Dry skin
Dry skin occurs when your skin loses too much water and oil. Dry skin is common and can affect anyone at any age. The medical term for dry skin is xerosis.
Causes
Dry skin can be caused by:
- The climate, such as cold, dry winter air or hot, dry desert environments
- Dry indoor air from heating or cooling systems
- Bathing too often or too long
- Some soaps and detergents
- Skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis
Eczema
Atopic dermatitis is a long-term (chronic) skin disorder that involves scaly and itchy rashes. It is a type of eczema. Other forms of dermatitis inc...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
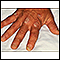
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticlePsoriasis
Psoriasis is a skin condition that causes skin redness, silvery scales, and irritation. Most people with psoriasis have thick, red, well-defined pat...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Diseases, such as diabetes, underactive thyroid, Sjögren syndrome, among others
Underactive thyroid
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. This condition is often called underactive thyroid....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleSjögren syndrome
Sjögren syndrome is an autoimmune disorder in which the glands that produce tears and saliva are destroyed. This causes dry mouth and dry eyes. The...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Certain medicines (both topical and oral)
- Aging, during which skin gets thinner and produces less natural oil
Symptoms
Your skin may get dry, scaly, itchy, and red. You may also have fine cracks on the skin.
The problem is usually worse on the arms and legs.
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will examine your skin. You'll be asked about your health history and skin symptoms.
If your provider suspects the dry skin is caused by a health problem that hasn't been diagnosed yet, tests will likely be ordered.
Treatment
Your provider may suggest home care measures, including:
Home care measures
Dry skin occurs when your skin loses too much water and oil. Dry skin is common and can affect anyone at any age. Symptoms of dry skin include:Scali...

- Moisturizers, especially creams or lotions that contain urea and lactic acid
- Topical steroids for areas that get very inflamed and itchy
If your dry skin is from a health problem, you'll likely be treated for it as well.
Prevention
To prevent dry skin:
- Do not expose your skin to water more often than needed.
- Use lukewarm bath water. Afterward, pat the skin dry with the towel instead of rubbing.
- Choose gentle skin cleansers that are free from dyes and perfumes.
Reviewed By
Ramin Fathi, MD, FAAD, Director, Phoenix Surgical Dermatology Group, Phoenix, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
American Academy of Dermatology Association website. Dry skin: Overview. www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/dry-skin-overview. Accessed October 22, 2024.
Coulson IH. Xerosis. In: Lebwohl MG, Heymann WR, Coulson IH, Murrell DF, eds. Treatment of Skin Disease: Comprehensive Therapeutic Strategies. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier, 2022:chap 258.
Dinulos JGH. Atopic dermatitis. In: Dinulos JGH, ed. Habif's Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 5.
Ständer S, Pereira MP, Weisshaar E, Bernhard JD. Pruritus and dysesthesia. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 6.

 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.