Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
TTPThrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP) is a blood disorder in which platelet clumps form in small blood vessels. This leads to a low platelet count (thrombocytopenia).
Thrombocytopenia
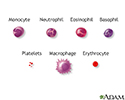
Thrombocytopenia means there is an abnormally low amount of platelets. Platelets are parts of the blood that help blood to clot. This condition is ...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleCauses
This disease may be caused by problems with an enzyme (a type of protein) that is involved in blood clotting. This enzyme is called ADAMTS13. Absence of this enzyme results in platelet clumping. This is usually caused by an autoimmune disorder where antibodies attack the ADAMTS 13 enzyme. Platelets are particles in the blood that aid in blood clotting.
As the platelets clump together, fewer platelets are available in the blood in other parts of the body to help with clotting. This can lead to bleeding under the skin. The platelets that clump in blood vessels affects the blood supply to various organs such as the kidneys and the brain, which can damage these organs.
In some cases, the disorder is passed down through families (inherited) and is called congenital TTP. In these cases, people are born with naturally low levels of this enzyme.
This condition also may be caused by:
-
Cancer
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy
The term chemotherapy is used to describe cancer-killing drugs. Chemotherapy may be used to:Cure the cancerShrink the cancerPrevent the cancer from ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
A bone marrow transplant is a procedure to replace damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy bone marrow stem cells. Bone marrow is the soft, fatt...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
HIV infection
HIV infection
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hormone replacement therapy and estrogens
Hormone replacement therapy
Hormone therapy (HT) uses one or more hormones to treat symptoms of menopause. HT uses estrogen, progestin (a type of progesterone), or both. Somet...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Medicines (including clopidogrel, quinine, and cyclosporine A)
Symptoms
Symptoms may include any of the following:
-
Bleeding into the skin or mucus membranes
Bleeding into the skin
Bleeding into the skin can occur from broken blood vessels that form tiny red dots (called petechiae). Blood also can collect under the tissue in la...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Confusion
Confusion
Confusion is the inability to think as clearly or quickly as you normally do. You may feel disoriented and have difficulty paying attention, remembe...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fast heart rate (over 100 beats per minute)
-
Fatigue, weakness
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fever
Fever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Headache
Headache
A headache is pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck. Serious causes of headaches are rare. Most people with headaches can feel much better...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Pale skin color (pallor)
Pale skin color
Paleness is an abnormal loss of color from normal skin or mucous membranes.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Shortness of breath
Shortness of breath
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
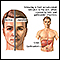
Yellowish skin color (jaundice)
Yellowish skin color
Jaundice is a yellow color of the skin, mucus membranes, or eyes. The yellow coloring comes from bilirubin, a byproduct of old red blood cells. Jau...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Tests that may be ordered include:
- ADAMTS 13 activity level
-
Blood bilirubin level
Blood bilirubin
The bilirubin blood test measures the level of bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin is a yellowish pigment found in bile, a fluid made by the liver. Bi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
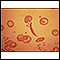
Blood smear
Blood smear
A blood smear is a blood test that gives information about the number and shape of blood cells. It is often done as part of or along with a complete...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Complete blood count (CBC)
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Blood creatinine level
Blood creatinine
The creatinine blood test measures the level of creatinine in the blood. This test is done to see how well your kidneys are working. Creatinine in t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level
Lactate dehydrogenase
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) is a protein that helps produce energy in the body. An LDH test measures the amount of LDH in the blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Platelet count
Platelet count
A platelet count is a lab test to measure how many platelets you have in your blood. Platelets are particles in the blood that help the blood clot. ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Urinalysis
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Serum haptoglobin level
Serum haptoglobin
The haptoglobin blood test measures the level of haptoglobin in your blood. Haptoglobin is a protein produced by the liver. It attaches to hemoglobi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Coombs test
Coombs test
The Coombs test looks for antibodies that may stick to your red blood cells and cause red blood cells to die too early.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
You may have a treatment called plasma exchange. It removes the abnormal proteins in your plasma and replaces it with normal plasma from a healthy donor. Plasma is the liquid part of blood that contains blood cells and platelets. Plasma exchange also replaces the missing enzyme.
The procedure is done as follows:
- First, you have your blood drawn as if donating blood.
- As the blood is passed through a machine that separates blood into its different parts, the abnormal plasma is removed and your blood cells are saved.
- Your blood cells are then combined with normal plasma from a donor, and then given back to you through an intravenous (IV) line.
This treatment is repeated daily until blood tests show improvement.
To treat congenital TTP, plasma infusion is used. For this, donor plasma is given through an IV line.
People who do not respond to this treatment or whose condition often returns may need medicine, such as steroids or rituximab, which suppress the immune system.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most people with TTP who undergo plasma exchange recover completely. But some people die of this disease, especially if it is not diagnosed right away. In people who do not recover, this condition can become long-term (chronic).
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
-
Kidney failure
Kidney failure
Acute kidney failure is the rapid (less than 2 days) loss of your kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in your b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Low platelet count (thrombocytopenia)
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia means there is an abnormally low amount of platelets. Platelets are parts of the blood that help blood to clot. This condition is ...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Low red blood cell count (caused by the premature breakdown of red blood cells)
- Nervous system problems
- Severe bleeding (hemorrhage)
-
Stroke
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you have any unexplained bleeding.
Prevention
Because the cause is unknown, there is no known way to prevent this condition.
References
Abrams CS. Thrombocytopenia. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 158.
George G, Friedman KD. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and the hemolytic uremic syndromes. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 132.
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute website. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/thrombotic-thrombocytopenic-purpura. Updated February 18, 2025. Accessed July 9, 2025.
Review Date: 2/3/2025
Reviewed By: Warren Brenner, MD, Oncologist, Lynn Cancer Institute, Boca Raton, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.