Quantitative nephelometry test
Quantitative immunoglobulinsQuantitative nephelometry is a lab test to quickly and accurately measure levels of certain proteins called immunoglobulins in the blood. Immunoglobulins are antibodies that help fight infection.
Antibodies
An antibody is a protein produced by the body's immune system when it detects harmful substances, called antigens. Examples of antigens include micr...
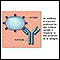
This test specifically measures the immunoglobulins IgM, IgG, and IgA.
How the Test is Performed
Blood sample is needed
Venipuncture is the collection of blood from a vein. It is most often done for laboratory testing.

How to Prepare for the Test
You may be asked not to eat or drink anything for 4 hours before the test.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain. Others feel only a prick or stinging. Afterward, there may be some throbbing or slight bruising. This soon goes away.
Why the Test is Performed
The test provides a rapid and accurate measurement of the amounts of the immunoglobulins IgM, IgG, and IgA.
Normal Results
Normal results for the three immunoglobulins are:
- IgG: 650 to 1600 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), or 6.5 to 16.0 grams per liter (g/L)
- IgM: 54 to 300 mg/dL, or 540 to 3000 mg/L
- IgA: 40 to 350 mg/dL, or 400 to 3500 mg/L
The examples above show the common measurements for these test results. Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Talk to your doctor about the meaning of your specific test results. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples.
What Abnormal Results Mean
An increased level of IgG may be due to:
-
Chronic infection or inflammation
Chronic
Chronic refers to something that continues over an extended period of time. A chronic condition is usually long-lasting and does not easily or quick...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Hyperimmunization (higher than normal number of specific antibodies)
Hyperimmunization
Hyperimmunization is the presence of a larger than normal number of antibodies to a specific antigen. This creates a state of immunity that is great...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - IgG multiple myeloma (a type of blood cancer)
Multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a blood cancer that starts in the plasma cells in the bone marrow. Bone marrow is the soft, spongy tissue found inside most bone...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Liver disease
Liver disease
The term "liver disease" applies to many conditions that stop the liver from working or prevent it from functioning well. Abdominal pain or swelling...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a disease that leads to inflammation of the joints and surrounding tissues. It is a long-term disease. It can also aff...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Decreased levels of IgG may be due to:
-
Agammaglobulinemia (very low levels of immunoglobulins, a very rare disorder)
Agammaglobulinemia
Agammaglobulinemia is an inherited disorder in which a person has very low levels of protective immune system proteins called immunoglobulins. Immun...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Leukemia (blood cancer)
Leukemia
Leukemia is a type of blood cancer that begins in the bone marrow. Bone marrow is the soft tissue in the center of the bones, where blood cells are ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Multiple myeloma (bone marrow cancer)
Multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a blood cancer that starts in the plasma cells in the bone marrow. Bone marrow is the soft, spongy tissue found inside most bone...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Preeclampsia (high blood pressure during pregnancy)
Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is high blood pressure and signs of liver or kidney damage that occur in women after the 20th week of pregnancy. While it is rare, pree...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Treatment with certain chemotherapy drugs
Increased levels of IgM may be due to:
-
Mononucleosis
Mononucleosis
Mononucleosis, or mono, is a viral infection that causes fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph glands, most often in the neck.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lymphoma (cancer of the lymph tissue)
-
Waldenström macroglobulinemia (cancer of the white blood cells)
Waldenström macroglobulinemia
Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM) is a cancer of the B lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). WM is associated with the overproduction of protei...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Multiple myeloma
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Infection
Decreased levels of IgM may be due to:
- Agammaglobulinemia (very rare)
- Leukemia
- Multiple myeloma
Increased levels of IgA may be due to:
- Chronic infections, especially of the gastrointestinal tract
- Inflammatory bowel disease, such as Crohn disease
Crohn disease
Crohn disease is a disease where parts of the digestive tract become inflamed. It most often involves the lower end of the small intestine and the be...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Multiple myeloma
Decreased levels of IgA may be due to:
- Agammaglobulinemia (very rare)
- Hereditary IgA deficiency
- Multiple myeloma
- Gut disease that leads to protein loss
Other tests are needed to confirm or diagnose any of the conditions above.
Risks
There is little risk involved with having your blood taken. Veins and arteries vary in size from one person to another and from one side of the body to the other. Taking blood from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Other risks associated with having blood drawn are slight, but may include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Multiple punctures to locate veins
- Hematoma (blood accumulating under the skin)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
References
Abraham RS. Assessment of functional immune responses in lymphocytes. In: Rich RR, Fleisher TA, Shearer WT, Schroeder HW, Few AJ, Weyand CM, eds. Clinical Immunology: Principles and Practice. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 93.
McPherson RA. Specific proteins. In: McPherson RA, Pincus MR, eds. Henry's Clinical Diagnosis and Management by Laboratory Methods. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 20.
-
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
-
Blood test - illustration
Blood is drawn from a vein (venipuncture), usually from the inside of the elbow or the back of the hand. A needle is inserted into the vein, and the blood is collected in an air-tight vial or a syringe. Preparation may vary depending on the specific test.
Blood test
illustration
Review Date: 4/29/2022
Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.



