Fungal arthritis
Mycotic arthritis; Infectious arthritis - fungalFungal arthritis is swelling and irritation (inflammation) of a joint by a fungal infection. It is also called mycotic arthritis.
Swelling
Swelling is the enlargement of organs, skin, or other body parts. It is caused by a buildup of fluid in the tissues. The extra fluid can lead to a ...

Causes
Fungal arthritis is a rare condition. It can be caused by any of the invasive types of fungi. The infection can result from an infection in another organ, such as the lungs and travel to a joint through the bloodstream. A joint can also become infected during a surgery. People with weakened immune systems who travel or live in areas where the fungi are common, are more susceptible to most causes of fungal arthritis.
Conditions that can cause fungal arthritis include:
-
Blastomycosis
Blastomycosis
Blastomycosis is an infection caused by breathing in the Blastomyces dermatitidis fungus. This fungus is found in decaying wood and soil.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Candidiasis
Candidiasis
Vaginal yeast infection is an infection of the vagina. It is most often due to the fungus Candida albicans.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Coccidioidomycosis
Coccidioidomycosis
Valley fever is an infection that occurs when the spores of the fungus Coccidioides immitis or Coccidioides posadasii enter your body through the lun...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cryptococcosis
Cryptococcosis
Cryptococcosis is infection with the fungi Cryptococcus neoformans or Cryptococcus gattii.
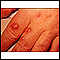 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Histoplasmosis
Histoplasmosis
Histoplasmosis is an infection that occurs from breathing in the spores of the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Sporotrichosis
Sporotrichosis
Sporotrichosis is a long-term (chronic) skin infection that is caused by a fungus called Sporothrix schenckii.
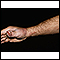 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms
The fungus can affect bone or joint tissue. One or more joints can be affected, most often the large, weight-bearing joints, such as the knees.
Symptoms may include any of the following:
- Fever
- Joint pain
- Joint stiffness
-
Joint swelling
Joint swelling
Joint swelling is the buildup of fluid in the soft tissue surrounding the joint or the joint itself.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Swelling of the ankles, feet, and legs
Swelling of the ankles, feet, and legs
Painless swelling of the feet and ankles is a common problem, especially among older people. Abnormal buildup of fluid in the ankles, feet, and legs ...
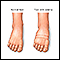 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will examine you.
Tests that may be ordered include:
- Removal of joint fluid to look for fungus under a microscope
-
Culture of joint fluid to look for fungus
Culture of joint fluid
Joint fluid culture is a laboratory test to detect infection-causing germs in a sample of fluid that is in a joint.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Joint x-ray that may show joint changes
Joint x-ray
This test is an x-ray of a knee, shoulder, hip, wrist, ankle, or other joint.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Positive antibody test (serology) for fungal disease
-
Synovial biopsy showing fungus
Synovial biopsy
A synovial biopsy is the removal of a piece of tissue lining a joint for examination. The tissue is called the synovial membrane.
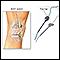 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to cure the infection using antifungal medicines. Commonly used antifungal medicines are amphotericin B or medicines in the azole family (fluconazole, ketoconazole, or itraconazole).
Chronic or advanced bone or joint infection may require surgery (debridement) to remove the infected tissue.
Outlook (Prognosis)
How well you do depends on the underlying cause of the infection and your overall health. A weakened immune system, cancer, and certain medicines can affect the outcome.
Possible Complications
Joint damage may occur and the risk of damage is higher if the infection is not treated right away.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider for an appointment if you have any symptoms of fungal arthritis.
Prevention
Thorough treatment of fungal infections elsewhere in the body may help prevent fungal arthritis.
References
Ohl CA. Infectious arthritis of native joints. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 103.
Ruderman EM, Flaherty JP. Fungal infections of bones and joints. In: Firestein GS, Budd RC, Gabriel SE, Koretzky GA, McInnes IB, O'Dell JR, eds. Firestein and Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 119.
-
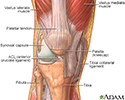
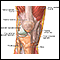
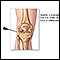
The structure of a joint - illustration
Joints, particularly hinge joints like the elbow and the knee, are complex structures made up of bone, muscles, synovium, cartilage, and ligaments that are designed to bear weight and move the body through space. The knee consists of the femur (thigh bone) above, and the tibia (shin bone) and fibula below. The kneecap (patella) glides through a shallow groove on the front part of the lower thigh bone. Ligaments and tendons connect the three bones of the knee, which are contained in the joint capsule (synovium) and are cushioned by cartilage.
The structure of a joint
illustration
-
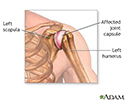
Shoulder joint inflammation - illustration
An inflammation of the shoulder joint can cause pain and restricted joint movement.
Shoulder joint inflammation
illustration
-
Fungus - illustration
Fungal infections are caused by microscopic organisms (fungi) that can live on the skin. They can live on the dead tissues of the hair, nails, and outer skin layers.
Fungus
illustration
-
The structure of a joint - illustration
Joints, particularly hinge joints like the elbow and the knee, are complex structures made up of bone, muscles, synovium, cartilage, and ligaments that are designed to bear weight and move the body through space. The knee consists of the femur (thigh bone) above, and the tibia (shin bone) and fibula below. The kneecap (patella) glides through a shallow groove on the front part of the lower thigh bone. Ligaments and tendons connect the three bones of the knee, which are contained in the joint capsule (synovium) and are cushioned by cartilage.
The structure of a joint
illustration
-
Shoulder joint inflammation - illustration
An inflammation of the shoulder joint can cause pain and restricted joint movement.
Shoulder joint inflammation
illustration
-
Fungus - illustration
Fungal infections are caused by microscopic organisms (fungi) that can live on the skin. They can live on the dead tissues of the hair, nails, and outer skin layers.
Fungus
illustration
-
Rheumatoid arthritis - InDepth
(In-Depth)
-
Psoriasis-In-Depth
(In-Depth)
Review Date: 12/31/2023
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Associate Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Associate in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.