Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome
Fulminant meningococcemia - Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome; Fulminant meningococcal sepsis - Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome; Hemorrhagic adrenalitis
Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome (WFS) is a group of symptoms caused when the adrenal glands fail to function normally. This occurs as a result of bleeding into the glands.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
Causes
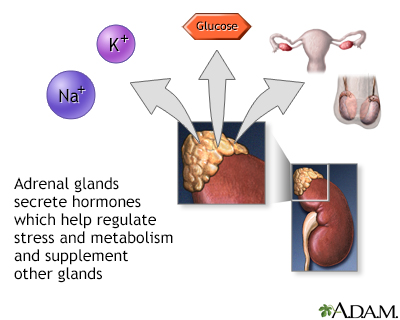
The adrenal glands are two triangle-shaped glands. One gland is located on top of each kidney. The adrenal glands produce and release different hormones that the body needs to function normally. The adrenal glands can be affected by many diseases, such as infections like WFS.
WFS is caused by severe infection with meningococcus bacteria or other bacteria such as:
- Group B streptococcus
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Staphylococcus aureus
Symptoms
Symptoms occur suddenly. They are due to the bacteria growing in large numbers inside the body. Symptoms include:
- Fever and chills
- Joint and muscle pain
- Headache
- Vomiting
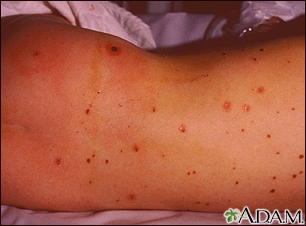
The infection with bacteria causes bleeding throughout the body, which causes:
- A rash throughout the body
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation in which small blood clots cut off blood supply to the organs
- Septic shock
Bleeding into the adrenal glands makes the glands unable to produce enough adrenal hormones. This is called adrenal crisis, and it leads to symptoms such as:
- Dizziness, weakness
- Very low blood pressure
- Very fast heart rate
- Confusion or coma
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your symptoms.
Blood tests will be done to confirm a bacterial infection. Tests may include:
If your provider suspects the infection is caused by meningococcus bacteria, other tests that may be done include:
- Lumbar puncture to get a sample of spinal fluid for culture
- Skin biopsy and Gram stain
- Urine analysis
Tests that may be ordered to help diagnose acute adrenal crisis include:
- ACTH (cosyntropin) stimulation test
- Cortisol blood test
- Blood sugar
- Potassium blood test
- Sodium blood test
- Blood pH test
Treatment
Antibiotics are started right away to treat the bacterial infection. Glucocorticoid medicines will also be given to treat adrenal gland insufficiency. Supportive treatments will be needed for other symptoms.
Outlook (Prognosis)
WFS is fatal unless treatment for the bacterial infection is started right away and glucocorticoid drugs are given.
Prevention
To prevent WFS caused by meningococcal bacteria, a vaccine is available.
Related Information
ShockReferences
Newell-Price JDC, Auchus RJ. The adrenal cortex. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology. 14th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 15.
Stephens DS. Neisseria meningitides. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 211.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 8/26/2023
Reviewed By: Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Associate Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Associate in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
