Potter syndrome
Potter syndrome and Potter phenotype refers to a group of findings associated with a lack of amniotic fluid and kidney failure in an unborn infant.
Amniotic fluid
Amniotic fluid is a clear, slightly yellowish liquid that surrounds the unborn baby (fetus) during pregnancy. It is contained in the amniotic sac....

Kidney failure
Acute kidney failure is the rapid (less than 2 days) loss of your kidneys' ability to remove waste and help balance fluids and electrolytes in your b...

Causes
In Potter syndrome, the primary problem is kidney failure. The kidneys fail to develop properly as the baby is growing in the womb. The kidneys normally produce the amniotic fluid (as urine) that surrounds the unborn baby.
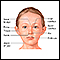
Potter phenotype refers to a typical facial appearance that occurs in a newborn when there is no amniotic fluid. The lack of amniotic fluid is called oligohydramnios. Without amniotic fluid, the infant is not cushioned from the walls of the uterus. The pressure of the uterine wall leads to an unusual facial appearance, including widely separated eyes.
Potter phenotype may also lead to abnormal limbs, or limbs that are held in abnormal positions or contractures.
Contractures
A contracture develops when the normally stretchy (elastic) tissues are replaced by nonstretchy (inelastic) fiber-like tissue. This tissue makes it ...

Oligohydramnios also stops development of the lungs, so the lungs do not work properly at birth.
Symptoms
Symptoms include:
- Widely separated eyes with epicanthal folds, broad nasal bridge, low set ears, and receding chin
Epicanthal folds
An epicanthal fold is skin of the upper eyelid that covers the inner corner of the eye. The fold runs from nose to the inner side of the eyebrow....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleBroad nasal bridge
Broad nasal bridge is a widening of the top part of the nose.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleLow set ears
Low-set ears and pinna abnormalities refer to an abnormal shape or position of the outer ear (pinna or auricle).
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleReceding chin
Micrognathia is a term for a lower jaw that is smaller than normal.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Absence of urine output
- Difficulty breathing
Exams and Tests
A pregnancy ultrasound may show lack of amniotic fluid, absence of fetal kidneys, or severely abnormal kidneys in the unborn baby.
Ultrasound
A pregnancy ultrasound is an imaging test that uses sound waves to create a picture of how a baby is developing in the womb (uterus). It is also use...
The following tests may be used to help diagnose the condition in a newborn:
-
X-ray of the abdomen
X-ray of the abdomen
An abdominal x-ray is an imaging test to look at organs and structures in the abdomen. Organs include the liver, spleen, stomach, and intestines. Wh...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
X-ray of the lungs
X-ray of the lungs
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Resuscitation at delivery may be attempted pending the diagnosis. Treatment will be provided for any urinary outlet obstruction.
Outlook (Prognosis)
This is a very serious condition. Most of the time it is deadly. The short-term outcome depends on the severity of lung involvement. Long-term outcome depends on the severity of kidney involvement.
Prevention
There is no known prevention.
Reviewed By
Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Miyashita Y, Formeck C, Moritz M. Nephrology. In: Zitelli BJ, McIntire SC, Nowalk AJ, Garrison J, eds. Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 14.
Marcdante KJ, Kliegman RM, Schuh AM. Congenital and developmental abnormalities of the urinary tract. In: Marcdante KJ, Kliegman RM, Schuh AM, eds. Nelson Essentials of Pediatrics. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 168.
Mitchell AL. Congenital anomalies. In: Martin RJ, Fanaroff AA, Walsh MC, eds. Fanaroff and Martin's Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine. 11th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 30.
Disclaimer



 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.