Acoustic neuroma
Vestibular schwannoma; Tumor - acoustic; Cerebellopontine angle tumor; Angle tumor; Hearing loss - acoustic; Tinnitus - acousticAn acoustic neuroma is a slow-growing tumor of the nerve that connects the ear to the brain. This nerve is called the vestibular cochlear nerve. It is behind the ear, right under the brain. An acoustic neuroma is a benign tumor. This means that it does not spread to other parts of the body. However, it can damage several important nearby...
The Basics
Tests for nervous system tumor
A Closer Look
- Brain tumors - primary - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Brain cancer (Alternative Medicine)
- Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Colon and rectal cancers - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Vitamins and Phytonutrients - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Pneumonia - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Leukemia (Alternative Medicine)
- Acute lymphocytic leukemia - InDepth (Detailed Report)
Tuberous sclerosis, angiofibromas - face
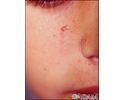
These red (erythematous) elevated skin lesions (papules) are tumors made-up of fibrous tissue (angiofibroma) and occur with tuberous sclerosis. Tuberous sclerosis affects both the nervous system and the skin (neurocutaneous) and may also produce other skin lesions including shagreen spots, ash-leaf macula, and periungual fibromas (a type of skin tumor).
Tuberous sclerosis, angiofibromas - face
illustration
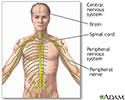
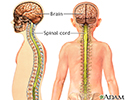
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
The central nervous system comprises the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
illustration
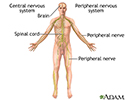
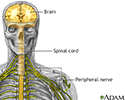
Nervous system
The central nervous system is comprised of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes all peripheral nerves.
Nervous system
illustration
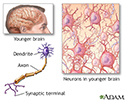
Brain and nervous system
The nervous system controls the many complicated and interconnected functions of the body and mind. Motor, sensory cognitive and autonomic function are all coordinated and driven by the brain and nerves. As people age, nerve cells deteriorated in number and facility, causing some lessening in function.
Brain and nervous system
illustration
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The brain functions to receive nerve impulses from the spinal cord and cranial nerves. The spinal cord contains the nerves that carry messages between the brain and the body.
Central nervous system
illustration
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The brain functions to receive nerve impulses from the spinal cord and cranial nerves. The spinal cord contains the nerves that carry messages between the brain and the body. Spinal cord injury can occur when there is damage to the cells within the spinal cord or when the tracts of nerves that run up and down the spinal cord are severed.
Central nervous system
illustration
Nervous system
Peripheral Neuropathy is not a distinct disease, but the manifestation of many conditions that damage the peripheral nerves (nervous tissue other than the brain and spinal cord). Symptoms depend on whether sensory nerves (the nerves that transmit sensory information from the body to the brain and spinal cord) or motor nerves (the nerves that transmit impulses from the brain and spinal cord to the body) are affected. If the sensory nerves are damaged, sensation may be diminished, lacking or abnormal. Damaged motor nerves impair movement or function. Peripheral neuropathy may be caused by direct or indirect injury, or by a systemic cause such as a metabolic disorder.
Nervous system
illustration
Tuberous sclerosis, angiofibromas - face
These red (erythematous) elevated skin lesions (papules) are tumors made-up of fibrous tissue (angiofibroma) and occur with tuberous sclerosis. Tuberous sclerosis affects both the nervous system and the skin (neurocutaneous) and may also produce other skin lesions including shagreen spots, ash-leaf macula, and periungual fibromas (a type of skin tumor).
Tuberous sclerosis, angiofibromas - face
illustration
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
The central nervous system comprises the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
illustration
Nervous system
The central nervous system is comprised of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes all peripheral nerves.
Nervous system
illustration
Brain and nervous system
The nervous system controls the many complicated and interconnected functions of the body and mind. Motor, sensory cognitive and autonomic function are all coordinated and driven by the brain and nerves. As people age, nerve cells deteriorated in number and facility, causing some lessening in function.
Brain and nervous system
illustration
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The brain functions to receive nerve impulses from the spinal cord and cranial nerves. The spinal cord contains the nerves that carry messages between the brain and the body.
Central nervous system
illustration
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The brain functions to receive nerve impulses from the spinal cord and cranial nerves. The spinal cord contains the nerves that carry messages between the brain and the body. Spinal cord injury can occur when there is damage to the cells within the spinal cord or when the tracts of nerves that run up and down the spinal cord are severed.
Central nervous system
illustration
Nervous system
Peripheral Neuropathy is not a distinct disease, but the manifestation of many conditions that damage the peripheral nerves (nervous tissue other than the brain and spinal cord). Symptoms depend on whether sensory nerves (the nerves that transmit sensory information from the body to the brain and spinal cord) or motor nerves (the nerves that transmit impulses from the brain and spinal cord to the body) are affected. If the sensory nerves are damaged, sensation may be diminished, lacking or abnormal. Damaged motor nerves impair movement or function. Peripheral neuropathy may be caused by direct or indirect injury, or by a systemic cause such as a metabolic disorder.
Nervous system
illustration
Acoustic neuroma
Vestibular schwannoma; Tumor - acoustic; Cerebellopontine angle tumor; Angle tumor; Hearing loss - acoustic; Tinnitus - acousticAn acoustic neuroma is a slow-growing tumor of the nerve that connects the ear to the brain. This nerve is called the vestibular cochlear nerve. It is behind the ear, right under the brain. An acoustic neuroma is a benign tumor. This means that it does not spread to other parts of the body. However, it can damage several important nearby...
The Basics
Tests for nervous system tumor
A Closer Look
- Brain tumors - primary - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Brain cancer (Alternative Medicine)
- Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Colon and rectal cancers - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Vitamins and Phytonutrients - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Pneumonia - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Leukemia (Alternative Medicine)
- Acute lymphocytic leukemia - InDepth (Detailed Report)
Acoustic neuroma
Vestibular schwannoma; Tumor - acoustic; Cerebellopontine angle tumor; Angle tumor; Hearing loss - acoustic; Tinnitus - acousticAn acoustic neuroma is a slow-growing tumor of the nerve that connects the ear to the brain. This nerve is called the vestibular cochlear nerve. It is behind the ear, right under the brain. An acoustic neuroma is a benign tumor. This means that it does not spread to other parts of the body. However, it can damage several important nearby...
The Basics
Tests for nervous system tumor
A Closer Look
- Brain tumors - primary - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Brain cancer (Alternative Medicine)
- Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Colon and rectal cancers - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Vitamins and Phytonutrients - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Pneumonia - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Leukemia (Alternative Medicine)
- Acute lymphocytic leukemia - InDepth (Detailed Report)
Review Date: 5/2/2024
Reviewed By: Josef Shargorodsky, MD, MPH, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.