Anti-glomerular basement membrane blood test
GBM antibody test; Antibody to human glomerular basement membrane; Anti-GBM antibodies
The glomerular basement membrane is the part of the kidney that helps filter waste and extra fluid from the blood.
Anti-glomerular basement membrane antibodies are antibodies against this membrane. They can lead to kidney damage. This article describes the blood test used to detect these antibodies.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
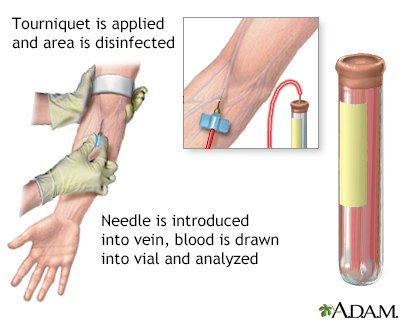
How the Test is Performed
How to Prepare for the Test
No special preparation is necessary.
How the Test will Feel
When the needle is inserted to draw blood, some people feel moderate pain, while others feel only a prick or stinging. Afterward, there may be some throbbing or a slight bruise. This soon goes away.
Why the Test is Performed
This test is used to diagnose certain kidney diseases, such as Goodpasture syndrome and anti-glomerular basement membrane disease.
Normal Results
Normally, there are none of these antibodies in the blood. Normal value ranges may vary slightly among different laboratories. Some labs use different measurements or test different samples. Talk to your doctor about the meaning of your specific test results.
What Abnormal Results Mean
Antibodies in the blood may mean any of the following:
- Anti-glomerular basement membrane disease
- Goodpasture syndrome
Risks
There is little risk involved with having your blood taken. Veins and arteries vary in size from one person to another and from one side of the body to the other. Taking blood from some people may be more difficult than from others.
Other risks:
- Excessive bleeding
- Fainting or feeling lightheaded
- Multiple punctures to locate veins
- Hematoma (blood accumulating under the skin)
- Infection (a slight risk any time the skin is broken)
Related Information
AntibodyAntigen
Anti-glomerular basement membrane disease
Acute nephritic syndrome
References
Phelps RG, Turner AN. Anti-glomerular basement membrane disease and Goodpasture disease. In: Johnson RJ, Floege J, Tonelli M, eds. Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 25.
Saha MK, Pendergraft WF, Jennette JC, Falk RJ. Primary glomerular disease. In: Yu ASL, Chertow GM, Luyckx VA, Marsden PA, Skorecki K, Taal MW, eds. Brenner and Rector's The Kidney. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 31.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 8/28/2023
Reviewed By: Walead Latif, MD, Nephrologist and Clinical Associate Professor, Rutgers Medical School, Newark, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
