Cholestasis
Intrahepatic cholestasis; Extrahepatic cholestasisCholestasis is any condition in which the flow of bile from the liver is slowed or blocked.
Bile
Bile is a fluid that is made and released by the liver and stored in the gallbladder. Bile helps with digestion. It breaks down fats into fatty acid...

Causes
There are many causes of cholestasis.
Extrahepatic cholestasis occurs outside the liver. It can be caused by:
- Bile duct tumors
- Cysts affecting the bile duct
- Narrowing of the bile duct (strictures)
- Stones in the common bile duct
- Pancreatitis
- Pancreatic tumor or pseudocyst
- Pressure on the bile ducts due to a nearby mass or tumor
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis
Intrahepatic cholestasis occurs inside the liver. It can be caused by:
- Alcoholic liver disease
- Amyloidosis
-
Bacterial abscess in the liver
Abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus in any part of the body. In most cases, the area around an abscess is swollen and inflamed.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Being fed exclusively through a vein (IV)
- Lymphoma
- Pregnancy
- Primary biliary cholangitis (previously called primary biliary cirrhosis)
- Primary or metastatic liver cancer
Metastatic
Liver metastases refer to cancer that has spread to the liver from somewhere else in the body. Liver metastases are not the same as cancer that start...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Primary sclerosing cholangitis
-
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis is a disease in which inflammation occurs in the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, eyes, skin, and/or other tissues.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Serious infections that have spread through the bloodstream (sepsis)
- Tuberculosis
- Viral hepatitis
Certain medicines can also cause cholestasis, including:
- Antibiotics, such as ampicillin and other penicillin
- Anabolic steroids
- Birth control pills
- Chlorpromazine
- Cimetidine
- Estradiol
- Imipramine
- Prochlorperazine
- Terbinafine
- Tolbutamide
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Clay-colored or pale stools
- Dark urine
- Inability to digest certain foods
- Itching
- Nausea or vomiting
- Pain in the right upper part of the abdomen
- Yellow skin or eyes
Exams and Tests
Blood tests may show that you have elevated bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase.
Bilirubin
The bilirubin blood test measures the level of bilirubin in the blood. Bilirubin is a yellowish pigment found in bile, a fluid made by the liver. Bi...

Alkaline phosphatase
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is a protein found in all body tissues. Tissues with higher amounts of ALP include the liver, bile ducts, and bone. A blo...

Imaging tests are used to diagnose this condition. Tests include:
- CT scan of the abdomen
- MRI of the abdomen
- Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), can also determine cause
- Ultrasound of the abdomen
Treatment
The underlying cause of cholestasis must be treated.
Outlook (Prognosis)
How well a person does depends on the disease causing the condition. Stones in the common bile duct can often be removed. This can cure the cholestasis.
Stents can be placed to open areas of the common bile duct that are narrowed or blocked by cancers.
If the condition is caused by the use of a certain medicine, it will often go away when you stop taking that drug.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Diarrhea
- Organ failure can occur if sepsis develops
- Poor absorption of fat and fat-soluble vitamins
- Severe itching
- Weak bones (osteomalacia) due to having cholestasis for a very long time
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if you have:
- Itching that does not go away
- Yellow skin or eyes
- Other symptoms of cholestasis
Prevention
Get vaccinated for hepatitis A and B if you are at risk. Do not use intravenous drugs and share needles.
References
Eaton JE, Lindor KD. Primary biliary cholangitis. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 91.
Fogel EL, Sherman S. Diseases of the gallbladder and bile ducts. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 146.
Lidofsky SD. Jaundice. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 21.
-
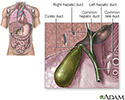
Gallstones - illustration
The gallbladder is an organ that normally functions to store bile excreted from the liver. Bile is a solution composed of water, bile salts, lecithin, cholesterol and some other small solutes. Changes in the relative concentration of these components may cause precipitation from solution and formation of a nidus, or nest, around which gallstones are formed. Gallstones can become large and block the opening from the gallbladder or cystic duct. This produces pain in the right upper quadrant or midepigastrum (above the belly button) in the abdomen that feels like cramping.
Gallstones
illustration
-
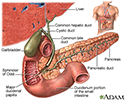
Gallbladder - illustration
The gallbladder is a sac located under the liver. It stores and concentrates the bile produced in the liver. Bile is released from the gallbladder in response to food, especially fats, in the upper small intestine.
Gallbladder
illustration
-
Gallbladder - illustration
The gallbladder is a muscular sac located under the liver. It stores and concentrates the bile produced in the liver that is not immediately needed for digestion. Bile is released from the gallbladder into the small intestine in response to food. The pancreatic duct joins the common bile duct at the small intestine adding enzymes to aid in digestion.
Gallbladder
illustration
-
Gallstones - illustration
The gallbladder is an organ that normally functions to store bile excreted from the liver. Bile is a solution composed of water, bile salts, lecithin, cholesterol and some other small solutes. Changes in the relative concentration of these components may cause precipitation from solution and formation of a nidus, or nest, around which gallstones are formed. Gallstones can become large and block the opening from the gallbladder or cystic duct. This produces pain in the right upper quadrant or midepigastrum (above the belly button) in the abdomen that feels like cramping.
Gallstones
illustration
-
Gallbladder - illustration
The gallbladder is a sac located under the liver. It stores and concentrates the bile produced in the liver. Bile is released from the gallbladder in response to food, especially fats, in the upper small intestine.
Gallbladder
illustration
-
Gallbladder - illustration
The gallbladder is a muscular sac located under the liver. It stores and concentrates the bile produced in the liver that is not immediately needed for digestion. Bile is released from the gallbladder into the small intestine in response to food. The pancreatic duct joins the common bile duct at the small intestine adding enzymes to aid in digestion.
Gallbladder
illustration
Review Date: 5/4/2022
Reviewed By: Michael M. Phillips, MD, Emeritus Professor of Medicine, The George Washington University School of Medicine, Washington, DC. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.