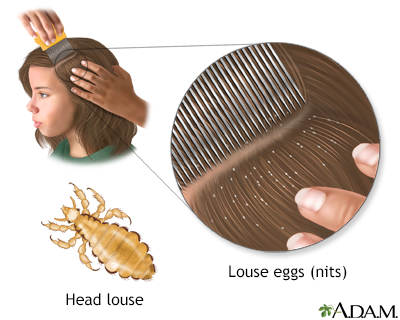
Head lice
Pediculosis capitis - head lice; Cooties - head liceHead lice are tiny insects that live on the skin covering the top of your head (scalp). Head lice may also be found in the eyebrows and eyelashes.
Lice spread by close contact with other people.
Causes
Head lice infect hair on the head. Tiny eggs on the hair may look like flakes of dandruff. However, instead of flaking off the scalp, they stay in place.
Dandruff
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common inflammatory skin condition. It causes flaky, white to yellowish scales to form on oily areas such as the scalp, f...
Head lice can live up to 30 days on a human. Their eggs can live for more than 2 weeks.
Head lice spread easily, particularly among school children ages 3 to 11 years. Head lice are more common in close, overcrowded living conditions.
You can get head lice if:
- You come in close contact with a person who has lice.
- You touch the clothing or bedding of someone who has lice.
- You share hats, towels, brushes, or combs of someone who has lice.
Having head lice causes intense itching but does not lead to serious medical problems. Unlike body lice, head lice never carry or spread diseases.
Having head lice does not mean the person has poor hygiene or low social status.
Symptoms
Symptoms of head lice include:
- Very bad itching of the scalp
- Small, red bumps on the scalp, neck, and shoulders (bumps may become crusty and ooze)
- Tiny white specks (eggs, or nits) on the bottom of each hair that are hard to get off
Exams and Tests
Head lice can be hard to see. You need to look closely. Use disposable gloves and look at the person's head under a bright light. Full sun or the brightest lights in your home during daylight hours work well. A magnifying glass can help.
To look for head lice:
- Part the hair all the way down to the scalp in very small sections.
- Examine the scalp and hair for moving lice and eggs (nits).
- Look at the whole head in the same way.
- Look closely around the top of the neck and ears (the most common locations for eggs).
Both children and adults should be treated right away if any lice or eggs are found.
Treatment
Lotions and shampoos containing 1% permethrin (Nix) often work well. You can buy these medicines at the store without a prescription. If these products do not work, a health care provider can give you a prescription for stronger medicine. Always use the medicines exactly as directed. Using them too often or in the wrong way can cause side effects.
To use the medicine shampoo:
- Rinse and dry the hair.
- Apply the medicine to the hair and scalp.
- Wait 10 minutes, then rinse it off.
- Check for lice and nits again in 8 to 12 hours.
- If you find active lice, contact your provider before doing another treatment.
You also need to get rid of the lice eggs (nits) to keep lice from coming back.
To get rid of nits:
- You can use products that make the nits easier to remove. Some dishwashing detergents can help dissolve the "glue" that makes the nits stick to the hair shaft.
- Remove the eggs with a nit comb. Before doing this, rub olive oil in the hair or run the metal comb through beeswax. This helps make the nits easier to remove.
- Metal combs with very fine teeth are stronger and work better than plastic nit combs. These metal combs are easier to find in pet stores or on the Internet.
- Comb for nits again in 7 to 10 days.
When treating head lice, wash all clothes and bed linens in hot water with detergent. This also helps prevent head lice from spreading to others during the short period when head lice can survive off the human body.
Ask your provider if people who share bedding or clothes with the person who has head lice need to be treated as well.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most of the time, lice are killed with the proper treatment. However, lice can come back if you do not get rid of them at the source.
Possible Complications
Some people will develop a skin infection from scratching. Antihistamines can help ease itching.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You still have symptoms after home treatment.
- You develop areas of red, tender skin, which could signal an infection.
Prevention
Some of the steps to prevent head lice are:
- Never share hair brushes, combs, hair pieces, hats, bedding, towels, or clothing with someone who has head lice.
- If your child has lice, be sure to check policies at schools and daycare. Many places do not allow infected children to be at school until the lice have been completely treated.
- Some schools may have policies to make sure the environment is clear of lice. Cleaning of carpets and other surfaces often helps prevent spread of all types of infections, including head lice.
References
Burkhart CN, Burkhart GG, Morrell DS. Infestations. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 84.
James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA, Neuhaus IM. Parasitic infestations, stings, and bites. In: James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA, Neuhaus IM, eds. Andrew's Diseases of the Skin Clinical Dermatology. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 20.
Seifert SA, Dart RC, White J. Envenomation, bites, and stings. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 98.
Head lice - illustration
Head lice infect the scalp and hair and can be seen at the nape of the neck and over the ears. Head lice spread easily and quickly but do not carry disease as other lice do.
Head lice
illustration
Nit on human hair - illustration
This photograph shows a nit, or tiny white egg sack, attached to the shaft of a human hair. Image courtesy of D. Scott Smith, MD, MSc, DTMH.
Nit on human hair
illustration
Head louse emerging from egg - illustration
This is a photograph of a head louse emerging from an egg. Head lice have become an increasing problem in schools and day care centers. Some grade schools have started programs to examine children for head lice.
Head louse emerging from egg
illustration
Head louse, male - illustration
This is a photograph of a male Pediculus humanus var. capitis, a head louse. Head lice have become an increasing problem in schools and day care centers. Some grade schools have started programs to examine children for head lice.
Head louse, male
illustration
Head louse - female - illustration
This is a photograph of a female Pediculus humanus var. capitis, a head louse. Head lice have become an increasing problem in schools and day care centers. Some grade schools have started programs to examine children for head lice.
Head louse - female
illustration
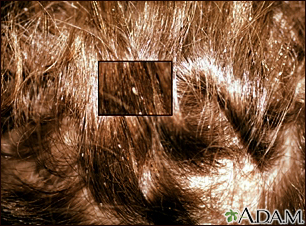
Head louse infestation - scalp - illustration
This is a close-up picture of lice egg sacks (nits) on the hair. They cling to individual hair shafts. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
Head louse infestation - scalp
illustration
Lice, head - nits in the hair with close-up - illustration
This photograph shows the nits or tiny white egg sacks attached to the hairs. Schools often insist that these be entirely removed before a child returns to school.
Lice, head - nits in the hair with close-up
illustration
Head lice - illustration
Head lice infect the scalp and hair and can be seen at the nape of the neck and over the ears. Head lice spread easily and quickly but do not carry disease as other lice do.
Head lice
illustration
Nit on human hair - illustration
This photograph shows a nit, or tiny white egg sack, attached to the shaft of a human hair. Image courtesy of D. Scott Smith, MD, MSc, DTMH.
Nit on human hair
illustration
Head louse emerging from egg - illustration
This is a photograph of a head louse emerging from an egg. Head lice have become an increasing problem in schools and day care centers. Some grade schools have started programs to examine children for head lice.
Head louse emerging from egg
illustration
Head louse, male - illustration
This is a photograph of a male Pediculus humanus var. capitis, a head louse. Head lice have become an increasing problem in schools and day care centers. Some grade schools have started programs to examine children for head lice.
Head louse, male
illustration
Head louse - female - illustration
This is a photograph of a female Pediculus humanus var. capitis, a head louse. Head lice have become an increasing problem in schools and day care centers. Some grade schools have started programs to examine children for head lice.
Head louse - female
illustration
Head louse infestation - scalp - illustration
This is a close-up picture of lice egg sacks (nits) on the hair. They cling to individual hair shafts. (Image courtesy of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.)
Head louse infestation - scalp
illustration
Lice, head - nits in the hair with close-up - illustration
This photograph shows the nits or tiny white egg sacks attached to the hairs. Schools often insist that these be entirely removed before a child returns to school.
Lice, head - nits in the hair with close-up
illustration
Review Date: 2/17/2024
Reviewed By: Charles I. Schwartz, MD, FAAP, Clinical Assistant Professor of Pediatrics, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, General Pediatrician at PennCare for Kids, Phoenixville, PA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.