Pulmonary nocardiosis
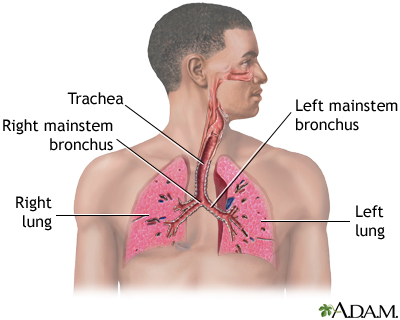
Pulmonary nocardiosis is an infection of the lung with Nocardia bacteria.
Causes
Nocardia infection develops when you breathe in (inhale) the bacteria. The infection causes pneumonia-like symptoms. The infection can spread to any part of the body.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a breathing (respiratory) condition in which there is an infection of the lung. This article covers community-acquired pneumonia (CAP). ...

People with a weak immune system are at a high risk for nocardia infection. This includes people who have:
- Been taking steroids or other medicines that weaken the immune system for a long time
- Cushing disease
- An organ transplant
-
HIV/AIDS
HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). When a person becomes infected with HIV, the ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Lymphoma (a type of cancer)
Cancer
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article
Other people at risk include those with long-term (chronic) lung problems related to smoking, emphysema, or tuberculosis.
Emphysema
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease. Having COPD makes it hard to breathe. There are two main forms of COPD:Chroni...
Tuberculosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection that involves the lungs. It may spread to other organs.
Symptoms
Pulmonary nocardiosis mainly affects the lungs. But, nocardiosis can also spread to other organs in the body. Common symptoms may include:
ENTIRE BODY
-
Fever (comes and goes)
Fever
Fever is the temporary increase in the body's temperature in response to a disease or illness. A child has a fever when the temperature is at or abov...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - General ill feeling (malaise)
Malaise
Malaise is a general feeling of discomfort, illness, or lack of well-being.
Read Article Now Book Mark Article - Night sweats
GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
- Nausea
- Liver and spleen swelling (hepatosplenomegaly)
Hepatosplenomegaly
Enlarged liver refers to swelling of the liver beyond its normal size. Hepatomegaly is another word to describe this problem. If both the liver and ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Loss of appetite
- Unintentional weight loss
- Vomiting
LUNGS AND AIRWAYS
-
Breathing difficulty
Breathing difficulty
Breathing difficulty may involve:Difficult breathing Uncomfortable breathingFeeling like you are not getting enough air
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Chest pain not due to heart problems
- Coughing up blood or mucus
- Rapid breathing
- Shortness of breath
MUSCLES AND JOINTS
NERVOUS SYSTEM
- Change in mental state
- Confusion
- Dizziness
- Headache
-
Seizures
Seizures
A seizure is the physical changes in behavior that occurs during an episode of specific types of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. The term ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Changes in vision
SKIN
- Skin rashes or lumps
- Skin sores (abscesses)
-
Swollen lymph nodes
Swollen lymph nodes
Lymph nodes are present throughout your body. They are an important part of your immune system. Lymph nodes help your body recognize and fight germ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will examine you and listen to your lungs using a stethoscope. You may have abnormal lung sounds, called crackles. Tests that may be done include:
- Bronchoalveolar lavage -- fluid is sent for stain and culture, which is taken by bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is a test to view the airways and diagnose lung disease. It may also be used during the treatment of some lung conditions.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chest x-ray
Chest x-ray
A chest x-ray is an x-ray of the chest, lungs, heart, large arteries, ribs, and diaphragm.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Chest CT
Chest CT
A chest CT (computed tomography) scan is an imaging method that uses x-rays to create cross-sectional pictures of the chest and upper abdomen....
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
MRI scan of the chest
MRI scan of the chest
A chest MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan is an imaging test that uses powerful magnetic fields and radio waves to create pictures of the chest (...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article -
Pleural fluid culture and stain
Pleural fluid culture
Pleural fluid culture is a test that examines a sample of fluid that has been collected in the pleural space to see if you have an infection to help ...
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Sputum stain and culture
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to control the infection. Antibiotics are used, but it may take a while to get better. Your provider will tell you how long you need to take the medicines. This may be for up to a year.
Surgery may be needed to remove or drain infected areas.
Your provider may tell you to stop taking any medicines that weaken your immune system. Never stop taking any medicine before talking to your provider first.
Outlook (Prognosis)
The outcome is often good when the condition is diagnosed and treated quickly.
The outcome is poor when the infection:
- Spreads outside the lung.
- Treatment is delayed.
- The person has a serious disease that leads to or requires long-term suppression of the immune system.
Possible Complications
Complications of pulmonary nocardiosis may include:
-
Brain abscesses
Brain abscesses
A brain abscess is a collection of pus, immune cells, and other material in the brain, caused by a bacterial or fungal infection.
 ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article
ImageRead Article Now Book Mark Article - Skin infections
- Kidney infections
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if you have symptoms of this disorder. Early diagnosis and treatment may improve the chance of a good outcome.
Prevention
Be careful when using corticosteroids. Use these medicines sparingly, in the lowest effective doses and for the shortest periods of time possible.
Some people with a weak immune system may need to take antibiotics for long periods of time or indefinitely to prevent the infection from returning.
Reviewed By
Denis Hadjiliadis, MD, MHS, Paul F. Harron Jr. Professor of Medicine, Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Care, Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Dockrell DH, Ho A, Gordon SB. Community-acquired pneumonia. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King Jr TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 46.
Southwick FS. Nocardiosis. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 314.
Disclaimer

 All rights reserved.
All rights reserved.