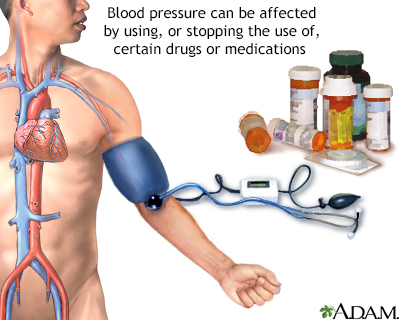
High blood pressure - medicine-related
Hypertension - medication related; Drug-induced hypertensionDrug-induced hypertension is high blood pressure caused by a chemical substance or medicine.
High blood pressure
Blood pressure is a measurement of the force exerted against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps blood to your body. Hypertension is the ...

Causes
Blood pressure is determined by the:
- Amount of blood the heart pumps
- Condition of the heart valves
- Pulse rate
- Pumping power of the heart
- Size and condition of the arteries
There are several types of high blood pressure:
- Essential hypertension has no cause that can be found (many different genetic traits contribute to essential hypertension, each one having a relatively small effect).
- Secondary hypertension occurs because of another disorder.
- Drug-induced hypertension is a form of secondary hypertension caused by the effects of a chemical substance or medicine.
- Pregnancy-induced hypertension.
Chemical substances and medicines that can cause high blood pressure include:
- Acetaminophen
- Alcohol, amphetamines, ecstasy (MDMA and derivatives), and cocaine
- Angiogenesis inhibitors (including tyrosine kinase inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies)
- Antidepressants (including venlafaxine, bupropion, and desipramine)
- Black licorice
- Caffeine (including the caffeine in coffee and energy drinks)
- Corticosteroids and mineralocorticoids
- Ephedra and many other herbal products
- Erythropoietin
- Estrogens (including birth control pills)
- Immunosuppressants (such as cyclosporine)
- Many over-the-counter medicines such as cough/cold and asthma medicines, particularly when the cough/cold medicine is taken with certain antidepressants, such as tranylcypromine or tricyclics
Asthma
Asthma is a chronic disease that causes the airways of the lungs to swell and narrow. It leads to breathing difficulty such as wheezing, shortness o...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Migraine medicines
Migraine
A migraine is a type of headache. It may occur with symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or sensitivity to light and sound. In most people, a throbbi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nasal decongestants
- Nicotine
Nicotine
The nicotine in tobacco can be addictive like alcohol, cocaine, and morphine.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Phentermine (a weight loss medicine)
- Testosterone and other anabolic steroids and performance-enhancing medicines
- Thyroid hormone (when taken in excess)
- Yohimbine (and Yohimbe extract)
Rebound hypertension occurs when blood pressure rises after you stop taking or lower the dose of a medicine (typically a medicine you are taking to lower high blood pressure).
- This is common for medicines that block the sympathetic nervous system like beta blockers and clonidine.
- Talk to your health care provider to see if your medicine needs to be gradually tapered before stopping.
Many other factors can also affect blood pressure, including:
- Age
- Condition of the kidneys, nervous system, or blood vessels
- Genetics
- Foods eaten, weight, and other body-related variables, including the amount of added sodium in processed foods
Sodium in processed foods
Sodium is an element that the body needs to work properly. Salt contains sodium.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Levels of various hormones in the body
- Volume of water in the body
References
Azizi M, Lorthioir A, Amar L. Resistant hypertension. In: Bakris GL, Sorrentino MJ, Laffin LJ, eds. Hypertension: A Companion to Braunwald's Heart Disease. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 47.
Foy MC, Vaishnav J, Sperati CJ. Drug-induced hypertension. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2019;48(4):859-873. PMIID: 31655781 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31655781/.
Jurca SJ, Elliott WJ. Common substances that may contribute to resistant hypertension, and recommendations for limiting their clinical effects. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2016;18(10):73. PMID: 27671491 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27671491/.
Peixoto AJ. Secondary hypertension. In: Gilbert S, ed. National Kidney Foundation Primer on Kidney Diseases. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 65.
Drug induced hypertension - illustration
Drug-induced hypertension is high blood pressure caused by a response to using, or stopping the use of, a chemical substance, drug, or medicine.
Drug induced hypertension
illustration
Untreated hypertension - illustration
Hypertension is a disorder characterized by chronically high blood pressure. It must be monitored, treated and controlled by medicines, lifestyle changes, or a combination of both.
Untreated hypertension
illustration
Hypertension - illustration
Hypertension is a disorder characterized by consistently high blood pressure. Blood pressure readings are given as two numbers. The top number is called systolic blood pressure, and it represents the pressure generated when the heart beats. The bottom number is called diastolic blood pressure, and it represents the pressure in the vessels when the heart is at rest. Persistent high blood pressure can lead to abnormal changes in the heart.
Hypertension
illustration
Drug induced hypertension - illustration
Drug-induced hypertension is high blood pressure caused by a response to using, or stopping the use of, a chemical substance, drug, or medicine.
Drug induced hypertension
illustration
Untreated hypertension - illustration
Hypertension is a disorder characterized by chronically high blood pressure. It must be monitored, treated and controlled by medicines, lifestyle changes, or a combination of both.
Untreated hypertension
illustration
Hypertension - illustration
Hypertension is a disorder characterized by consistently high blood pressure. Blood pressure readings are given as two numbers. The top number is called systolic blood pressure, and it represents the pressure generated when the heart beats. The bottom number is called diastolic blood pressure, and it represents the pressure in the vessels when the heart is at rest. Persistent high blood pressure can lead to abnormal changes in the heart.
Hypertension
illustration
- High blood pressure(Alt. Medicine)
- High blood pressure - InDepth(In-Depth)
- Atherosclerosis(Alt. Medicine)
- Stroke(Alt. Medicine)
- Stroke - InDepth(In-Depth)
- Myocardial infarction(Alt. Medicine)
- Diabetes - type 1 - InDepth(In-Depth)
- Coronary artery disease - InDepth(In-Depth)
- Mind-body medicine(Alt. Medicine)
- Macular degeneration(Alt. Medicine)
Review Date: 10/27/2024
Reviewed By: Laura J. Martin, MD, MPH, ABIM Board Certified in Internal Medicine and Hospice and Palliative Medicine, Atlanta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.