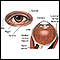
Vernal conjunctivitis
Vernal conjunctivitis is long-term (chronic) swelling (inflammation) of the outer lining of the eyes. It is due to an allergic reaction.
Allergic reaction
The conjunctiva is a clear layer of tissue lining the eyelids and covering the white of the eye. Allergic conjunctivitis occurs when the conjunctiva...
Causes
Vernal conjunctivitis often occurs in people with a strong family history of allergies. These may include allergic rhinitis, asthma, and eczema. It is most common in young males, and most often occurs during the spring and summer.
Allergic rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis is a diagnosis associated with a group of symptoms affecting the nose. These symptoms occur when you breathe in something you are ...
Asthma
Asthma is a chronic disease that causes the airways of the lungs to swell and narrow. It leads to breathing difficulty such as wheezing, shortness o...

Symptoms
Symptoms include:
-
Burning eyes.
Burning eyes
Eye burning with discharge is burning, itching, or drainage from the eye of any substance other than tears.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Discomfort in bright light (photophobia).
-
Itching eyes.
Itching eyes
Eye burning with discharge is burning, itching, or drainage from the eye of any substance other than tears.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - The area around the cornea where the white of the eye and the cornea meet (limbus) may become rough and swollen.
- The inside of the eyelids (most often the upper ones) may become rough and covered with bumps and a white mucus.
- Watering eyes.
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform an eye exam.
Treatment
Avoid allergy triggers (allergens).
Avoid rubbing the eyes because this can irritate them more.
Cold compresses (a clean cloth soaked in cold water and then placed over the closed eyes) may be soothing.
Lubricating drops may also help soothe the eye.
If home-care measures do not help, you may need to be treated by your provider. Treatment may include:
- Antihistamine or anti-inflammatory drops that are placed into the eye
- Eye drops that prevent a type of white blood cell called mast cells from releasing histamine (may help prevent future attacks)
- Mild steroids that are applied directly to the surface of the eye (for severe reactions)
Cyclosporine 0.1% eye drops contain a mild form of the immune-suppressing medicine and may help treat acute episodes of vernal conjunctivitis. They may also help prevent recurrences.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The condition continues over time (is chronic). It gets worse during certain seasons of the year, most often in the spring and summer. Treatment may provide relief.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Continuing discomfort
- Reduced vision
- Scarring of cornea
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if your symptoms continue or get worse.
Prevention
Using air conditioning or moving to a cooler climate may help prevent the problem from getting worse in the future.
References
Barney NP. Allergic and immunologic diseases of the eye. In: Burks AW, Holgate ST, O'Hehir RE, et al, eds. Middleton's Allergy: Principles and Practice. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 38.
Cho CB, Boguniewicz M, Sicherer SH. Ocular allergies. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 172.
Nehls SM. Vernal and atopic keratoconjunctivitis. In: Mannis MJ, Holland EJ, eds. Cornea. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 43.
Rubenstein JB, Patel P. Allergic conjunctivitis. In: Yanoff M, Duker JS, eds. Ophthalmology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 4.7.
Yucel OE, Ulus ND. Efficacy and safety of topical cyclosporine A 0.05% in vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Singapore Med J. 2016;57(9):507-510. PMID: 26768065 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26768065/.
-
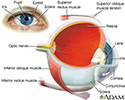
Eye - illustration
The eye is the organ of sight, a nearly spherical hollow globe filled with fluids (humors). The outer layer (sclera, or white of the eye, and cornea) is fibrous and protective. The middle layer (choroid, ciliary body and the iris) is vascular. The innermost layer (retina) is sensory nerve tissue that is light sensitive. The fluids in the eye are divided by the lens into the vitreous humor (behind the lens) and the aqueous humor (in front of the lens). The lens itself is flexible and suspended by ligaments which allow it to change shape to focus light on the retina, which is composed of sensory neurons.
Eye
illustration
-
Eye - illustration
The eye is the organ of sight, a nearly spherical hollow globe filled with fluids (humors). The outer layer (sclera, or white of the eye, and cornea) is fibrous and protective. The middle layer (choroid, ciliary body and the iris) is vascular. The innermost layer (retina) is sensory nerve tissue that is light sensitive. The fluids in the eye are divided by the lens into the vitreous humor (behind the lens) and the aqueous humor (in front of the lens). The lens itself is flexible and suspended by ligaments which allow it to change shape to focus light on the retina, which is composed of sensory neurons.
Eye
illustration
Review Date: 1/29/2024
Reviewed By: Audrey Tai, DO, MS, Athena Eye Care, Mission Viejo, CA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.