Cystinuria
Stones - cystine; Cystine stonesCystinuria is a rare condition in which stones made from an amino acid called cysteine form in the kidney, ureter, and bladder. Cystine is formed when two molecules of an amino acid called cysteine are bound together. The condition is passed down through families.
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules that combine to form proteins. Amino acids and proteins are the building blocks of life. When proteins are digested or bro...

Causes
To have the symptoms of cystinuria, you must inherit the faulty gene from both parents. Your children will also inherit a copy of the faulty gene from you.
Cystinuria is caused by too much cystine in the urine. Normally, most cystine dissolves and returns to the bloodstream after entering the kidneys. People with cystinuria have a genetic defect that interferes with this process. As a result, cystine builds up in the urine and forms crystals or stones. These crystals may get stuck in the kidneys, ureters, or bladder.
About one in every 7000 people have cystinuria. Cystine stones are most common in young adults under age 40. Less than 3% of urinary tract stones are cystine stones.
Urinary tract stones
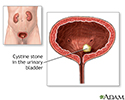
Bladder stones are hard buildups of minerals. These form in the urinary bladder.

Symptoms
Symptoms include:
- Blood in the urine
Blood in the urine
Blood in your urine is called hematuria. The amount may be very small and only detected with urine tests or under a microscope. In other cases, the...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Flank pain or pain in the side or back. Pain is most often on one side. It is rarely felt on both sides. Pain is often severe. It may get worse over days. You may also feel pain in the pelvis, groin, genitals, or between the upper abdomen and back.
Flank pain
Flank pain is pain in one side of the body between the upper belly area (abdomen) and the back.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
The condition is most often diagnosed after an episode of kidney stones. Testing the stones after they are removed shows that they are made of cystine.
Unlike calcium-containing stones, cystine stones do not show up well on plain x-rays.
Tests that may be done to detect these stones and diagnose the condition include:
- 24-hour urine collection
24-hour urine collection
The urine 24-hour volume test measures the amount of urine produced in a day. The amounts of creatinine, protein, and other chemicals released into ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Abdominal CT scan, or ultrasound
Abdominal CT scan
An abdominal CT scan is an imaging method. This test uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the belly area. CT stands for computed tomog...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Intravenous pyelogram (IVP)
Intravenous pyelogram (IVP)
An intravenous pyelogram (IVP) is a special x-ray exam of the kidneys, bladder, and ureters (the tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladd...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Urinalysis
Urinalysis
Urinalysis is the physical, chemical, and microscopic examination of urine. It involves a number of tests to detect and measure various compounds th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to relieve symptoms and prevent more stones from forming. A person with severe symptoms may need to go into the hospital.
Treatment involves drinking plenty of fluids, especially water, to produce large amounts of urine. You should drink at least 6 to 8 glasses per day. You should drink water at night as well so that you get up at night at least once to pass urine.
In some cases, fluids may need to be given through a vein (by IV).
Making the urine more alkaline may help dissolve the cystine crystals. This may be done with use of potassium citrate or sodium bicarbonate. Eating less salt can also decrease cystine release and stone formation.
You may need pain relievers to control pain in the kidney or bladder area when you pass stones. Smaller stones (of 5 mm or less than 5 mm) most often pass through the urine on their own. Larger stones (more than 5 mm) may need extra treatments. Some large stones may need to be removed using procedures such as:
- Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL): Sound waves are passed through the body and are focused on the stones to break them into small, passable fragments. ESWL may not work well for cystine stones because they are very hard as compared with other types of stones.
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy
Lithotripsy is a procedure that uses shock waves to break up stones in the kidney and parts of the ureter (tube that carries urine from your kidneys ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Percutaneous nephrostolithotomy or nephrolithotomy: A small tube is placed through the flank directly into the kidney. A telescope is then passed through the tube to fragment the stone under direct vision.
Percutaneous nephrostolithotomy or neph...
Percutaneous (through the skin) urinary procedures help drain urine from your kidney and get rid of kidney stones.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Ureteroscopy and laser lithotripsy: The laser is used to break up the stones and can be used to treat stones that are not too large.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Cystinuria is a chronic, lifelong condition. Stones commonly return. However, the condition rarely results in kidney failure. It does not affect other organs.
Chronic
Chronic refers to something that continues over an extended period of time. A chronic condition is usually long-lasting and does not easily or quick...
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Bladder injury from stone
Bladder injury
Traumatic injury of the bladder and urethra involves damage caused by an outside force.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Kidney injury from stone
Kidney injury
Injury to the kidney and ureter is damage to the organs of the upper urinary tract.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Kidney infection
- Chronic kidney disease
- Ureteral obstruction
Ureteral obstruction
Obstructive uropathy is a condition in which the flow of urine is blocked. This causes the urine to back up and injure one or both kidneys.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Urinary tract infection
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you have symptoms of urinary tract stones.
Prevention
There are medicines that can be taken so cystine does not form a stone. Ask your provider about these medicines and their side effects.
Any person with a known history of stones in the urinary tract should drink plenty of fluids to regularly produce a high amount of urine. This allows stones and crystals to leave the body before they become large enough to cause symptoms. Decreasing your intake of salt or sodium will help as well.
References
Elder JS. Urinary lithiasis. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 562.
Guay-Woodford LM. Hereditary nephropathies and developmental abnormalities of the urinary tract. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 119.
Miller NL, Borofsky MS. Evaluation and medical management of urinary lithiasis. In: Partin AW, Dmochowski RR, Kavoussi LR, Peters CA, eds. Campbell-Walsh-Wein Urology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 92.
Sakhaee K, Moe OW. Urolithiasis. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 38.
Kidney stones
Animation
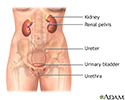
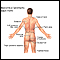
Female urinary tract - illustration
The female and male urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Female urinary tract
illustration
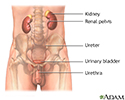
Male urinary tract - illustration
The male and female urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Male urinary tract
illustration
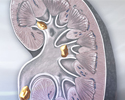
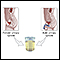
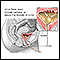
Cystinuria - illustration
Cystinuria is a disorder characterized by cystine stones in the kidney, ureter, and bladder. A genetic abnormality results in abnormal transport of amino acids in the kidney. The high levels of the amino acid cystine in the urine lead to stone formation.
Cystinuria
illustration
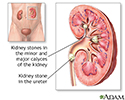
Nephrolithiasis - illustration
Kidney stones result when urine becomes too concentrated and substances in the urine crystalize to form stones. Symptoms arise when the stones begin to move down the ureter causing intense pain. Kidney stones may form in the pelvis or calyces of the kidney or in the ureter.
Nephrolithiasis
illustration
Female urinary tract - illustration
The female and male urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Female urinary tract
illustration
Male urinary tract - illustration
The male and female urinary tracts are relatively the same except for the length of the urethra.
Male urinary tract
illustration
Cystinuria - illustration
Cystinuria is a disorder characterized by cystine stones in the kidney, ureter, and bladder. A genetic abnormality results in abnormal transport of amino acids in the kidney. The high levels of the amino acid cystine in the urine lead to stone formation.
Cystinuria
illustration
Nephrolithiasis - illustration
Kidney stones result when urine becomes too concentrated and substances in the urine crystalize to form stones. Symptoms arise when the stones begin to move down the ureter causing intense pain. Kidney stones may form in the pelvis or calyces of the kidney or in the ureter.
Nephrolithiasis
illustration
Review Date: 1/1/2022
Reviewed By: Kelly L. Stratton, MD, FACS, Associate Professor, Department of Urology, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, OK. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.