Pneumonia - weakened immune system
Pneumonia is a lung infection. It can be caused by many different germs, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Pneumonia - Animation
Everyone coughs from time to time. You might pick up a cold, have an allergy, or just get a tickle from something irritating your throat. But if you're really hacking and coughing up yellow or green mucus, and you've also got a fever, chills, and shortness of breath, you may have picked up a more serious infection, called pneumonia. And sometimes pneumonia's symptoms aren't as obvious. Pneumonia is caused by an infection in your lung. Bacteria or viruses like these can sometimes get into your lungs through your nose or mouth and make you sick. You're more likely to get pneumonia if you've got a problem with your immune system that makes it harder to fight off infections. You're also at greater risk if you've got a lung disease like COPD or cystic fibrosis, you've recently had the flu, or you're exposed to cigarette smoke. People who live in nursing homes are also more likely to get pneumonia. With pneumonia, you may cough up greenish or yellow phlegm. You also may run a fever and have the chills. Pneumonia can make it hard to breathe. You may feel like you've run up a flight of stairs when you were just sitting still. Your doctor can tell that you have pneumonia and not just a cold by listening with a stethoscope for crackle sounds in your chest. You may need a chest x-ray or blood tests to know for sure that you have pneumonia. If bacteria caused your pneumonia, your doctor can give you antibiotics, drugs that kill bacteria. Keep taking the antibiotic until you finish the whole prescription so you don't re-infect yourself. To help loosen all of that mucus clogging your lungs, breathe in the warm mist from a humidifier and drink plenty of water. Take it easy too. Don't try to run back to work and infect everyone else. Rest until you feel better. Whatever you do, don't smoke, it will only make your pneumonia worse. If your pneumonia is really severe or you have another serious health problem, your doctor may recommend that you get treated in the hospital. While there, you'll get antibiotics and fluids through a vein. You may also be given oxygen to help you breathe easier. The best way to deal with pneumonia is to avoid getting it in the first place. Older adults, children, and people with serious conditions like diabetes, asthma, cancer, and emphysema should talk to their doctor about getting vaccinated against pneumonia and the illnesses that cause it. Once you get treated, your pneumonia should clear up within a couple of weeks. Your doctor may want to check your lungs to make sure they're clear. Sometimes pneumonia can lead to serious lung complications, so call your doctor right away if your breathing problems get worse, you have chest pain, or you cough up blood.
This article discusses pneumonia that occurs in a person who has a hard time fighting off infection because of problems with the immune system. This type of disease is called "pneumonia in an immunocompromised host."
Related conditions include:
-
Hospital-acquired pneumonia
Hospital-acquired pneumonia
Hospital-acquired pneumonia is an infection of the lungs that occurs during a hospital stay. This type of pneumonia can be very severe. Sometimes, ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Pneumocystis jiroveci
(previously called Pneumocystis carinii) pneumonia
Pneumocystis jiroveci
Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia is a fungal infection of the lungs. The disease used to be called Pneumocystis carinii or PCP pneumonia.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
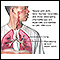
Pneumonia cytomegalovirus
Pneumonia cytomegalovirus
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) pneumonia is a viral infection of the lungs that can occur in people who have a suppressed immune system.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Fungal pneumonia
-
Pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). This type of pneu...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Viral pneumonia
Viral pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. Viral pneumonia is caused by a virus.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Walking pneumonia
Walking pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. With atypical pneumonia, the infection is caused by different bacteria tha...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Causes
People whose immune system is not working well are less able to fight off germs. This makes them prone to infections from germs that do not often cause disease in healthy people. They are also more vulnerable to regular causes of pneumonia, which can affect anyone.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is inflamed or swollen lung tissue due to infection with a germ. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). This type of pneu...

Your immune system may be weakened or not work well because of:
-
Bone marrow transplant
Bone marrow transplant
A bone marrow transplant is a procedure to replace damaged or diseased bone marrow with healthy bone marrow stem cells. Bone marrow is the soft, fatt...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
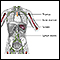
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy
The term chemotherapy is used to describe cancer-killing drugs. Chemotherapy may be used to:Cure the cancerShrink the cancerPrevent the cancer from ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - HIV infection
-
Leukemia, lymphoma, and other conditions that harm your bone marrow
Leukemia
Leukemia is a type of blood cancer that begins in the bone marrow. Bone marrow is the soft tissue in the center of the bones, where blood cells are ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Autoimmune disorders
Autoimmune disorders
An autoimmune disorder occurs when the body's immune system attacks and destroys healthy body tissue by mistake. There are more than 80 autoimmune d...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Medicines (including steroids, and those used to treat cancer and control autoimmune diseases)
- Organ transplant (including kidney, heart, and lung)
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
-
Cough (may be dry or produce mucus-like, greenish, or pus-like sputum)
Cough
Coughing is an important way to keep your throat and airways clear. But too much coughing may mean you have a disease or disorder. Some coughs are d...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chills with shaking
Chills
Chills refers to feeling cold after being in a cold environment. The word can also refer to an episode of shivering along with paleness and feeling ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fatigue
Fatigue
Fatigue is a feeling of weariness, tiredness, or lack of energy.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Fever
Fever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - General discomfort, uneasiness, or ill feeling (malaise)
Malaise
Malaise is a general feeling of discomfort, illness, or lack of well-being.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Headache
Headache
A headache is pain or discomfort in the head, scalp, or neck. Serious causes of headaches are rare. Most people with headaches can feel much better...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Loss of appetite
-
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea and vomiting
Nausea is feeling an urge to vomit. It is often called "being sick to your stomach. "Vomiting or throwing-up forces the contents of the stomach up t...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sharp or stabbing chest pain that gets worse with deep breathing or coughing
Chest pain
Chest pain is discomfort or pain that you feel anywhere along the front of your body between your neck and upper abdomen.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Shortness of breath
Shortness of breath
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Other symptoms that may occur:
- Heavy sweating or night sweats
- Stiff joints (rare)
- Stiff muscles (rare)
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider may hear crackles or other abnormal breath sounds when listening to your chest with a stethoscope. Decreased volume of breath sounds is a key sign. This finding may mean there is a buildup of fluid between the chest wall and lung (pleural effusion).
Pleural effusion
A pleural effusion is a buildup of fluid between the layers of tissue that line the lungs and chest cavity.

Tests may include:
-
Arterial blood gases
Arterial blood gases
Blood gases are a measurement of how much oxygen and carbon dioxide are in your blood. They also determine the acidity (pH) of your blood.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Blood chemistries
-
Blood culture
Blood culture
A blood culture is a laboratory test to check for bacteria or other germs in a blood sample.
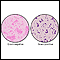 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
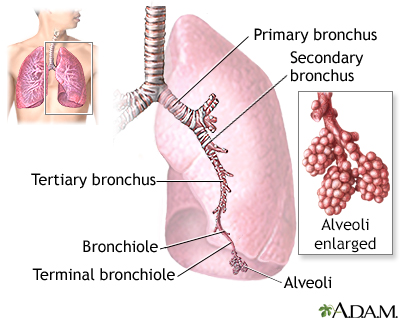
Bronchoscopy (in certain cases)
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is a test to view the airways and diagnose lung disease. It may also be used during the treatment of some lung conditions.
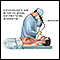 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chest CT scan (in certain cases)
Chest CT scan
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Complete blood count
Complete blood count
A complete blood count (CBC) test measures the following:The number of white blood cells (WBC count)The number of red blood cells (RBC count)The numb...
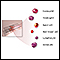 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - COVID test
-
Lung biopsy (in certain cases)
Lung biopsy
An open lung biopsy is surgery to remove a small piece of tissue from the lung. The sample is then examined for cancer, infection, or lung disease....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Serum cryptococcus antigen test
- Serum galactomannan test
- Galactomannan test from bronchial alveolar fluid
-
Sputum culture
Sputum culture
Routine sputum culture is a laboratory test that looks for germs that cause infection. Sputum is the material that comes up from air passages when y...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
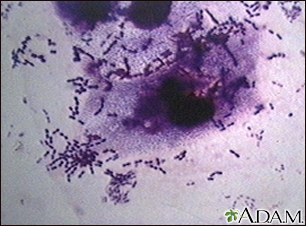
Sputum Gram stain
Sputum Gram stain
A sputum Gram stain is a lab test used to detect bacteria in a sputum sample. Sputum is the material that comes up from your air passages when you c...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Sputum immunofluorescence tests (or other immune tests)
Sputum immunofluorescence tests
Sputum direct fluorescent antibody (DFA) is a lab test that looks for micro-organisms in lung secretions.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Urine tests (to diagnose Legionnaire's disease or Histoplasmosis)
Legionnaire's disease
Legionnaires disease is an infection of the lungs and airways. It is caused by Legionella bacteria.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Treatment
Antibiotics or antifungal medicines may be used, depending on the type of germ that is causing the infection. Antibiotics are not helpful for viral infections, but newer medicines may treat some viral infections for example COVID-19. You may need to stay in the hospital during the early stages of the illness.
Oxygen and treatments to remove fluid and mucus from the respiratory system are often needed.
Outlook (Prognosis)
Factors that may lead to a worse outcome include:
- The pneumonia that is caused by a fungus.
- The person has a very weak immune system.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Respiratory failure (a condition in which a patient can't take in oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide without the use of a machine to deliver breaths.)
-
Sepsis
Sepsis
Sepsis is an illness in which the body has a severe, inflammatory response to bacteria or other germs.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Spread of the infection
- Death
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have a weakened immune system and you have symptoms of pneumonia.
Prevention
If you have a weakened immune system, you may receive daily antibiotics to prevent some types of pneumonia.
Ask your provider if you should receive the influenza (flu), pneumococcal (pneumonia), and COVID-19 vaccines.
Practice good hygiene. Thoroughly wash your hands with soap and water:
- After being outdoors
- After changing a diaper
- After doing housework
- After going to the bathroom
- After touching body fluids, such as mucus or blood
- After using the telephone
- Before handling food or eating
Other things you can do to reduce your exposure to germs include:
- Consider wearing a face mask when outside of your house.
- Keep your house clean.
- Stay away from crowds.
- Ask visitors who have a cold to wear a mask or not to visit.
- Do not do yard work or handle plants or flowers (they can carry germs).
Reviewed By
Jatin M. Vyas, MD, PhD, Associate Professor in Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Associate in Medicine, Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Medicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Blijlevens NMA, van der Velden WJFM. Infections in the immunocompromised host: general principles. In: Bennett JE, Dolin R, Blaser MJ, eds. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 305.
Perkins J, Waasdorp CP. The immunocompromised patient. In: Walls RM, ed. Rosen's Emergency Medicine: Concepts and Clinical Practice. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 182.
Sifri CD, Marr KA. Approach to fever and suspected infection in the immunocompromised host. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 265.
Wunderink RG, Restrepo MI. Pneumonia: considerations for the critically ill. In: Parrillo JE, Dellinger RP, eds. Critical Care Medicine: Principles of Diagnosis and Management in the Adult. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019:chap 40.
Disclaimer


 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.