Factor V deficiency
Parahemophilia; Owren disease; Bleeding disorder - factor V deficiencyFactor V deficiency is a bleeding disorder that is passed down through families. It affects the ability of the blood to clot.
Bleeding disorder
Bleeding disorders are a group of conditions in which there is a problem with the body's blood clotting process. These disorders can lead to heavy a...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleCauses
When you bleed, a series of reactions take place in the body that helps blood clots form. This process is called the coagulation cascade. It involves as many as 20 different special proteins called coagulation, or clotting, factors. You may have a higher chance of excess bleeding if one or more of these factors are missing or are not functioning like they should.
Factor V deficiency is caused by a lack of factor V. When certain blood clotting factors are low or missing, your blood does not clot properly.
Factor V deficiency is rare. It may be caused by:
- A variant factor V gene passed down through families (inherited)
- An antibody that interferes with normal factor V function
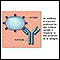
Antibody
An antibody is a protein produced by the body's immune system when it detects harmful substances, called antigens. Examples of antigens include micr...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
You can develop an antibody that interferes with factor V:
- After giving birth
- After being treated with a certain type of fibrin glue
- After surgery
- With autoimmune diseases and certain cancers
Sometimes the cause is unknown.
The disease is similar to hemophilia, except bleeding into joints is less common. In the inherited form of factor V deficiency, a family history of a bleeding disorder is a risk factor.
Hemophilia
Hemophilia refers to a group of bleeding disorders in which blood clotting takes a longer time than normal. There are two forms of hemophilia:Hemophi...

Symptoms
Excessive bleeding with menstrual periods and after childbirth often occurs. Other symptoms can include:
-
Bleeding into the skin
Bleeding into the skin
Bleeding into the skin can occur from broken blood vessels that form tiny red dots (called petechiae). Blood also can collect under the tissue in la...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Bleeding of the gums
Bleeding of the gums
Bleeding gums can be a sign that you have or may develop gum disease. Ongoing gum bleeding may be due to plaque buildup on the teeth. It can also b...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Excessive bruising
Bruising
Bleeding into the skin can occur from broken blood vessels that form tiny red dots (called petechiae). Blood also can collect under the tissue in la...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Nosebleeds
Nosebleeds
A nosebleed is loss of blood from the tissue lining the nose. Bleeding most often occurs from one nostril only.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Prolonged or excessive loss of blood with surgery or trauma
- Umbilical stump bleeding
Exams and Tests
Tests to detect factor V deficiency include:
-
Factor V assay
Factor V assay
The factor V assay is a blood test to measure the activity of factor V. This is one of the proteins in the body that helps the blood clot.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood clotting tests, including partial thromboplastin time (PTT) and prothrombin time (PT)
Partial thromboplastin time
Partial thromboplastin time (PTT) is a blood test that looks at how long it takes for blood to clot. It can help tell if you have a bleeding problem...
Read Article Now Book Mark ArticleProthrombin time
Prothrombin time (PT) is a blood test that measures the time it takes for the liquid portion (plasma) of your blood to clot. It measures the functio...
Read Article Now Book Mark Article -
Bleeding time
Bleeding time
Bleeding time is a medical test that measures how fast small blood vessels in the skin stop bleeding. Because it is difficult to perform correctly, i...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
You will be given fresh blood plasma or fresh frozen plasma infusions during a bleeding episode or after surgery. These treatments will correct the deficiency temporarily.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outlook is good with diagnosis and proper treatment.
Possible Complications
Severe bleeding (hemorrhage) could occur.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Go to the emergency room or call 911 or the local emergency number if you have an unexplained or prolonged loss of blood.
References
Gailani D, Benjamin FT, Wheeler AP. Rare coagulation factor deficiencies. In: Hoffman R, Benz EJ, Silberstein LE, et al, eds. Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 135.
Ragni MV. Coagulation factor deficiencies. In: Goldman L, Cooney KA, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 27th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2024:chap 160.
Samelson-Jones BJ, Branchford BR, Flood VH. Hereditary clotting factor deficiencies (bleeding disorders). In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, et al, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 22nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2025:chap 525.
-
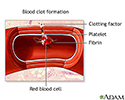
Blood clot formation - illustration
Blood clotting normally occurs when there is damage to a blood vessel. Platelets immediately begin to adhere to the cut edges of the vessel and release chemicals to attract even more platelets. A platelet plug is formed, and the external bleeding stops. Next, small molecules, called clotting factors, cause strands of blood-borne materials, called fibrin, to stick together and seal the inside of the wound. Eventually, the cut blood vessel heals and the blood clot dissolves after a few days.
Blood clot formation
illustration
-
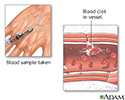
Blood clots - illustration
Blood clots (fibrin clots) are the clumps that result when blood coagulates.
Blood clots
illustration
-
Blood clot formation - illustration
Blood clotting normally occurs when there is damage to a blood vessel. Platelets immediately begin to adhere to the cut edges of the vessel and release chemicals to attract even more platelets. A platelet plug is formed, and the external bleeding stops. Next, small molecules, called clotting factors, cause strands of blood-borne materials, called fibrin, to stick together and seal the inside of the wound. Eventually, the cut blood vessel heals and the blood clot dissolves after a few days.
Blood clot formation
illustration
-
Blood clots - illustration
Blood clots (fibrin clots) are the clumps that result when blood coagulates.
Blood clots
illustration
Review Date: 3/31/2024
Reviewed By: Todd Gersten, MD, Hematology/Oncology, Florida Cancer Specialists & Research Institute, Wellington, FL. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.