Congenital protein C or S deficiency
Protein S deficiency; Protein C deficiency
Congenital protein C or S deficiency is a lack of proteins C or S in the fluid part of the blood. The proteins are natural substances that help prevent blood clots.
Images
I Would Like to Learn About:
Causes
Congenital protein C or S deficiency is an inherited disorder. This means it is passed down through families. Congenital means it is present at birth.
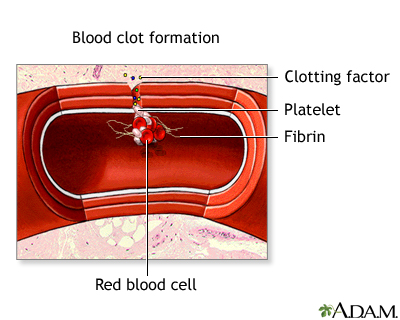
The disorder causes abnormal blood clotting.
One in 300 people has one normal gene and one faulty gene for protein C deficiency.
Protein S deficiency is much less common and occurs in about 1 in 20,000 people.
Symptoms
If you have this condition, you are more likely to develop blood clots, especially at a younger age. The symptoms are the same as for deep vein thrombosis, and include:
- Pain or tenderness in the affected area
- Redness or swelling in the affected area
Exams and Tests
The health care provider will perform a physical exam and ask about your medical history and symptoms.
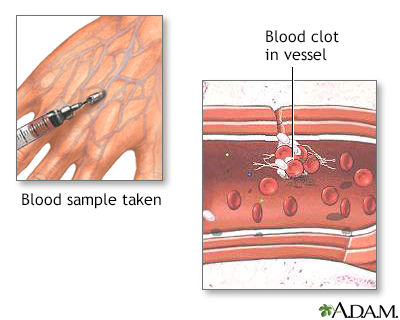
Laboratory tests will be done to check for proteins C and S.
Treatment
Blood-thinning drugs are used to treat and prevent blood clots.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outcome is usually good with treatment, but symptoms may return, especially if blood-thinning agents are stopped.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Childhood stroke
- More than one pregnancy loss (recurrent miscarriage)
- Recurrent clots in the veins
- Pulmonary embolism (blood clot in a lung artery)
In rare cases, using warfarin to thin the blood and prevent clots can cause brief increased clotting and severe skin wounds. People with these conditions are at risk if they are not treated with the blood-thinning drug heparin before taking warfarin.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of clotting in a vein (swelling and redness of the leg).
Prevention
If your provider diagnoses you with this disorder, you should be careful to prevent clots from forming. This can occur when the blood moves slowly in the veins, such as from prolonged bed rest during an illness, surgery, pregnancy or hospital stay. It may also occur after long airplane or car trips.
Related Information
Protein in dietBlood clots
Pulmonary embolus
Stroke
References
Anderson JA, Hogg KE, Weitz JI. Hypercoagulable states. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 140.
Patterson JW. The vasculopathic reaction pattern. In: Patterson JW, ed. Weedon's Skin Pathology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 9.
BACK TO TOPReview Date: 10/16/2022
Reviewed By: Mark Levin, MD, Hematologist and Oncologist, Monsey, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.

Health Content Provider
06/01/2025
|
A.D.A.M., Inc. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (www.urac.org). URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. A.D.A.M. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy, editorial process and privacy policy. A.D.A.M. is also a founding member of Hi-Ethics. This site complied with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information from 1995 to 2022, after which HON (Health On the Net, a not-for-profit organization that promoted transparent and reliable health information online) was discontinued. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997- 2024 A.D.A.M., a business unit of Ebix, Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.
