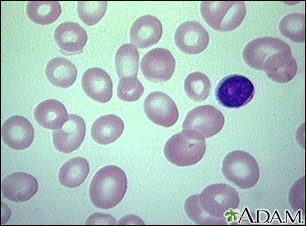
Vitamin B12 deficiency anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. There are many types of anemia.
Anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. Different type...
Vitamin B12 deficiency anemia is a low red blood cell count due to a lack (deficiency) of vitamin B12.
Causes
Your body needs vitamin B12 to make red blood cells. In order to provide vitamin B12 to your cells:
- You must eat foods that contain vitamin B12, such as meat, poultry, shellfish, eggs, fortified breakfast cereals, and dairy products.
- Your body must absorb enough vitamin B12. A special protein, called intrinsic factor, helps your body do this. This protein is released by cells in the stomach.
A lack of vitamin B12 may be due to dietary factors, including:
- Eating a strict vegetarian diet
- Poor diet in infants
- Poor nutrition during pregnancy
Certain health conditions can make it difficult for your body to absorb enough vitamin B12. They include:
- Alcohol use
- Crohn disease, celiac disease, infection with the fish tapeworm, or other problems that make it difficult for your body to digest foods
Crohn disease
Crohn disease is a disease where parts of the digestive tract become inflamed. It most often involves the lower end of the small intestine and the be...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark ArticleCeliac disease
Celiac disease is an autoimmune condition that damages the lining of the small intestine. This damage comes from a reaction to eating gluten. This ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Pernicious anemia, a type of vitamin B12 anemia that occurs when your body destroys cells in your stomach that make intrinsic factor
Pernicious anemia
Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. There are man...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Surgery that removes certain parts of your stomach or small intestine, such as some weight-loss surgeries
- Taking antacids and other heartburn medicines for a long period of time
- Abuse of laughing gas (nitrous oxide)
- Long term use of the medicine metformin
Symptoms
You may not have symptoms. Symptoms may be mild.
Symptoms may include:
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Fatigue, lack of energy, or lightheadedness when standing up or with exertion
- Loss of appetite
- Pale skin
Pale skin
Paleness is an abnormal loss of color from normal skin or mucous membranes.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Feeling irritable
- Shortness of breath, mostly during exercise
Shortness of breath
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Swollen, red tongue or bleeding gums
If you have low vitamin B12 level for a long time, you can have nerve damage. Symptoms of nerve damage include:
- Confusion or change in mental status (dementia) in severe cases
- Problems concentrating
- Psychosis (losing contact with reality)
- Loss of balance
- Numbness and tingling of hands and feet
- Hallucinations
Hallucinations
Hallucinations involve sensing things such as visions, sounds, or smells that seem real but are not. These things are created by the mind.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam. This may reveal problems with your reflexes.
Tests that may be done include:
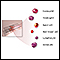
- Complete blood count (CBC)
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Reticulocyte count
- Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) level
- Serum bilirubin level
- Serum vitamin B12 level
Serum vitamin B12 level
The vitamin B12 level is a blood test that measures how much vitamin B12 is in your blood.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Serum methylmalonic acid (MMA) level
- Serum homocysteine level (amino acid found in blood)
Other procedures that may be done include:
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) to examine the stomach and small intestine
- Bone marrow biopsy if the diagnosis is not clear
Bone marrow biopsy
A bone marrow biopsy is the removal of marrow from inside bone. Bone marrow is the soft tissue inside bones that helps form blood cells. It is foun...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause of B12 deficiency anemia.
The goal of treatment is to increase your vitamin B12 level.
- Treatment may include a shot of vitamin B12 once a month. If you have a very low level of B12, you may need more shots in the beginning. It is possible you may need shots every month for the rest of your life.
- Some people may respond to treatment by taking large doses of vitamin B12 supplements by mouth.
Your provider will also recommend that you eat a variety of foods.
Outlook (Prognosis)
People with this type of anemia often do well with treatment.
Long-term vitamin B12 deficiency can cause nerve damage. This may be permanent if you do not start treatment within 6 months of when your symptoms begin.
Vitamin B12 deficiency anemia most often responds well to treatment. It will likely get better when the underlying cause of the deficiency is treated.
Possible Complications
A woman with a low B12 level may have a false positive Pap smear. This is because vitamin B12 deficiency affects the way certain cells (epithelial cells) in the cervix look.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have any of the symptoms of anemia.
Prevention
You can prevent anemia caused by a lack of vitamin B12 by eating a well-balanced diet.
Shots of vitamin B12 can prevent anemia if you've had a surgery known to cause vitamin B12 deficiency.
Early diagnosis and prompt treatment can reduce or prevent complications related to a low vitamin B12 level.
Reviewed By
Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Antony AC. Megaloblastic anemias. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 40.
Means Jr. RT. Approach to the anemias. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 144.
Stabler SP. Megaloblastic anemias. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 150.