti-inflammatory medicines called corticosteroids, such as prednisone, may be used to reduce swelling and pain. These medicines do not work in all people.
Other medicines may include:
- Antihistamines to reduce itching (taken by mouth or applied to the skin)
- Pain medicines
- Zostrix, a cream containing capsaicin (an extract of pepper) to reduce pain
Follow your provider's instructions about how to care for yourself at home.
How to care for yourself at home
Shingles is a painful, blistering skin rash that is caused by the varicella-zoster virus. This is the same virus that causes chickenpox. Shingles i...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleOther measures may include:
- Caring for your skin by applying cool, wet compresses to reduce pain, and taking soothing baths
- Resting in bed until the fever goes down
Stay away from people while your sores are oozing to avoid infecting those who have never had chickenpox -- especially pregnant women.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Shingles usually clear in 2 to 3 weeks and rarely returns. If the virus affects the nerves that control movement (the motor nerves), you may have temporary or permanent weakness or paralysis.
Sometimes the pain in the area where the shingles occurred may last from months to years. This pain is called postherpetic neuralgia.
Postherpetic neuralgia
Postherpetic neuralgia is pain that continues longer than a month after a bout of shingles. This pain may last from months to years. Shingles is a p...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleIt occurs when the nerves have been damaged after an outbreak of shingles. Pain ranges from mild to very severe. Postherpetic neuralgia is more likely to occur in people age 60 or over.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Another attack of shingles
- Bacterial skin infections
- Blindness (if shingles occur in the eye)
- Deafness
- Infection, including encephalitis or sepsis (blood infection) in people with a weakened immune system
Encephalitis
Encephalitis is irritation and swelling (inflammation) of the brain, most often due to infections.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleSepsis
Sepsis is an illness in which the body has a severe, inflammatory response to bacteria or other germs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Ramsay Hunt syndrome if shingles affect the nerves of the face or ear
Ramsay Hunt syndrome
Ramsay Hunt syndrome is a painful rash around the ear, on the face, or on the mouth. It occurs when the varicella-zoster virus infects a specific ne...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of shingles, particularly if you have a weakened immune system or if your symptoms persist or worsen. Shingles that affects the eye may lead to permanent blindness if you do not receive emergency medical care.
Prevention
Do not touch the rash and blisters on people with shingles or chickenpox if you have never had chickenpox or the chickenpox vaccine.
The shingles vaccine is different than the chickenpox vaccine. Older adults who receive the shingles vaccine are much less likely to have complications from the condition.
Shingles vaccine
All content below is taken in its entirety from the CDC Recombinant Shingles Vaccine Information Statement (VIS): www. cdc. gov/vaccines/hcp/current-...
References
Dinulos JGH. Warts, herpes simplex, and other viral infections. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 12.
Whitley RJ. Chickenpox and herpes zoster (varicella-zoster virus). In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 136.
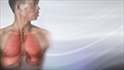
Herpes zoster (shingles) on the back - illustration
A classical pattern for shingles. The infection follows a nerve root from the spine, along a rib, to the front of the chest. The area innervated by the nerve is called a dermatome.
Herpes zoster (shingles) on the back
illustration
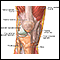
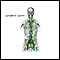
Adult dermatome - illustration
Understanding the nerve distribution along the dermatomes is helpful in determining how certain diseases, such as shingles and some other neurological conditions, target one area of the body. The letter-number combinations show the relationship between each area and its corresponding sensory nerve. The vertebrae are classified as C for cervical, T for thoracic, L for lumbar, and S for sacral. The trigeminal nerve is the fifth cranial nerve, represented by V.
Adult dermatome
illustration
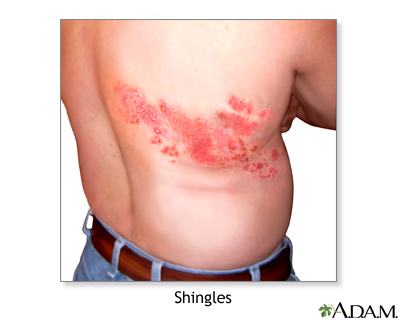
Shingles - illustration
Shingles, or herpes zoster, is caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. The virus can lie dormant in the body for many years and re-emerge as shingles. Shingles appear as a painful rash. It consists of red patches of skin with small blisters (vesicles) that look very similar to early chickenpox. Shingles usually clears in 2 to 3 weeks and rarely recurs.
Shingles
illustration
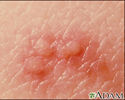
Herpes zoster (shingles) - close-up of lesion - illustration
A close-up picture of herpes zoster skin lesions. Four small blisters are shown with redness around them. These vesicles will break, crust over, scab, and finally heal.
Herpes zoster (shingles) - close-up of lesion
illustration
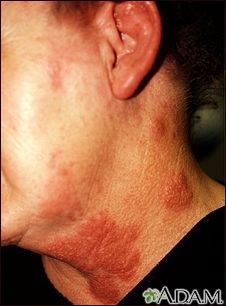
Herpes zoster (shingles) on the neck and cheek - illustration
This is a picture of herpes zoster (shingles) on the neck and cheek. Shingles are caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. Outbreaks of shingles often follow the distribution of nerves in the skin. This distribution pattern is called a dermatome (see the dermatomes picture).
Herpes zoster (shingles) on the neck and cheek
illustration
Herpes zoster (shingles) on the hand - illustration
Shingles occurs more commonly on the chest and back, but can involve the arms and legs. The small blisters on this person's hand represent involvement of the dermatome innervated by the 7th cervical nerve. (See the Dermatomes picture.)
Herpes zoster (shingles) on the hand
illustration
Herpes zoster (shingles) disseminated - illustration
Herpes zoster (shingles) normally occurs in a limited area that follows a dermatome (see the dermatome picture). In individuals with damaged immune systems, herpes zoster may be widespread (disseminated), causing serious illness. Herpes zoster is caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox.
Herpes zoster (shingles) disseminated
illustration
Herpes zoster (shingles) on the arm - illustration
This is a picture of herpes zoster (shingles) on the arm. Shingles are caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. Outbreaks of shingles follow the distribution of nerves in the skin. This distribution pattern, seen here on the arm, follows a dermatome.
Herpes zoster (shingles) on the arm
illustration
Herpes zoster (shingles) on the chest - illustration
This is a picture of herpes zoster (shingles) on the chest. Shingles are caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. Outbreaks of shingles often follow the distribution of nerves in the skin. This distribution pattern is called a dermatome. The linear distribution of the nerve in the skin is very easily seen in this photograph.
Herpes zoster (shingles) on the chest
illustration
Herpes zoster (shingles) on the back - illustration
A classical pattern for shingles. The infection follows a nerve root from the spine, along a rib, to the front of the chest. The area innervated by the nerve is called a dermatome.
Herpes zoster (shingles) on the back
illustration
Adult dermatome - illustration
Understanding the nerve distribution along the dermatomes is helpful in determining how certain diseases, such as shingles and some other neurological conditions, target one area of the body. The letter-number combinations show the relationship between each area and its corresponding sensory nerve. The vertebrae are classified as C for cervical, T for thoracic, L for lumbar, and S for sacral. The trigeminal nerve is the fifth cranial nerve, represented by V.
Adult dermatome
illustration
Shingles - illustration
Shingles, or herpes zoster, is caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. The virus can lie dormant in the body for many years and re-emerge as shingles. Shingles appear as a painful rash. It consists of red patches of skin with small blisters (vesicles) that look very similar to early chickenpox. Shingles usually clears in 2 to 3 weeks and rarely recurs.
Shingles
illustration
Herpes zoster (shingles) - close-up of lesion - illustration
A close-up picture of herpes zoster skin lesions. Four small blisters are shown with redness around them. These vesicles will break, crust over, scab, and finally heal.
Herpes zoster (shingles) - close-up of lesion
illustration
Herpes zoster (shingles) on the neck and cheek - illustration
This is a picture of herpes zoster (shingles) on the neck and cheek. Shingles are caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. Outbreaks of shingles often follow the distribution of nerves in the skin. This distribution pattern is called a dermatome (see the dermatomes picture).
Herpes zoster (shingles) on the neck and cheek
illustration
Herpes zoster (shingles) on the hand - illustration
Shingles occurs more commonly on the chest and back, but can involve the arms and legs. The small blisters on this person's hand represent involvement of the dermatome innervated by the 7th cervical nerve. (See the Dermatomes picture.)
Herpes zoster (shingles) on the hand
illustration
Herpes zoster (shingles) disseminated - illustration
Herpes zoster (shingles) normally occurs in a limited area that follows a dermatome (see the dermatome picture). In individuals with damaged immune systems, herpes zoster may be widespread (disseminated), causing serious illness. Herpes zoster is caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox.
Herpes zoster (shingles) disseminated
illustration
Herpes zoster (shingles) on the arm - illustration
This is a picture of herpes zoster (shingles) on the arm. Shingles are caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. Outbreaks of shingles follow the distribution of nerves in the skin. This distribution pattern, seen here on the arm, follows a dermatome.
Herpes zoster (shingles) on the arm
illustration
Herpes zoster (shingles) on the chest - illustration
This is a picture of herpes zoster (shingles) on the chest. Shingles are caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. Outbreaks of shingles often follow the distribution of nerves in the skin. This distribution pattern is called a dermatome. The linear distribution of the nerve in the skin is very easily seen in this photograph.
Herpes zoster (shingles) on the chest
illustration
Review Date: 11/10/2024
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Associate in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.