Guillain-Barre syndrome
GBS; Landry-Guillain-Barre syndrome; Acute idiopathic polyneuritis; Infectious polyneuritis; Acute inflammatory polyneuropathy; Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy; Ascending paralysis; Guillain-Barré syndromeGuillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is a serious health problem that occurs when the body's defense (immune) system mistakenly attacks part of the peripheral nervous system. This leads to nerve inflammation that causes muscle weakness or paralysis and other symptoms.
Causes
The exact cause of GBS is unknown. It is thought that GBS is an autoimmune disorder. With an autoimmune disorder, the body's immune system attacks itself by mistake. The incidence of GBS increases with aging, but can occur at any age. People older than 50 years are at the greatest risk.
Autoimmune disorder
An autoimmune disorder occurs when the body's immune system attacks and destroys healthy body tissue by mistake. There are more than 80 autoimmune d...
GBS may occur following infections from viruses or bacteria, such as:
- Influenza
- Some gastrointestinal illnesses
- Mycoplasma pneumonia
Mycoplasma pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. Mycoplasma pneumonia is caused by the bacteria Mycoplasma pneumoniae (M pn...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - HIV, the virus that causes HIV/AIDS (very rare)
HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Herpes simplex
- Mononucleosis
Mononucleosis
Mononucleosis, or mono, is a viral infection that causes fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph glands, most often in the neck.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - COVID-19
COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a respiratory illness that causes fever, coughing, and shortness of breath, but many other symptoms can occur....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
GBS may also occur with other medical conditions, such as:
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease. In this disease, the immune system of the body mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. It c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Hodgkin disease
Hodgkin disease
Hodgkin lymphoma is a cancer of lymph tissue. Lymph tissue is found in the lymph nodes, spleen, liver, bone marrow, and other sites.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - After surgery
GBS damages parts of nerves. This nerve damage causes tingling, muscle weakness, loss of balance, and paralysis. GBS most often affects the nerve covering (myelin sheath). This damage is called demyelination. It causes nerve signals to move more slowly. Damage to other parts of the nerve can cause the nerve to stop working.
Myelin
Myelin is an insulating layer, or sheath that forms around nerves, including those in the brain and spinal cord. It is made up of protein and fatty ...

Symptoms
Symptoms of GBS can get worse quickly. It may take only a few hours for the most severe symptoms to appear. But weakness that increases over several days is also common.
Muscle weakness or loss of muscle function (paralysis) affects both sides of the body. In most cases, the muscle weakness starts in the legs and spreads to the arms. This is called ascending paralysis.
If the inflammation affects the nerves of the chest and diaphragm (the large muscle under your lungs that helps you breathe) and those muscles are weak, you may need breathing assistance.
Breathing assistance
A ventilator is a machine that breathes for you or helps you breathe. It is also called a breathing machine or respirator. The ventilator: Is attac...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleOther typical signs and symptoms of GBS include:
- Loss of tendon reflexes in the arms and legs
- Tingling or numbness (mild loss of sensation)
Numbness
Numbness and tingling are abnormal sensations that can occur anywhere in your body, but they are often felt in your fingers, hands, feet, arms, or le...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Muscle tenderness or pain (may be a cramp-like pain)
- Uncoordinated movement (cannot walk without help)
Uncoordinated movement
Uncoordinated movement is due to a muscle control problem that causes an inability to coordinate movements. It leads to a jerky, unsteady, to-and-fr...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Low blood pressure or poor blood pressure control
- Abnormal heart rate
Other symptoms may include:
- Blurred vision and double vision
Blurred vision
There are many types of eye problems and vision disturbances, such as: Halos Blurred vision (the loss of sharpness of vision and the inability to see...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Clumsiness and falling
- Difficulty moving face muscles
- Feeling your heart beat (palpitations)
Emergency symptoms (seek medical help right away):
- Breathing temporarily stops
- Cannot take a deep breath
- Difficulty breathing
Difficulty breathing
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Difficulty swallowing
- Drooling
- Fainting
- Feeling light headed when standing
Exams and Tests
A history of increasing muscle weakness and paralysis over a short period of time may be a sign of GBS, especially if there was a recent illness.
A medical exam may show muscle weakness. There may also be problems with blood pressure and heart rate. These are functions that are controlled automatically by the nervous system. The exam may also show that reflexes such as the ankle or knee jerk are decreased or missing.
There may be signs of decreased breathing caused by paralysis of the breathing muscles.
The following tests may be done:
- Cerebrospinal fluid sample (spinal tap)
Cerebrospinal fluid sample
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collection is a test to look at the fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. CSF acts as a cushion, protecting the b...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Electrocardiogram (ECG) to check the electrical activity in the heart
Electrocardiogram
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a test that records the electrical activity of the heart.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Electromyography (EMG) to test the electrical activity in muscles
Electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a test that checks the health of the muscles and the nerves that control the muscles.
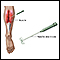 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Nerve conduction velocity test to measure how fast electrical signals move through a nerve
Nerve conduction velocity
Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) is a test to see how fast electrical signals move through a nerve. This test is done along with electromyography (EM...
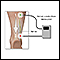 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pulmonary function tests to measure breathing capacity and how well the lungs are functioning
Pulmonary function tests
Pulmonary function tests are a group of tests that measure breathing and how well the lungs are functioning.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
While there is no cure for GBS, most people will notice improvement within days to weeks. Treatment is aimed at reducing symptoms, treating complications, and speeding up recovery.
In the early stages of the illness, a treatment called apheresis or plasmapheresis may be given. It involves removing the proteins, called antibodies, which attack the nerve cells. Another treatment is intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg). Both treatments lead to faster improvement, and both are equally effective. But there is no advantage to using both treatments at the same time. Other treatments help reduce inflammation.
Antibodies
An antibody is a protein produced by the body's immune system when it detects harmful substances, called antigens. Examples of antigens include micr...
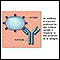
When symptoms are severe, treatment in the hospital will be needed. Breathing support will likely be given.
Other treatments in the hospital focus on preventing complications. These may include:
- Blood thinners to prevent blood clots
- Breathing support or a breathing tube and ventilator, if the diaphragm is weak
- Pain medicines or other medicines to treat pain
- Proper body positioning or a feeding tube to prevent choking during feeding, if the muscles used for swallowing are weak
- Physical therapy to help keep joints and muscles healthy
Support Groups
These resources may provide more information about GBS:
- GBS/CIDP Foundation International -- www.gbs-cidp.org
- National Organization for Rare Disorders -- rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/guillain-barre-syndrome
Outlook (Prognosis)
Recovery can take weeks, months, or years. Most people survive and recover completely. In some people, mild weakness may persist. The outcome is likely to be good when the symptoms go away soon after they first started.
Possible Complications
Possible complications of GBS include:
- Breathing difficulty (respiratory failure)
- Shortening of tissues in the joints (contractures) or other deformities
Contractures
A contracture develops when the normally stretchy (elastic) tissues are replaced by nonstretchy (inelastic) fiber-like tissue. This tissue makes it ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood clots (deep vein thrombosis) that form when the person with GBS is inactive or has to stay in bed
Blood clots
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a vein deep inside a part of the body. DVT mainly affects the large...
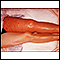 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Increased risk of infections
- Low or unstable blood pressure
- Paralysis that is permanent
- Pneumonia
- Skin damage (ulcers)
Ulcers
An ulcer is a crater-like sore on the skin or mucous membrane. Ulcers form when the top layers of skin or tissue have been removed. They can occur ...
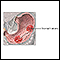 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Breathing food or fluids into the lungs (aspiration)
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Seek medical help right away if you have any of these symptoms:
- Trouble taking a deep breath
- Decreased feeling (sensation)
- Difficulty breathing
- Difficulty swallowing
- Fainting
- Loss of strength in the legs that gets worse over time
References
Chang CWJ. Myasthenia gravis and Guillain-Barré syndrome. In: Parrillo JE, Dellinger RP, eds. Critical Care Medicine: Principles of Diagnosis and Management in the Adult. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 61.
Katirji B. Disorders of peripheral nerves. In: Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, Pomeroy SL, Newman NJ, eds. Bradley and Daroff's Neurology in Clinical Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 106.
Sejvar JJ, Baughman AL, Wise M, Morgan OW. Population incidence of Guillain-Barré syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroepidemiology. 2011;36(2):123-133. PMID: 21422765 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21422765/.
Trujillo Gittermann LM, Valenzuela Feris SN, von Oetinger Giacoman A. Relation between COVID-19 and Guillain-Barré syndrome in adults. Systematic review. Neurologia (Engl Ed). 2020;35(9):646-654. PMID: 32896460 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32896460/.
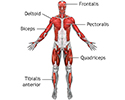
Superficial muscles are close to the surface of the skin. Muscles which lie closer to bone or internal organs are called deep muscles.
Superficial anterior muscles
illustration
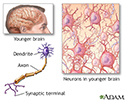
The nervous system controls the many complicated and interconnected functions of the body and mind. Motor, sensory cognitive and autonomic function are all coordinated and driven by the brain and nerves. As people age, nerve cells deteriorated in number and facility, causing some lessening in function.
Brain and nervous system
illustration
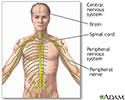
The central nervous system comprises the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
illustration
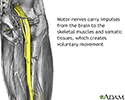
Motor nerves are the nerves responsible for all voluntary skeletal and somatic movement such as moving the leg or arm.
Motor nerves
illustration
Superficial muscles are close to the surface of the skin. Muscles which lie closer to bone or internal organs are called deep muscles.
Superficial anterior muscles
illustration
The nervous system controls the many complicated and interconnected functions of the body and mind. Motor, sensory cognitive and autonomic function are all coordinated and driven by the brain and nerves. As people age, nerve cells deteriorated in number and facility, causing some lessening in function.
Brain and nervous system
illustration
The central nervous system comprises the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system
illustration
Motor nerves are the nerves responsible for all voluntary skeletal and somatic movement such as moving the leg or arm.
Motor nerves
illustration
Review Date: 4/29/2023
Reviewed By: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School of Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.