Neurosciences
Neurosciences refers to the branch of medicine that focuses on the nervous system. The nervous system is made of two parts:
The central nervous system (CNS) consists of your brain and spinal cord.
The peripheral nervous system consists of all your nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord, including those in your head, arms, legs, and trunk of the body. Your peripheral nervous system is divided into two parts:
- Autonomic nervous system (ANS). This controls your internal body processes such as blood pressure, breathing, digestion, and so on.
- Somatic nervous system (SNS). This controls your muscles and sends signals from your ears, eyes, mouth, and skin to your CNS.
Together, your brain and spinal cord serve as the main "processing center" for the entire nervous system, and control all the functions of your body. Your brain defines who you are. It is also responsible for all of your thoughts, emotions, memories, and behaviors.
Information
Many different different medical conditions can affect the nervous system, including:
- Blood vessel disorders in the brain, including arteriovenous malformations and cerebral aneurysms
Arteriovenous malformations
A cerebral arteriovenous malformation (AVM) is an abnormal connection between the arteries and veins in the brain that usually forms before birth....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCerebral aneurysms
An aneurysm is a weak area in the wall of a blood vessel that causes the blood vessel to bulge or balloon out. When an aneurysm occurs in a blood ve...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tumors, benign and malignant (cancer)
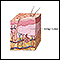
Benign
Benign refers to a condition, tumor, or growth that is not cancerous. This means that it does not spread to other parts of the body. It does not in...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Degenerative diseases, including Alzheimer disease and Parkinson disease
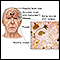
Alzheimer disease
Dementia is a loss of brain function that occurs with certain diseases. Alzheimer disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia. It affects memo...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Disorders of the pituitary gland
- Epilepsy
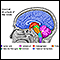
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a brain disorder in which a person has repeated seizures over time. Seizures are episodes of uncontrolled and abnormal electrical activi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Headaches, including migraines
Migraines
A migraine is a type of headache. It may occur with symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or sensitivity to light and sound. In most people, a throbbi...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Head injuries such as concussions and brain trauma
- Movement disorders, such as tremors and Parkinson disease
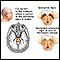
Parkinson disease
Parkinson disease results from certain brain cells dying. These cells help control movement and coordination. The disease leads to shaking (tremors...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Demyelinating diseases such as multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease that affects the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Neuro-ophthalmologic diseases, which are vision problems that result from damage to the optic nerve or its connections to the brain
- Peripheral nerve diseases (neuropathy), which affect the nerves that carry information to and from the brain and spinal cord
- Mental disorders, such as schizophrenia
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder that makes it hard to tell the difference between what is real and not real. It also makes it hard to think clearl...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Spine disorders
- Infections, such as meningitis
Meningitis
Meningitis is an infection of the membranes covering the brain and spinal cord. This covering is called the meninges.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Stroke
Stroke
A stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain stops. A stroke is sometimes called a "brain attack. " If blood flow is cut off for longer th...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Autoimmune disorders such as myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis is a neuromuscular disorder. Neuromuscular disorders involve the muscles and the nerves that control them.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
Neurologists and other neuroscience specialists use special tests and imaging techniques to see how the nerves and brain are working.
Along with blood and urine tests, tests done to diagnose nervous system diseases may include:
- Computed tomography (CT scan)
Computed tomography
A computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create pictures of cross-sections of the body. Related tests include:Abdomin...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) to check for infection of the spinal cord and brain, or to measure the pressure of the cerebro-spinal fluid (CSF)
Lumbar puncture
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or magnetic resonance angiography (MRA)
Magnetic resonance imaging
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the body. It does not us...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleMagnetic resonance angiography
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is an MRI exam of the blood vessels. Unlike traditional angiography that involves placing a tube (catheter) int...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Angiography to take pictures of the brain's blood vessels
- Electroencephalography (EEG) to look at brain electrical activity
Electroencephalography
An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a test to measure the electrical activity of the brain.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Electromyography (EMG) to test nerve and muscle function
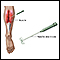
Electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a test that checks the health of the muscles and the nerves that control the muscles.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Electronystagmography (ENG) to check for abnormal eye movements, which can be a sign of a brain disorder
Electronystagmography
Electronystagmography is a test that looks at eye movements to see how well nerves in the brain are working. These nerves are:Vestibular nerve (eigh...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Evoked potentials (or evoked response), which looks at how the brain responds to sounds, sight, and touch
Evoked potentials
Brainstem auditory evoked response (BAER) is a test to measure the brain wave activity that occurs in response to sounds such as clicks or certain to...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
- Myelogram of the spine to diagnose nerve injury
- Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) test
Nerve conduction velocity
Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) is a test to see how fast electrical signals move through a nerve. This test is done along with electromyography (EM...
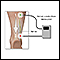 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Neurocognitive testing (neuropsychological testing)
- Polysomnogram to see how the brain reacts during sleep
Polysomnogram
Polysomnography is a sleep study. This test records certain body functions as you sleep, or try to sleep. Polysomnography is used to diagnose sleep...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scan to look at brain metabolic activity
Positron emission tomography
A positron emission tomography (PET) scan is a type of imaging test. It uses a radioactive substance called a tracer to look for disease in the body...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Biopsy of the brain, nerve, skin, or muscle to determine if there's a problem with the nervous system
TREATMENT
Most neurological conditions are treated with medicine. Most medicines are taken by mouth, but some need to be infused (through a vein), or injected into the spinal fluid. Medicines can be used to:
- Treat pain
- Improve neurological function
- Reduce degeneration
- Prevent autoimmune attack on the nervous system
- Treat infections of the nervous system
Neuroradiology is a branch of neuroscience medicine. It focuses on diagnosing and treating nervous system problems.
Interventional neuroradiology involves inserting tiny, flexible tubes called catheters into blood vessels leading to the brain. This allows the doctor (radiologist) to treat blood vessel disorders that can affect the nervous system, such as stroke.
Interventional neuroradiology treatments include:
- Balloon angioplasty and stenting of carotid or vertebral artery
- Endovascular embolization and coiling to treat cerebral aneurysms
Endovascular embolization
Endovascular embolization is a procedure to treat abnormal blood vessels in the brain and other parts of the body. It is an alternative to open surg...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Intra-arterial therapy for stroke
- Myelography to take pictures of the spinal structures
- Radiation oncology of the brain and spine
- Needle biopsies, spine and soft tissues
- Kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty to treat vertebral fractures
Open or traditional neurosurgery may be needed to treat problems in the brain and surrounding structures. Surgery may be needed to treat brain tumors or hemorrhage (bleeding) in the brain. This is invasive surgery that requires the surgeon to make an opening called a craniotomy, in the skull. Surgery can sometimes help treat epilepsy or dementia. Spine disease such as herniated disks can also be treated with surgery.
Craniotomy
Brain surgery is an operation to treat problems in the brain and surrounding structures.
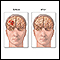
Microsurgery allows the surgeon to work on very small structures in the brain using a microscope and very small, precise instruments.
Stereotactic radiosurgery may be needed for certain types of nervous system disorders. This is a form of radiation therapy that focuses high-powered x-rays on a small area of the body. This helps to avoid damage to surrounding brain tissue.
Stereotactic radiosurgery
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is a form of radiation therapy that focuses high-power energy on a small area of the body. Despite its name, radiosu...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleTreatment of nervous system-related diseases or disorders may also include:
- Deep brain stimulation
- Spinal cord stimulation
- Rehabilitation/physical therapy after brain injury or stroke
- Spinal surgery
WHO IS INVOLVED
The neurosciences medical team is often made up of health care providers from different specialties. This may include:
- Neurologist -- a doctor who has received extra training in the treatment of brain and nervous system disorders
- Vascular surgeon -- a doctor who has received extra training in the surgical treatment of blood vessel disorders
- Neurosurgeon -- a doctor who has received extra training in brain and spine surgery
- Neuropsychologist -- a doctor specially trained in administering and interpreting tests of the cognitive function of the brain
- Pain physician -- a doctor who received training in treating complex pain with procedures and medicines
- Psychiatrist -- a doctor who treats brain-behavioral disease with drugs
- Psychologist -- a doctor who treats brain-behavioral conditions with talk therapy
- Radiologist -- a doctor who received extra training in interpreting medical images and in performing different procedures using imaging technology specifically for treating brain and nervous system disorders
- Neuroscientist -- someone who does research on the nervous system
- Nurse practitioners (NPs)
- Physician assistants (PAs)
- Social workers
- Nutritionists or dietitians
- Primary care doctors
- Physical therapists, who help with mobility, strength, balance, and flexibility
- Occupational therapists, who help keep people functioning well in the home and at work
- Speech-language therapists, who help with speech, language, and understanding
This list is not all-inclusive.
References
Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Newman NJ, Pomeroy SL. Diagnosis of neurological disease. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 1.
Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Newman NJ, Pomeroy SL. Investigations in diagnosis and management of neurological disease. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 34.
Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Newman NJ, Pomeroy SL. Management of neurological disease. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SK, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 51.
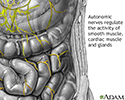
Autonomic Nerves - illustration
Autonomic nerves are concerned with muscular functions which are reflexive, such as breathing, heartbeats and peristalsis (rhythmic movements of the intestines).
Autonomic Nerves
illustration
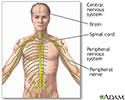
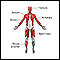
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system comprises the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
illustration
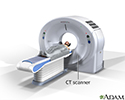
CT scan - illustration
CT stands for computerized tomography. In this procedure, a thin X-ray beam is rotated around the area of the body to be visualized. Using very complicated mathematical processes called algorithms, the computer is able to generate a 3-D image of a section through the body. CT scans are very detailed and provide excellent information for the physician.
CT scan
illustration
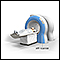
MRI scans - illustration
MRI stands for magnetic resonance imaging. It allows imaging of the interior of the body without using x-rays or other types of ionizing radiation. An MRI scan is capable of showing fine detail of different tissues.
MRI scans
illustration
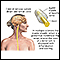
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) - illustration
A lumbar puncture, or spinal tap, is a procedure to collect cerebrospinal fluid to check for the presence of disease or injury. A spinal needle is inserted, usually between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae in the lower spine. Once the needle is properly positioned in the subarachnoid space (the space between the spinal cord and its covering, the meninges), pressures can be measured and fluid can be collected for testing.
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
illustration
Autonomic Nerves - illustration
Autonomic nerves are concerned with muscular functions which are reflexive, such as breathing, heartbeats and peristalsis (rhythmic movements of the intestines).
Autonomic Nerves
illustration
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system - illustration
The central nervous system comprises the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
illustration
CT scan - illustration
CT stands for computerized tomography. In this procedure, a thin X-ray beam is rotated around the area of the body to be visualized. Using very complicated mathematical processes called algorithms, the computer is able to generate a 3-D image of a section through the body. CT scans are very detailed and provide excellent information for the physician.
CT scan
illustration
MRI scans - illustration
MRI stands for magnetic resonance imaging. It allows imaging of the interior of the body without using x-rays or other types of ionizing radiation. An MRI scan is capable of showing fine detail of different tissues.
MRI scans
illustration
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) - illustration
A lumbar puncture, or spinal tap, is a procedure to collect cerebrospinal fluid to check for the presence of disease or injury. A spinal needle is inserted, usually between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae in the lower spine. Once the needle is properly positioned in the subarachnoid space (the space between the spinal cord and its covering, the meninges), pressures can be measured and fluid can be collected for testing.
Lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
illustration
Review Date: 12/31/2023
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.