Mumps
Mumps is a contagious disease that leads to painful swelling of the salivary glands. The salivary glands produce saliva, a liquid that moistens food and helps you chew and swallow.
Salivary glands
Salivary gland infections affect the glands that produce spit (saliva). The infection may be due to bacteria or viruses. There are 3 pairs of major ...
Causes
Mumps is caused by a virus. The virus spreads from person to person by drops of moisture from the nose and mouth, such as through sneezing. It is also spread through direct contact with items that have infected saliva on them.
Mumps most often occurs in children ages 2 through 12 who have not been vaccinated against the disease. However, the infection can occur at any age and may also be seen in college age students.
The time between being exposed to the virus and getting sick (incubation period) is about 12 to 25 days.
Mumps may also infect the:
-
Central nervous system
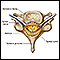
Central nervous system
The central nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. Your brain and spinal cord serve as the main "processing center" for your entir...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pancreas
-
Testes
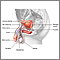
Testes
The testes are 2 egg-shaped male reproductive organs located in the scrotum. They produce sperm and the male hormone, testosterone.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Symptoms
Symptoms of mumps may include:
- Face pain
- Fever
-
Headache
Headache
A headache is pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck. Serious causes of headaches are rare. Most people with headaches can feel much better...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sore throat
- Loss of appetite
-
Swelling of the parotid glands (the largest salivary glands, located between the ear and the jaw)
Swelling
Swelling is the enlargement of organs, skin, or other body parts. It is caused by a buildup of fluid in the tissues. The extra fluid can lead to a ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Swelling of the temples or jaw (temporomandibular area)
Other symptoms that can occur in males are:
-
Testicle lump
Testicle lump
A testicle lump is swelling or a growth (mass) in one or both testicles.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Testicle pain
Testicle pain
Testicle pain is discomfort in one or both testicles. The pain can spread into the lower abdomen.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Scrotal swelling
Scrotal swelling
Scrotal swelling is abnormal enlargement of the scrotum. This is the name for the sac surrounding the testicles.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform an exam and ask about your symptoms, especially when they started.
No tests are needed in most cases. Your provider can usually diagnose mumps by looking at your symptoms.
Blood tests may be needed to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for mumps. The following things can be done to relieve symptoms:
- Apply ice or heat packs to the neck area.
- Take acetaminophen (Tylenol) to relieve pain. Do not give aspirin to children with a viral illness because of the risk for Reye syndrome.
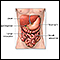
Reye syndrome
Reye syndrome is characterized by sudden (acute) brain damage and liver function problems. This condition does not have a known cause. This syndrome...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Drink extra fluid.
- Eat soft foods.
- Gargle with warm salt water.
Outlook (Prognosis)
People with this disease do well most of the time, even if organs other than the salivary glands are involved. After the illness is over (usually in about 7 days), they'll acquire immunity to mumps for the rest of their life.
Immunity
The immune response is how your body recognizes and defends itself against bacteria, viruses, and substances that appear foreign and harmful....
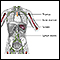
Possible Complications
Infection of other organs may occur, including testicle swelling (orchitis).
Orchitis
Orchitis is swelling (inflammation) of one or both of the testicles.

When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you or your child has mumps along with:
- Red eyes
- Constant drowsiness
Drowsiness
Drowsiness refers to feeling more sleepy than normal during the day. People who are drowsy may fall asleep when they do not want to or at times whic...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Constant vomiting or abdominal pain
- Severe headache
- Pain or a lump in testicle
Call 911 or the local emergency number or visit the emergency room if seizures occur.
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...

Prevention
MMR immunization (vaccine) protects against measles, mumps, and rubella. It should be given to children at these ages:
MMR immunization (vaccine)
All content below is taken in its entirety from the CDC MMR (Measles, Mumps, & Rubella) Vaccine Information Statement (VIS): www. cdc. gov/vaccines/h...
Measles
Measles is a very contagious (easily spread) illness caused by a virus.
Rubella
Rubella, also known as the German measles, is an infection in which there is a rash on the skin. Congenital rubella is when a pregnant woman with rub...
- First dose: 12 through 15 months old
- Second dose: 4 through 6 years old
Adults can also receive the vaccine. Talk to your provider about this.
Recent outbreaks of the mumps have supported the importance of having all children vaccinated.
Reviewed By
Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Gans HA. Mumps. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 295.
Litman N, Baum SG. Mumps virus. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 157.
Rosen JB, Zucker JR. Mumps. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 340.
Disclaimer



 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.