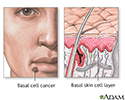
Basal cell skin cancer
Basal cell carcinoma; Rodent ulcer; Skin cancer - basal cell; Cancer - skin - basal cell; Nonmelanoma skin cancer; Basal cell NMSC; Basal cell epitheliomaBasal cell cancer is the most common form of cancer in the United States. Most skin cancers are basal cell cancer. Other common types of skin cancer are:Squamous cell cancerMelanoma
The Basics
Tests for Skin cancer - basal cell
A Closer Look
- Melanoma and other skin cancers - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Skin cancer (Alternative Medicine)
- Skin wrinkles and blemishes - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Psoriasis-In-Depth (Detailed Report)
- Vitamin A (Retinol) (Alternative Medicine)
- Acute lymphocytic leukemia - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Photodermatitis (Alternative Medicine)
- Brain tumors - primary - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Diabetes - type 1 - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Weight control and diet - InDepth (Detailed Report)
Self Care
Basal cell carcinoma - Animation
Basal cell carcinoma
Animation
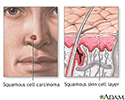
Squamous cell cancer
Squamous cell cancer involves cancerous changes to the cells of the middle portion of the epidermal skin layer. It is a malignant tumor, and is more aggressive than basal cell cancer, but still may be relatively slow-growing. It is more likely than basal cell cancer to spread (metastasize) to other locations, including internal organs. Treatment usually involves surgical removal of the tumor along with some surrounding tissue.
Squamous cell cancer
illustration
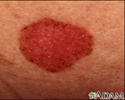
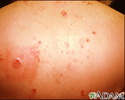
Skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma - spreading
This skin cancer, a basal cell carcinoma, is 5 to 6 centimeters across, red (erythematous), with well defined (demarcated) borders and sprinkled brown pigment along the margins. This cancer is located on the person's back.
Skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma - spreading
illustration
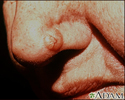
Skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma - nose
The typical basal cell skin cancer appears as a small, pearly, dome-shaped nodule with small visible blood vessels (telangiectasias).
Skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma - nose
illustration
Skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma - pigmented
This skin cancer appears as a 2 to 3 centimeter skin spot. The tissue has become destroyed (forming an atrophic plaque). There is a brownish color because of increased skin pigment (hyperpigmentation) and a slightly elevated, rolled, pearl-colored margin. This growth is located along the hair line.
Skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma - pigmented
illustration
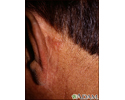
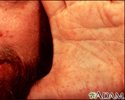
Skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma - behind ear
This skin cancer appears as a 1 to 1. 5 centimeter flesh-colored nodule with a central depression and a raised, pearly border. Small blood vessels are visible (telangiectatic).
Skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma - behind ear
illustration
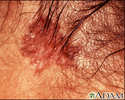
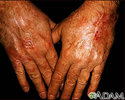
Skin cancer - squamous cell on the hands
This is a picture of squamous cell skin cancer on the hands. Squamous cell carcinoma is one of the three most common types of skin cancer: basal cell, squamous cell, and melanoma. Squamous cell cancers can metastasize (spread) and should be removed surgically as soon as they are diagnosed.
Skin cancer - squamous cell on the hands
illustration
Skin cancer, squamous cell - close-up
Squamous cell carcinoma is one of the three most common types of skin cancer: basal cell, squamous cell, and melanoma. Squamous cell cancers can metastasize (spread) and should be removed surgically as soon as they are diagnosed.
Skin cancer, squamous cell - close-up
illustration
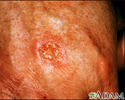
Basal cell cancer
Basal cell cancer is a malignant skin tumor involving cancerous changes of basal skin cells. Basal cell skin cancers usually occur on areas of skin that are regularly exposed to sunlight or other ultraviolet radiation. Once a suspicious lesion is found, a biopsy is needed to prove the diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma. Treatment varies depending on the size, depth, and location of the cancer. Early treatment by a dermatologist may result in a cure rate of more than 95%, but regular examination by a health care provider is required to watch for new sites of basal cell cancer.
Basal cell cancer
illustration
Multiple basal cell cancer due to x-ray therapy for acne
Basal cell carcinomas are more prevalent on sun or radiation exposed areas of skin. Here the typical lesion with raised, rolled, pearly borders with ulcerated center is seen on the back of a person previously irradiated for acne.
Multiple basal cell cancer due to x-ray therapy for acne
illustration
Basal cell nevus syndrome - face and hand
Basal cell nevus syndrome is an inherited disorder characterized by wide-set eyes, saddle nose, frontal bossing (prominent forehead), prognathism (prominent chin), numerous basal cell carcinomas (a type of skin cancer), and skeletal abnormalities. This individual has multiple flesh-colored, dome-shaped bumps on the face which are basal cell cancers, and palmar pits.
Basal cell nevus syndrome - face and hand
illustration
Squamous cell cancer
Squamous cell cancer involves cancerous changes to the cells of the middle portion of the epidermal skin layer. It is a malignant tumor, and is more aggressive than basal cell cancer, but still may be relatively slow-growing. It is more likely than basal cell cancer to spread (metastasize) to other locations, including internal organs. Treatment usually involves surgical removal of the tumor along with some surrounding tissue.
Squamous cell cancer
illustration
Skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma - spreading
This skin cancer, a basal cell carcinoma, is 5 to 6 centimeters across, red (erythematous), with well defined (demarcated) borders and sprinkled brown pigment along the margins. This cancer is located on the person's back.
Skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma - spreading
illustration
Skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma - nose
The typical basal cell skin cancer appears as a small, pearly, dome-shaped nodule with small visible blood vessels (telangiectasias).
Skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma - nose
illustration
Skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma - pigmented
This skin cancer appears as a 2 to 3 centimeter skin spot. The tissue has become destroyed (forming an atrophic plaque). There is a brownish color because of increased skin pigment (hyperpigmentation) and a slightly elevated, rolled, pearl-colored margin. This growth is located along the hair line.
Skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma - pigmented
illustration
Skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma - behind ear
This skin cancer appears as a 1 to 1. 5 centimeter flesh-colored nodule with a central depression and a raised, pearly border. Small blood vessels are visible (telangiectatic).
Skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma - behind ear
illustration
Skin cancer - squamous cell on the hands
This is a picture of squamous cell skin cancer on the hands. Squamous cell carcinoma is one of the three most common types of skin cancer: basal cell, squamous cell, and melanoma. Squamous cell cancers can metastasize (spread) and should be removed surgically as soon as they are diagnosed.
Skin cancer - squamous cell on the hands
illustration
Skin cancer, squamous cell - close-up
Squamous cell carcinoma is one of the three most common types of skin cancer: basal cell, squamous cell, and melanoma. Squamous cell cancers can metastasize (spread) and should be removed surgically as soon as they are diagnosed.
Skin cancer, squamous cell - close-up
illustration
Basal cell cancer
Basal cell cancer is a malignant skin tumor involving cancerous changes of basal skin cells. Basal cell skin cancers usually occur on areas of skin that are regularly exposed to sunlight or other ultraviolet radiation. Once a suspicious lesion is found, a biopsy is needed to prove the diagnosis of basal cell carcinoma. Treatment varies depending on the size, depth, and location of the cancer. Early treatment by a dermatologist may result in a cure rate of more than 95%, but regular examination by a health care provider is required to watch for new sites of basal cell cancer.
Basal cell cancer
illustration
Multiple basal cell cancer due to x-ray therapy for acne
Basal cell carcinomas are more prevalent on sun or radiation exposed areas of skin. Here the typical lesion with raised, rolled, pearly borders with ulcerated center is seen on the back of a person previously irradiated for acne.
Multiple basal cell cancer due to x-ray therapy for acne
illustration
Basal cell nevus syndrome - face and hand
Basal cell nevus syndrome is an inherited disorder characterized by wide-set eyes, saddle nose, frontal bossing (prominent forehead), prognathism (prominent chin), numerous basal cell carcinomas (a type of skin cancer), and skeletal abnormalities. This individual has multiple flesh-colored, dome-shaped bumps on the face which are basal cell cancers, and palmar pits.
Basal cell nevus syndrome - face and hand
illustration
Basal cell skin cancer
Basal cell carcinoma; Rodent ulcer; Skin cancer - basal cell; Cancer - skin - basal cell; Nonmelanoma skin cancer; Basal cell NMSC; Basal cell epitheliomaBasal cell cancer is the most common form of cancer in the United States. Most skin cancers are basal cell cancer. Other common types of skin cancer are:Squamous cell cancerMelanoma
The Basics
Tests for Skin cancer - basal cell
A Closer Look
- Melanoma and other skin cancers - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Skin cancer (Alternative Medicine)
- Skin wrinkles and blemishes - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Psoriasis-In-Depth (Detailed Report)
- Vitamin A (Retinol) (Alternative Medicine)
- Acute lymphocytic leukemia - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Photodermatitis (Alternative Medicine)
- Brain tumors - primary - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Diabetes - type 1 - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Weight control and diet - InDepth (Detailed Report)
Self Care
Basal cell skin cancer
Basal cell carcinoma; Rodent ulcer; Skin cancer - basal cell; Cancer - skin - basal cell; Nonmelanoma skin cancer; Basal cell NMSC; Basal cell epitheliomaBasal cell cancer is the most common form of cancer in the United States. Most skin cancers are basal cell cancer. Other common types of skin cancer are:Squamous cell cancerMelanoma
The Basics
Tests for Skin cancer - basal cell
A Closer Look
- Melanoma and other skin cancers - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Skin cancer (Alternative Medicine)
- Skin wrinkles and blemishes - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Psoriasis-In-Depth (Detailed Report)
- Vitamin A (Retinol) (Alternative Medicine)
- Acute lymphocytic leukemia - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Photodermatitis (Alternative Medicine)
- Brain tumors - primary - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Diabetes - type 1 - InDepth (Detailed Report)
- Weight control and diet - InDepth (Detailed Report)
Self Care
Review Date: 7/1/2023
Reviewed By: Ramin Fathi, MD, FAAD, Director, Phoenix Surgical Dermatology Group, Phoenix, AZ. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.