Hairy cell leukemia
Leukemic reticuloendotheliosis; HCL; Leukemia - hairy cellHairy cell leukemia (HCL) is an unusual cancer of the blood. It affects B lymphocyte cells, a type of white blood cell.
Causes
HCL is caused by the abnormal growth of certain B cells. The cells look "hairy" under the microscope because they have fine projections extending from their surface.
HCL usually leads to a low number of normal blood cells.
The cause of this disease is unknown. Certain genetic changes in the cancer cells may be the cause. It affects men more often than women. The average age of diagnosis is 55.
Symptoms
Symptoms of HCL may include any of the following:
- Easy bruising or bleeding
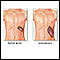
Bruising
A bruise is an area of skin discoloration. A bruise occurs when small blood vessels break and leak their contents into the soft tissue beneath the s...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Heavy sweating (especially at night)
-
Fatigue and weakness
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Feeling full after eating only a small amount
- Recurrent infections and fevers
- Pain or fullness in the upper left belly (enlarged spleen)
Enlarged spleen
Splenomegaly is a larger-than-normal spleen. The spleen is an organ in the upper left part of the belly.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Swollen lymph glands
Swollen lymph glands
Lymph nodes are present throughout your body. They are an important part of your immune system. Lymph nodes help your body recognize and fight germ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Weight loss
Weight loss
Unexplained weight loss is a decrease in body weight, when you did not try to lose the weight on your own. Many people gain and lose weight. Uninten...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
During a physical exam, your health care provider may be able to feel a swollen spleen or liver. An abdominal CT scan or ultrasound may be done to evaluate this swelling.
Swollen spleen
Splenomegaly is a larger-than-normal spleen. The spleen is an organ in the upper left part of the belly.

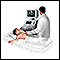
Abdominal CT scan
An abdominal CT scan is an imaging test that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the belly area. CT stands for computed tomography....

Ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound is a type of imaging test. It is used to look at organs in the abdomen, including the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and kidneys...
Blood tests that may be done include:
-
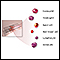
Complete blood count (CBC) to check low levels of white and red blood cells, as well as platelets.
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticlePlatelets
A platelet count is a lab test to measure how many platelets you have in your blood. Platelets are particles in the blood that help the blood clot. ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood tests and a bone marrow biopsy to check for hairy cells.
Bone marrow biopsy
A bone marrow biopsy is the removal of marrow from inside one of your bones. Bone marrow is the soft tissue inside bones that helps form blood cells...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Treatment may not be needed for the early stages of this disease. Some people may need an occasional blood transfusion.
If treatment is needed because of very low blood counts, chemotherapy medicines can be used.
Chemotherapy
The term chemotherapy is used to describe cancer-killing drugs. Chemotherapy may be used to:Cure the cancerShrink the cancerPrevent the cancer from ...
In most cases, chemotherapy can relieve the symptoms for many years. When the signs and symptoms go away, you are said to be in remission.
Removing the spleen may improve blood counts, but is unlikely to cure the disease. Antibiotics can be used to treat infections. People with low blood counts may receive growth factors and, possibly, transfusions.
Removing the spleen
Spleen removal is surgery to remove a diseased or damaged spleen. This surgery is called splenectomy. The spleen is in the upper part of the belly, ...
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most people with HCL can expect to live 10 years or longer after diagnosis and treatment.
Possible Complications
The low blood counts caused by hairy cell leukemia can lead to:
- Infections
- Fatigue
- Excessive bleeding
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have major bleeding. Also contact your provider if you have signs of infection, such as a persistent fever, cough, or general ill feeling.
Fever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...

Cough
Coughing is an important way to keep your throat and airways clear. But too much coughing may mean you have a disease or disorder. Some coughs are d...

General ill feeling
Malaise is a general feeling of discomfort, illness, or lack of well-being.
Prevention
There is no known way to prevent this disease.
References
National Cancer Institute website. Hairy cell leukemia treatment (PDQ) health professional version. www.cancer.gov/types/leukemia/hp/hairy-cell-treatment-pdq. Updated September 20, 2024. Accessed December 3, 2024.
Nasr MR, Hutchison RE. Leukocytic disorders. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 34.
Ravandi F. Hairy cell leukemia. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 77.
-
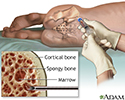
Bone marrow aspiration - illustration
A small amount of bone marrow is removed during a bone marrow aspiration. The procedure is uncomfortable, but can be tolerated by both children and adults. The marrow can be studied to determine the cause of anemia, the presence of leukemia or other malignancy, or the presence of some storage diseases, in which abnormal metabolic products are stored in certain bone marrow cells.
Bone marrow aspiration
illustration
-
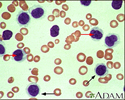
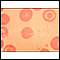
Hairy cell leukemia - microscopic view - illustration
All the cells in this field are hairy cells. The cell membranes appear irregular and serrated. The cytoplasm stains light blue (black arrows). The nuclei tend to be irregular (red arrows).
Hairy cell leukemia - microscopic view
illustration
-
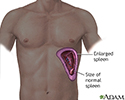
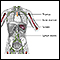
Enlarged spleen - illustration
Because of its wide variety of functions, the spleen may be affected by many conditions involving the blood or lymph system, and by infection, malignancies, liver disease, and parasites.
Enlarged spleen
illustration
-
Bone marrow aspiration - illustration
A small amount of bone marrow is removed during a bone marrow aspiration. The procedure is uncomfortable, but can be tolerated by both children and adults. The marrow can be studied to determine the cause of anemia, the presence of leukemia or other malignancy, or the presence of some storage diseases, in which abnormal metabolic products are stored in certain bone marrow cells.
Bone marrow aspiration
illustration
-
Hairy cell leukemia - microscopic view - illustration
All the cells in this field are hairy cells. The cell membranes appear irregular and serrated. The cytoplasm stains light blue (black arrows). The nuclei tend to be irregular (red arrows).
Hairy cell leukemia - microscopic view
illustration
-
Enlarged spleen - illustration
Because of its wide variety of functions, the spleen may be affected by many conditions involving the blood or lymph system, and by infection, malignancies, liver disease, and parasites.
Enlarged spleen
illustration
Review Date: 6/17/2024
Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.