Pulmonary actinomycosis
Actinomycosis - pulmonary; Actinomycosis - thoracicPulmonary actinomycosis is a rare lung infection caused by one of several specific bacteria.
Causes
Pulmonary actinomycosis is caused by certain bacteria normally found in the mouth and gastrointestinal tract. The bacteria often do not cause harm. But poor dental hygiene and tooth abscess can increase your risk for lung infections caused by these bacteria.
Dental hygiene
Tooth decay and gum disease are caused by plaque, a sticky combination of bacteria and food. Plaque begins to build up on teeth within a few minutes...

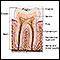
Tooth abscess
A tooth abscess is a pocket of pus caused by a bacterial infection.
People with the following health problems also have a higher chance of developing the infection:
-
Alcohol use
Alcohol use
Alcohol use disorder is when your drinking causes serious problems in your life, yet you keep drinking. You may also need more and more alcohol to f...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Scars on the lungs (bronchiectasis)
Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis is a disease in which the large airways in the lungs are damaged. This causes the airways to become permanently wider. Bronchiectasis...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease. Having COPD makes it hard to breathe. There are two main forms of COPD:Chroni...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
The disease is rare in the United States. It may occur at any age but is most common in people 30 to 60 years old. Men get this infection more often than women.
Symptoms
The infection often comes on slowly. It may be weeks or months before diagnosis is confirmed.
Symptoms may include any of the following:
- Chest pain when taking a deep breath
- Cough with phlegm (sputum)
- Fever
- Shortness of breath
- Unintentional weight loss
-
Lethargy
Lethargy
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Night sweats (uncommon)
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your medical history and symptoms. Tests that may be done include:
-
Bronchoscopy with culture
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is a test to view the airways and diagnose lung disease. It may also be used during the treatment of some lung conditions.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Complete blood count (CBC) with differential
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chest CT scan
Chest CT scan
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Lung biopsy
Lung biopsy
An open lung biopsy is surgery to remove a small piece of tissue from the lung. The sample is then examined for cancer, infection, or lung disease....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Modified AFB smear of sputum
AFB smear of sputum
Sputum stain for mycobacteria is a test to check for a type of bacteria that cause tuberculosis and other infections.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Sputum culture
Sputum culture
Routine sputum culture is a laboratory test that looks for germs that cause infection. Sputum is the material that comes up from air passages when y...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Tissue and sputum Gram stain
Sputum Gram stain
A sputum Gram stain is a lab test used to detect bacteria in a sputum sample. Sputum is the material that comes up from your air passages when you c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Thoracentesis with culture
Thoracentesis
Thoracentesis is a procedure to remove fluid from the space between the lining of the outside of the lungs (pleura) and the wall of the chest....
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Tissue culture
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to cure the infection. It may take a long time to get better. To be cured, you may need to receive the antibiotic penicillin through a vein (intravenously) for 2 to 6 weeks. Then you need to take penicillin by mouth for a long period. Some people need up to 18 months of antibiotic treatment.
If you cannot take penicillin, your provider will prescribe other antibiotics.
Surgery may be needed to drain fluid from the lungs and control the infection.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Most people get better after treatment with antibiotics.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
-
Brain abscess
Brain abscess
A brain abscess is a collection of pus, immune cells, and other material in the brain, caused by a bacterial or fungal infection.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Destruction of parts of the lungs
- COPD
-
Meningitis
Meningitis
Meningitis is an infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. This covering is called the meninges.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Osteomyelitis (bone infection)
Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis is a bone infection. It is caused by bacteria or other germs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You have symptoms of pulmonary actinomycosis
- Your symptoms get worse or do not improve with treatment
- You develop new symptoms
- You have a fever of 101°F (38.3°C) or higher
Prevention
Good dental hygiene may help reduce your risk for actinomycosis.
References
Brook I. Actinomycosis. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 304.
Russo TA. Agents of actinomycosis. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 254.
-
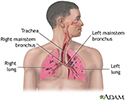
Respiratory system - illustration
Air is breathed in through the nasal passageways, travels through the trachea and bronchi to the lungs.
Respiratory system
illustration
-
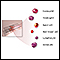
Gram stain of tissue biopsy - illustration
The gram stain procedure is a method of staining microorganisms on a slide using crystal violet to be viewed later under a microscope.
Gram stain of tissue biopsy
illustration
-
Respiratory system - illustration
Air is breathed in through the nasal passageways, travels through the trachea and bronchi to the lungs.
Respiratory system
illustration
-
Gram stain of tissue biopsy - illustration
The gram stain procedure is a method of staining microorganisms on a slide using crystal violet to be viewed later under a microscope.
Gram stain of tissue biopsy
illustration
Review Date: 3/16/2024
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Associate Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Associate in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.