Tongue problems
Tongue problems include pain, swelling, or a change in how the tongue looks or functions.
Considerations
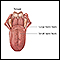
The tongue is mainly made up of muscles. It is covered with a mucous membrane. Small bumps (papillae) cover the surface of back part of the tongue.
Mucous membrane
Mucosa is moist tissue that lines certain parts of the inside of your body. It is in your: NoseMouthLungsDigestive tractUrinary and genital tracts G...

- Between the papillae are the taste buds, which allow you to taste.
- The tongue moves food to help you chew and swallow.
- The tongue also helps you form words.
There are many different reasons for changes in the tongue's function and appearance.
PROBLEMS MOVING THE TONGUE
Tongue movement problems are most often caused by nerve damage. Rarely, problems moving the tongue may also be caused by a disorder where the band of tissue that attaches the tongue to the floor of the mouth is too short. This is called ankyloglossia.
Tongue movement problems may lead to:
- Breastfeeding problems in newborns
- Difficulty moving food during chewing and swallowing
- Speech problems
TASTE PROBLEMS
Taste problems can be caused by:
- Damage to the taste buds
- Nerve problems
- Side effects of some medicines
- An infection, or other condition
The tongue normally senses sweet, salty, sour, and bitter tastes. Other "tastes" are actually a function of the sense of smell.
Video Transcript
Tasting - Animation
The tongue has about 10,000 taste buds. The taste buds are linked to the brain by nerve fibers. Food particles are detected by the taste buds, which send nerve signals to the brain. Certain areas of the tongue are more sensitive to certain tastes, like bitter at the back of the tongue, sour along either side toward the back, sweet on the front surface, or salty around the front edge. Often, taste sensations are a mixture of these qualities.
INCREASED SIZE OF THE TONGUE
Tongue swelling occurs with:
-
Acromegaly
Acromegaly
Acromegaly is a condition in which there is too much growth hormone (GH) in your body.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Amyloidosis
Amyloidosis
Primary amyloidosis is a rare disorder in which abnormal proteins build up in tissues and organs. Clumps of the abnormal proteins are called amyloid...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Down syndrome
Down syndrome
Down syndrome is a genetic condition in which a person has 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Myxedema
Myxedema
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. This condition is often called underactive thyroid....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Rhabdomyoma
-
Prader Willi Syndrome
Prader Willi Syndrome
Tongue problems include pain, swelling, or a change in how the tongue looks or functions.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Tongue cancer
The tongue may get wider in people who have no teeth and do not wear dentures.
Sudden swelling of the tongue can happen due to an allergic reaction or a side effect of medicines.
COLOR CHANGES
Color changes may occur when the tongue becomes inflamed (glossitis). Papillae (bumps on the tongue) are lost, causing the tongue to appear smooth. Geographic tongue is a patchy form of glossitis where the location of inflammation and the appearance of the tongue change from day to day.
Glossitis
Glossitis is a problem in which the tongue is swollen and inflamed. This often makes the surface of the tongue appear smooth. Geographic tongue is ...
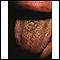
Geographic tongue
Geographic tongue is characterized by irregular patches on the surface of the tongue. This gives it a map-like appearance.

HAIRY TONGUE
Hairy tongue is a condition in which the tongue looks hairy or furry. It can sometimes be treated with antifungal medicine.
BLACK TONGUE
Sometimes the upper surface of the tongue turns black or brown in color. This is an unsightly condition, but it is not harmful.
PAIN IN THE TONGUE
Pain may occur with glossitis and geographic tongue. Tongue pain may also occur with:
-
Diabetic neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy
Nerve damage that occurs in people with diabetes is called diabetic neuropathy. This condition is a complication of diabetes.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Leukoplakia
Leukoplakia
Leukoplakia are white patches on the tongue, in the mouth, or on the inside of the cheek.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Mouth ulcers
Mouth ulcers
Mouth ulcers are sores or open lesions in the mouth.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Oral cancer
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
After menopause, some women have a sudden feeling that their tongue has been burned. This is called burning tongue syndrome or idiopathic glossopyrosis. There is no specific treatment for burning tongue syndrome, but capsaicin (the ingredient that makes peppers spicy) can offer relief to some people.
Causes
Minor infections or irritations are the most common cause of tongue soreness. Injury, such as biting the tongue, can cause painful sores. Heavy smoking can irritate the tongue and make it painful.
A benign ulcer on the tongue or elsewhere in the mouth is common. This is called a canker sore and can appear for no known reason.
Possible causes of tongue pain include:
-
Anemia
Anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. Different type...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Cancer
- Dentures that irritate the tongue
- Oral herpes (ulcers)
-
Neuralgia
Neuralgia
Neuralgia is a sharp, shocking pain that follows the path of a nerve and is due to irritation or damage to the nerve. Common neuralgias include:Posth...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
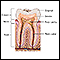
Pain from teeth and gums
Pain from teeth and gums
A toothache is pain in or around a tooth.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Pain from the heart
Pain from the heart
Chest pain is discomfort or pain that you feel anywhere along the front of your body between your neck and upper abdomen.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Possible causes of tongue tremor:
- Neurological disorder
-
Overactive thyroid
Overactive thyroid
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone. The condition is often called overactive thyroid.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Possible causes of white tongue:
- Local irritation
- Smoking and alcohol use
Possible causes of smooth tongue:
- Anemia
-
Vitamin B12 deficiency
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin. Water-soluble vitamins dissolve in water. After the body uses what it needs of these vitamins, leftover amo...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Possible causes of red (ranging from pink to reddish-purple) tongue:
-
Folic acid and vitamin B12 deficiency
Folic acid
Folic acid and folate are both terms for a type of B vitamin (vitamin B9). Folate is a B vitamin that occurs naturally in foods such as green leafy v...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
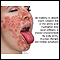
Pellagra
Pellagra
Pellagra is a disease that occurs when a person does not get enough niacin (one of the B complex vitamins) or tryptophan (an amino acid).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
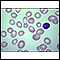
Pernicious anemia
Pernicious anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. There are man...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
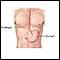
Plummer-Vinson syndrome
Plummer-Vinson syndrome
Plummer-Vinson syndrome is a condition that can occur in people with long-term (chronic) iron deficiency anemia. People with this condition have pro...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
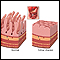
Sprue
Sprue
Celiac disease is an autoimmune condition that damages the lining of the small intestine. This damage comes from a reaction to eating gluten. This ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Possible causes of tongue swelling:
- Acromegaly
- Allergic reaction to food or medicine
- Amyloidosis
-
Angioedema
Angioedema
Angioedema is swelling that is similar to hives, but the swelling is under the skin instead of on the surface. Hives are often called welts. They a...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Beckwith syndrome
Beckwith syndrome
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome is a growth disorder that causes large body size, large organs, and other symptoms. It is a congenital condition, which ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Cancer of the tongue
Cancer of the tongue
Oral cancer is cancer that starts in the mouth.
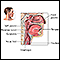 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Congenital micrognathia
- Down syndrome
-
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not make enough thyroid hormone. This condition is often called underactive thyroid....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Infection
- Leukemia
-
Lymphangioma
Lymphangioma
A cystic hygroma is a growth that often occurs in the head and neck area. It is a birth defect.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Neurofibromatosis
- Pellagra
- Pernicious anemia
-
Strep infection
Strep infection
Strep throat is a disease that causes a sore throat (pharyngitis). It is an infection with a bacteria called group A streptococcus.
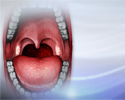 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Tumor of the pituitary gland
Tumor of the pituitary gland
A pituitary tumor is an abnormal growth in the pituitary gland. The pituitary is a small gland at the base of the brain. It regulates the body's ba...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Possible causes of a hairy tongue:
-
AIDS
AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Antibiotic therapy
-
Drinking coffee
Drinking coffee
Caffeine is a substance that is found in certain plants. It can also be man-made and added to foods. It is a central nervous system stimulant and a...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Dyes in drugs and food
Dyes in drugs and food
Food additives are substances that become part of a food product when they are added during the processing or making of that food. "Direct" food addi...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Chronic medical conditions
- Overuse of mouthwashes containing oxidizing or astringent ingredients
- Radiation of the head and neck
- Tobacco use
Home Care
Practicing good oral self-care can help hairy tongue and black tongue. Be sure to eat a well-balanced diet.
Oral self-care
Tooth decay and gum disease are caused by plaque, a sticky combination of bacteria and food. Plaque begins to build up on teeth within a few minutes...

Canker sores will heal on their own.
Canker sores
A canker sore is a painful, open sore in the mouth. Canker sores are white or yellow and surrounded by a bright red area. They are not cancerous. A...

See your dentist if you have a tongue problem caused by dentures.
Antihistamines can help relieve a swollen tongue caused by allergies. Avoid the food or drug that causes the tongue swelling. Seek medical attention right away if swelling is starting to make breathing difficult.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your health care provider if your tongue problem makes it difficult to eat or breathe or if the problem persists.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
The provider will perform a physical exam, to look closely at the tongue. You may be asked questions such as:
- When did you first notice the problem?
- Have you had similar symptoms before?
- Do you have pain, swelling, breathing problems, or difficulty swallowing? Are there problems with speaking or moving the tongue?
- Have you noticed changes in taste?
- Do you have a tongue tremor?
- What makes the problem worse? What have you tried that helps?
- Do you wear dentures?
- Are there problems with the teeth, gums, lips, or throat? Does the tongue bleed?
- Do you have a rash or fever? Do you have allergies?
- What medicines do you take?
- Do you use tobacco products or drink alcohol?
You may need blood tests or a biopsy to check for other conditions.
Treatment depends on the cause of the tongue problem. Possible treatments include:
- If nerve damage has caused a tongue movement problem, the condition must be treated. Therapy may be needed to improve speech and swallowing.
- Ankyloglossia may not need to be treated, unless you have speech or swallowing problems. Surgery to release the tongue can relieve the problem.
- Medicine may be prescribed for mouth ulcers, leukoplakia, oral cancer, and other mouth sores.
- Anti-inflammatory medicines may be prescribed for glossitis and geographic tongue.
Reviewed By
Josef Shargorodsky, MD, MPH, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA, Neuhaus IM. Pruritus and neurocutaneous dermatoses. In: James WD, Elston DM, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA, Neuhaus IM, eds. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 4.
Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, Chi AC. Oral manifestations of systemic diseases. In: Neville BW, Damm DD, Allen CM, Chi AC, eds. Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. 4th ed. St Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2016:chap 17.
Pham KL, Mirowski GW. Oral diseases and oral manifestations of gastrointestinal and liver disease. In: Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ, eds. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 24.
Disclaimer



 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.