High blood pressure
Blood pressure - high; High blood pressureHigh blood pressure, or hypertension, is a serious condition that affects about one in three American adults, and two-thirds of people over age 65. Blood pressure is the force of blood as it pumps through your arteries. The more blood your heart pumps and the narrower your arteries are, the higher the blood pressure. Normal blood pressure is an...
The Basics
Tests for high blood pressure
A Closer Look
Self Care
Talking to your MD
Blood pressure - Animation
Blood pressure
Animation
Essential hypertension - Animation
Essential hypertension
Animation
Hypertension - Animation
Hypertension
Animation
Tracking your blood pressure at home - Animation
Tracking your blood pressure at home
Animation
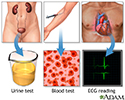
High blood pressure tests
Routine lab tests are recommended before beginning treatment of high blood pressure to determine organ or tissue damage or other risk factors. These lab tests include urinalysis, blood cell count, blood chemistry (potassium, sodium, creatinine, fasting glucose, total cholesterol and HDL cholesterol), and an ECG (electrocardiogram). Additional tests may be recommended based on your condition.
High blood pressure tests
illustration
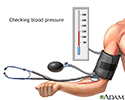
Blood pressure check
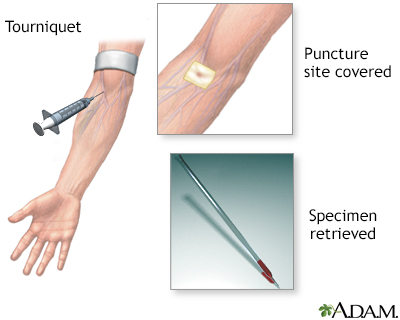
To measure blood pressure, your doctor uses an instrument call a sphygmomanometer, which is more often referred to as a blood pressure cuff. The cuff is wrapped around your upper arm and inflated to stop the flow of blood in your artery. As the cuff is slowly deflated, your doctor uses a stethoscope to listen to the blood pumping through the artery. These pumping sounds register on a gauge attached to the cuff. The first pumping sound your doctor hears is recorded as the systolic pressure, and the last sound is the diastolic pressure.
Blood pressure check
illustration
Effects of age on blood pressure
Blood vessels become less elastic with age. The average blood pressure increases from 120/70 to 150/90 and may persist slightly high, even if treated. The blood vessels respond more slowly to a change in body position.
Effects of age on blood pressure
illustration
Monitoring blood pressure
Hypertension is a disorder characterized by chronically high blood pressure. It must be monitored, treated and controlled by medicines, lifestyle changes, or a combination of both.
Monitoring blood pressure
illustration
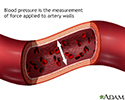
Blood pressure
Blood pressure is the force applied against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps blood through the body. The pressure is determined by the force and amount of blood pumped and the size and flexibility of the arteries.
Blood pressure
illustration
Exercise can lower blood pressure
Reducing your weight by just 10 pounds may be enough to lower your blood pressure. Losing weight can help to enhance the effects of high blood pressure medicine and may also reduce other risk factors, such as diabetes and high bad cholesterol.
Exercise can lower blood pressure
illustration
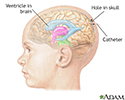
Intracranial pressure monitoring
Intracranial pressure monitoring is performed by inserting a catheter into the head with a sensing device to monitor the pressure around the brain. An increase in intracranial pressure can cause a decrease in blood flow to the brain causing brain damage.
Intracranial pressure monitoring
illustration
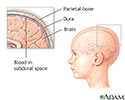
Increased intracranial pressure
Increased intracranial pressure is almost always indicative of severe medical problems. The pressure itself can be responsible for further damage to the central nervous system by decreasing blood flow to the brain or by causing the brain to herniate (push through) the opening in the back of the skull where the spinal cord is attached. Causes of increased intracranial pressure may include bleeding into the subdural space (subdural hematoma).
Increased intracranial pressure
illustration
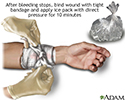
Stopping bleeding with pressure and ice
Bleeding from most injuries can be stopped by applying direct pressure to the injury. This keeps from cutting off the blood supply to the affected limb. When there is severe bleeding, where a major artery has been severed, pressure may be insufficient and a tourniquet may be necessary.
Stopping bleeding with pressure and ice
illustration
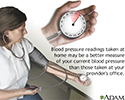
Taking your blood pressure at home
After you are diagnosed with high blood pressure, your health care provider may ask you to keep track of your blood pressure by measuring it at home. There are easy-to-use devices that can help you monitor your blood pressure at home. Practice with your provider to make sure you are taking your blood pressure correctly. Compare your home machine with the one at your provider's office to be sure it is reading correctly.
Taking your blood pressure at home
illustration
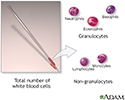
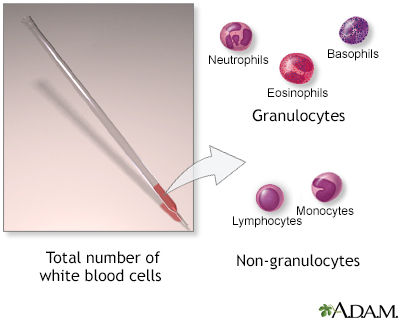
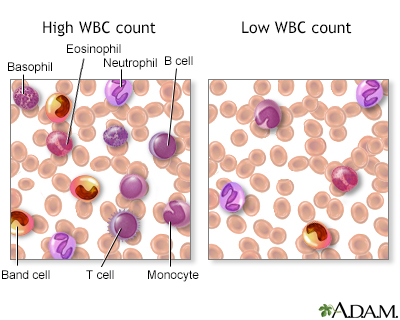
White blood cell count - series
Presentation
Blood pressure - Animation
Blood pressure
Animation
Essential hypertension - Animation
Essential hypertension
Animation
Hypertension - Animation
Hypertension
Animation
Tracking your blood pressure at home - Animation
Tracking your blood pressure at home
Animation
High blood pressure tests
Routine lab tests are recommended before beginning treatment of high blood pressure to determine organ or tissue damage or other risk factors. These lab tests include urinalysis, blood cell count, blood chemistry (potassium, sodium, creatinine, fasting glucose, total cholesterol and HDL cholesterol), and an ECG (electrocardiogram). Additional tests may be recommended based on your condition.
High blood pressure tests
illustration
Blood pressure check
To measure blood pressure, your doctor uses an instrument call a sphygmomanometer, which is more often referred to as a blood pressure cuff. The cuff is wrapped around your upper arm and inflated to stop the flow of blood in your artery. As the cuff is slowly deflated, your doctor uses a stethoscope to listen to the blood pumping through the artery. These pumping sounds register on a gauge attached to the cuff. The first pumping sound your doctor hears is recorded as the systolic pressure, and the last sound is the diastolic pressure.
Blood pressure check
illustration
Effects of age on blood pressure
Blood vessels become less elastic with age. The average blood pressure increases from 120/70 to 150/90 and may persist slightly high, even if treated. The blood vessels respond more slowly to a change in body position.
Effects of age on blood pressure
illustration
Monitoring blood pressure
Hypertension is a disorder characterized by chronically high blood pressure. It must be monitored, treated and controlled by medicines, lifestyle changes, or a combination of both.
Monitoring blood pressure
illustration
Blood pressure
Blood pressure is the force applied against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps blood through the body. The pressure is determined by the force and amount of blood pumped and the size and flexibility of the arteries.
Blood pressure
illustration
Exercise can lower blood pressure
Reducing your weight by just 10 pounds may be enough to lower your blood pressure. Losing weight can help to enhance the effects of high blood pressure medicine and may also reduce other risk factors, such as diabetes and high bad cholesterol.
Exercise can lower blood pressure
illustration
Intracranial pressure monitoring
Intracranial pressure monitoring is performed by inserting a catheter into the head with a sensing device to monitor the pressure around the brain. An increase in intracranial pressure can cause a decrease in blood flow to the brain causing brain damage.
Intracranial pressure monitoring
illustration
Increased intracranial pressure
Increased intracranial pressure is almost always indicative of severe medical problems. The pressure itself can be responsible for further damage to the central nervous system by decreasing blood flow to the brain or by causing the brain to herniate (push through) the opening in the back of the skull where the spinal cord is attached. Causes of increased intracranial pressure may include bleeding into the subdural space (subdural hematoma).
Increased intracranial pressure
illustration
Stopping bleeding with pressure and ice
Bleeding from most injuries can be stopped by applying direct pressure to the injury. This keeps from cutting off the blood supply to the affected limb. When there is severe bleeding, where a major artery has been severed, pressure may be insufficient and a tourniquet may be necessary.
Stopping bleeding with pressure and ice
illustration
Taking your blood pressure at home
After you are diagnosed with high blood pressure, your health care provider may ask you to keep track of your blood pressure by measuring it at home. There are easy-to-use devices that can help you monitor your blood pressure at home. Practice with your provider to make sure you are taking your blood pressure correctly. Compare your home machine with the one at your provider's office to be sure it is reading correctly.
Taking your blood pressure at home
illustration
White blood cell count - series
Presentation
High blood pressure
Blood pressure - high; High blood pressureHigh blood pressure, or hypertension, is a serious condition that affects about one in three American adults, and two-thirds of people over age 65. Blood pressure is the force of blood as it pumps through your arteries. The more blood your heart pumps and the narrower your arteries are, the higher the blood pressure. Normal blood pressure is an...
The Basics
Tests for high blood pressure
A Closer Look
Self Care
Talking to your MD
High blood pressure
Blood pressure - high; High blood pressureHigh blood pressure, or hypertension, is a serious condition that affects about one in three American adults, and two-thirds of people over age 65. Blood pressure is the force of blood as it pumps through your arteries. The more blood your heart pumps and the narrower your arteries are, the higher the blood pressure. Normal blood pressure is an...
The Basics
Tests for high blood pressure
A Closer Look
Self Care
Talking to your MD
Review Date: 4/7/2025
Reviewed By: Steven D. Ehrlich, NMD, Solutions Acupuncture, a private practice specializing in complementary and alternative medicine, Phoenix, AZ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network.