Primary alveolar hypoventilation
Ondine's curse; Ventilatory failure; Diminished hypoxic ventilator drive; Diminished hypercapnic ventilator driveAlveolar hypoventilation means that a person does not have enough respiratory function to keep the blood level of carbon dioxide in a normal range. Primary means that it is not due to an identifiable cause such as a lung or brain disease. The lungs and airways are normal.
Causes
Normally, when the oxygen level in the blood is low or the carbon dioxide level is high, there is a signal from the brain to breathe more deeply or quickly. In people with primary alveolar hypoventilation, this change in breathing does not happen.
The cause of this condition is unknown. Some babies have symptoms of this at birth, due to congenital central hypoventilation syndrome. This syndrome is due to a variant in the PHOX2B gene. Children and adults may have a less severe condition that has no definitive cause though some health care providers suspect it may be due to changes in the part of the brain that controls breathing.
Symptoms
Symptoms are usually worse during sleep. Episodes of stopped breathing (apnea) often occur while sleeping. Often there is no shortness of breath during the day.
Apnea
Breathing that stops from any cause is called apnea. Slowed breathing is called bradypnea. Labored or difficult breathing is known as dyspnea....
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleSymptoms include:
- Bluish coloration of the skin caused by lack of oxygen (cyanosis)
Bluish coloration of the skin
A bluish color to the skin or mucous membrane is usually due to a lack of oxygen in the blood. The medical term is cyanosis.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Daytime drowsiness
Drowsiness
Drowsiness refers to feeling more sleepy than normal during the day. People who are drowsy may fall asleep when they do not want to or at times whic...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fatigue
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Morning headaches
- Swelling of the ankles
- Waking up from sleep unrested
- Waking up many times at night
People with this disease may be very sensitive to even small doses of sedatives or narcotics. These medicines can make their breathing problem much worse.
Exams and Tests
Your provider will perform a physical exam and ask about symptoms.
Tests will be done to check for other causes. For example, muscular dystrophy can make the rib muscles weak, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) damages the lung tissue itself. A small stroke can affect the breathing center in the brain.
Muscular dystrophy
Muscular dystrophy (MD) is a group of inherited disorders that cause muscle weakness and loss of muscle tissue, which get worse over time.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease. Having COPD makes it hard to breathe. There are two main forms of COPD:Chroni...
Tests that may be done include:
- Measuring levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood (arterial blood gases)
Arterial blood gases
Blood gases are a measurement of how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in your blood. They also determine the acidity (pH) of your blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chest x-ray or CT scan
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCT scan
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - CBC to check oxygen carrying ability of red blood cells
- Lung function tests
Lung function tests
Pulmonary function tests are a group of tests that measure breathing and how well the lungs are functioning.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Overnight oxygen level measurements (oximetry)
- Sleep study (polysomnography)
Polysomnography
Polysomnography is a sleep study. This test records certain body functions as you sleep, or try to sleep. Polysomnography is used to diagnose sleep...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Medicines that stimulate the respiratory system may be used but do not always work. Mechanical devices that assist breathing, particularly at night, may be helpful in some people. Oxygen therapy may help in a few people, but may worsen night symptoms in others.
Respiratory
The words "respiratory" and "respiration" refer to the lungs and breathing.

Outlook (Prognosis)
Response to treatment varies.
Possible Complications
Low blood oxygen level can cause high blood pressure in the lung blood vessels. This can lead to cor pulmonale (right-sided heart failure).
Cor pulmonale
Cor pulmonale is a condition that causes the right side of the heart to fail. Long-term high blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries of the lung an...
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of this disorder. Seek medical care right away if bluish skin occurs.
Prevention
There is no known prevention. You should avoid using sleep medicines or other medicines that can cause drowsiness.
References
Malhotra A, Powell F. Disorders of ventilatory control. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 74.
Weinberger SE, Cockrill BA, Mandel J. Disorders of ventilatory control. In: Weinberger SE, Cockrill BA, Mandel J, eds. Principles of Pulmonary Medicine. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 18.
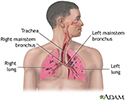
Respiratory system - illustration
Air is breathed in through the nasal passageways, travels through the trachea and bronchi to the lungs.
Respiratory system
illustration
Review Date: 8/19/2024
Reviewed By: Allen J. Blaivas, DO, Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine, VA New Jersey Health Care System, Clinical Assistant Professor, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, East Orange, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.