Sinusitis
Acute sinusitis; Sinus infection; Sinusitis - acute; Sinusitis - chronic; RhinosinusitisSinusitis is present when the tissue lining the sinuses become swollen or inflamed. It occurs as the result of an inflammatory reaction or an infection from a virus, bacteria, or fungus.
Common cold - Animation
Common cold
Animation
Ear infection - acute - Animation
Ear infection - acute
Animation
Ear infection - chronic - Animation
Ear infection - chronic
Animation
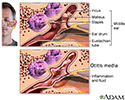
Middle ear infection (otitis media)
Otitis media is an inflammation or infection of the middle ear. Acute otitis media (acute ear infection) occurs when there is bacterial or viral infection of the fluid of the middle ear, which causes production of fluid or pus. Chronic otitis media occurs when the eustachian tube becomes blocked repeatedly due to allergies, multiple infections, ear trauma, or swelling of the adenoids.
Middle ear infection (otitis media)
illustration
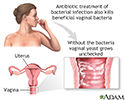
Secondary infection
Secondary infection occurs during or after treatment of a primary infection because the normal bacterial flora is destroyed, allowing yeast to flourish.
Secondary infection
illustration
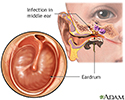
Middle ear infection
A middle ear infection is also known as otitis media. It is one of the most common of childhood infections. With this illness, the middle ear becomes red, swollen, and inflamed because of bacteria trapped in the eustachian tube.
Middle ear infection
illustration
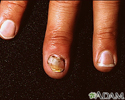
Nail infection - candidal
A paronychia is an infection around the nail. Many organisms can cause a paronychia. This particular case is caused by the yeast-like organism Candida. Note the inflammation (red, swollen area) at the base of the nail and the changes that are apparent in the nail itself.
Nail infection - candidal
illustration
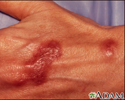
Mycobacterium marinum infection on the hand
This bacterial infection is caused by Mycobacterium marinum. Marinum is a relative of the organism which causes tuberculosis. This lesion is often referred to as a swimming pool granuloma. Atypical mycobacterial infections may cause life-threatening disease in people with weakened immune systems (immunocompromised individuals).
Mycobacterium marinum infection on the hand
illustration
Asymptomatic HIV infection
Asymptomatic HIV infection is characterized by a period of varying length in which there is slow deterioration of the immune system without clinical symptoms.
Asymptomatic HIV infection
illustration
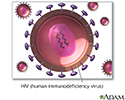
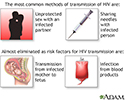
Primary HIV infection
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is more frequently transmitted through unprotected sex or sharing contaminated needles. Transmission from mother to fetus or through blood products has significantly declined in the United States.
Primary HIV infection
illustration
Common cold - Animation
Common cold
Animation
Ear infection - acute - Animation
Ear infection - acute
Animation
Ear infection - chronic - Animation
Ear infection - chronic
Animation
Middle ear infection (otitis media)
Otitis media is an inflammation or infection of the middle ear. Acute otitis media (acute ear infection) occurs when there is bacterial or viral infection of the fluid of the middle ear, which causes production of fluid or pus. Chronic otitis media occurs when the eustachian tube becomes blocked repeatedly due to allergies, multiple infections, ear trauma, or swelling of the adenoids.
Middle ear infection (otitis media)
illustration
Secondary infection
Secondary infection occurs during or after treatment of a primary infection because the normal bacterial flora is destroyed, allowing yeast to flourish.
Secondary infection
illustration
Middle ear infection
A middle ear infection is also known as otitis media. It is one of the most common of childhood infections. With this illness, the middle ear becomes red, swollen, and inflamed because of bacteria trapped in the eustachian tube.
Middle ear infection
illustration
Nail infection - candidal
A paronychia is an infection around the nail. Many organisms can cause a paronychia. This particular case is caused by the yeast-like organism Candida. Note the inflammation (red, swollen area) at the base of the nail and the changes that are apparent in the nail itself.
Nail infection - candidal
illustration
Mycobacterium marinum infection on the hand
This bacterial infection is caused by Mycobacterium marinum. Marinum is a relative of the organism which causes tuberculosis. This lesion is often referred to as a swimming pool granuloma. Atypical mycobacterial infections may cause life-threatening disease in people with weakened immune systems (immunocompromised individuals).
Mycobacterium marinum infection on the hand
illustration
Asymptomatic HIV infection
Asymptomatic HIV infection is characterized by a period of varying length in which there is slow deterioration of the immune system without clinical symptoms.
Asymptomatic HIV infection
illustration
Primary HIV infection
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is more frequently transmitted through unprotected sex or sharing contaminated needles. Transmission from mother to fetus or through blood products has significantly declined in the United States.
Primary HIV infection
illustration
Sinusitis
Acute sinusitis; Sinus infection; Sinusitis - acute; Sinusitis - chronic; RhinosinusitisSinusitis is present when the tissue lining the sinuses become swollen or inflamed. It occurs as the result of an inflammatory reaction or an infection from a virus, bacteria, or fungus.
Sinusitis
Acute sinusitis; Sinus infection; Sinusitis - acute; Sinusitis - chronic; RhinosinusitisSinusitis is present when the tissue lining the sinuses become swollen or inflamed. It occurs as the result of an inflammatory reaction or an infection from a virus, bacteria, or fungus.
Review Date: 5/2/2024
Reviewed By: Josef Shargorodsky, MD, MPH, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.